Abstract
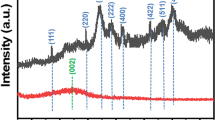
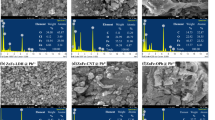
A novel magnetic zinc ferrite/porous biochar composite (c-PBC/ZF) was prepared and utilized to remove radioactive thorium (Th) (IV) from aqueous solutions. Zinc chloride (ZnCl2) not only activates biochar during the hydrothermal synthesis of c-PBC/ZF but also serves as a basic raw material for the synthesis of zinc ferrite. In addition, nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) plays a dual key role in catalyzing and generating large numbers of carboxyl groups (–COOH) during synthesis. The characterization results confirmed that ZnFe2O4 (ZF) particles with cubic spinel structures were successfully embedded into the porous biochar (PBC) matrix, which endowed the composite with superparamagnetism and enabled higher Th(IV) adsorption performance than that of single PBC and ZF nanoparticles. At room temperature, batch experiments showed that the removal rate of c-PBC/ZF for Th(IV) was 97.95% when the compound ratio of c-PBC/ZF was 1:1, the pH value was 4 and the adsorbent dosage was 1.2 g/L. Through the analysis of adsorption kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics, the Th(IV) adsorption process is in good agreement with the experimental data of the quasi-second-order kinetics model and Langmuir model, indicating that the process is a spontaneous, endothermic and monolayer adsorption process. FTIR analysis verified that the main mechanism of Th(IV) removal by c-PBC/ZF was Th–O and Th(IV) complexation with a carboxyl group and a hydroxyl group. Finally, the desorption and regeneration study proved that c-PBC/ZF has a highly efficient cycling performance as an adsorbent for recovering Th(IV) from wastewater. Therefore, c-PBC/ZF is a promising adsorbent for recovering Th(IV) from wastewater.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelhadi SO, Dosoretz CG, Rytwo G, Gerchman Y, Azaizeh H (2017) Production of biochar from olive mill solid waste for heavy metal removal. Biores Technol 244:759–767
Bhowmik M, Kanmani M, Debnath A, Saha B (2019) Sono-assisted rapid adsorption of anionic dye onto magnetic CaFe2O4/MnFe2O4 nanocomposite from aqua matrix. Powder Technol 354:496–504
Dehkhoda AM, Ellis N, Gyenge E (2015) Effect of activated biochar porous structure on the capacitive deionization of NaCl and ZnCl2 solutions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 224:217–228
dos Santos JMN, Pereira CR, Foletto EL, Dotto GL (2019) Alternative synthesis for ZnFe2O4/chitosan magnetic particles to remove diclofenac from water by adsorption. Int J Biol Macromol 131:301–308
Ghobadi M, Gharabaghi M, Abdollahi H, Boroumand Z, Moradian M (2018) MnFe2O4-graphene oxide magnetic nanoparticles as a high-performance adsorbent for rare earth elements: synthesis, isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics and desorption. J Hazard Mater 351:308–316
Harikishore Kumar Reddy D, Lee S-M (2014) Magnetic biochar composite: facile synthesis, characterization, and application for heavy metal removal. Colloids Surf A 454:96–103
He L, Liu S, Chen L, Dai X, Li J, Zhang M, Ma F, Zhang C, Yang Z, Zhou R (2019) Correction: mechanism unravelling for ultrafast and selective 99TcO4—uptake by a radiation-resistant cationic covalent organic framework: a combined radiological experiment and molecular dynamics simulation study. Chem Sci 10(19):5183–5184
Huang W, Liu ZM (2013) Biosorption of Cd(II)/Pb(II) from aqueous solution by biosurfactant-producing bacteria: isotherm kinetic characteristic and mechanism studies. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 105(4):113–119
Huang Z, Li Z, Zheng L, Wu W, Chai Z, Shi W (2019) Adsorption of Eu(III) and Th(IV) on three-dimensional graphene-based macrostructure studied by spectroscopic investigation. Environ Pollut 248:82–89
Huang X, Guida S, Jefferson B, Soares A (2020) Economic evaluation of ion-exchange processes for nutrient removal and recovery from municipal wastewater. npj Clean Water 3(1):7
Jung KW, Lee S, Lee YJ (2017) Synthesis of novel magnesium ferrite (MgFe2O4)/biochar magnetic composites and its adsorption behavior for phosphate in aqueous solutions. Biores Technol 245:751–759
Kokalj A (2012) On the HSAB based estimate of charge transfer between adsorbates and metal surfaces. Chem Phys 393(1):1–12
Kumar S, Nair RR, Pillai PB, Gupta SN, Sood AK (2014) Graphene oxide-MnFe2O4 magnetic nanohybrids for efficient removal of lead and arsenic from water. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(20):17426
Li K, Gao Q, Yadavalli G, Shen X, Lei H, Han B, Xia K, Zhou C (2015) Selective adsorption of Gd3+ on a magnetically retrievable imprinted chitosan/carbon nanotube composite with high capacity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(38):21047–21055
Li B, Wang N, Wan J, Xiong S, Liu H, Li S, Zhao R (2016) In-situ gamma-ray survey of rare-earth tailings dams—a case study in Baotou and Bayan Obo Districts, China. J Environ Radioact 151:304–310
Liang P-L, Yuan L-Y, Deng H, Wang X-C, Wang L, Li Z-J, Luo S-Z, Shi W-Q (2020) Photocatalytic reduction of uranium(VI) by magnetic ZnFe2O4 under visible light. Appl Catal B 267:118688
Liu J, Zeng M, Yu R (2016) Surfactant-free synthesis of octahedral ZnO/ZnFe2O4 heterostructure with ultrahigh and selective adsorption capacity of malachite green. Sci Rep 6(1):25074–25074
Mahmed N, Heczko O, Lancok A, Hannula SP (2014) The magnetic and oxidation behavior of bare and silica-coated iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized by reverse co-precipitation of ferrous ion (Fe2+) in ambient atmosphere. J Magn Magn Mater 353:15–22
Marcela S, Cornelia M et al (2015) Fine MnFe2O4 nanoparticles for potential environmental applications. J Therm Anal Calorim 121(123):1003–1010
Mohammadi M, Sedighi M, Hemati M (2020) Removal of petroleum asphaltenes by improved activity of NiO nanoparticles supported on green AlPO-5 zeolite: process optimization and adsorption isotherm. Petroleum 6(2):182–188
Oter C, Zorer OS (2020) Kinetic, isothermal and thermodynamic studies on Th(IV) adsorption by different modified activated carbons. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 323(1):341–351
Park CM, Kim YM, Kim K-H, Wang D, Su C, Yoon Y (2019) Potential utility of graphene-based nano spinel ferrites as adsorbent and photocatalyst for removing organic/inorganic contaminants from aqueous solutions: a mini review. Chemosphere 221:392–402
Perreault LL, Giret S, Gagnon M, Florek J, Lariviere D, Kleitz F (2017) Functionalization of mesoporous carbon materials for selective separation of lanthanides under acidic conditions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(13):12003–12012
Shen J, Ma G, Zhang J, Quan W, Li L (2015) Facile fabrication of magnetic reduced graphene oxide-ZnFe2O4 composites with enhanced adsorption and photocatalytic activity. Appl Surf Sci 359(DEC.30):455–468
Somvanshi SB, Khedkar MV, Kharat PB, Jadhav KM (2020) Influential diamagnetic magnesium (Mg2+) ion substitution in nano-spinel zinc ferrite (ZnFe2O4): thermal, structural, spectral, optical and physisorption analysis. Ceram Int 46(7):8640–8650
Sun S (2006) Recent advances in chemical synthesis, self-assembly, and applications of FePt nanoparticles. Adv Mater 18(4):393–403
Sun Q, Aguila B, Earl LD, Abney CW, Wojtas L, Thallapally PK, Ma S (2018) Covalent organic frameworks as a decorating platform for utilization and affinity enhancement of chelating sites for radionuclide sequestration. Adv Mater 30(20):1705479
Vergis BR, Kottam N, Hari Krishna R, Nagabhushana BM (2019) Removal of Evans Blue dye from aqueous solution using magnetic spinel ZnFe2O4 nanomaterial: adsorption isotherms and kinetics. Nano Struct Nano Objects 18:100290
Wang X, Chen L, Wang L, Fan Q, Pan D, Li J, Chi F, Xie Y, Yu S, Xiao C, Luo F, Wang J, Wang X, Chen C, Wu W, Shi W, Wang S, Wang X (2019) Synthesis of novel nanomaterials and their application in efficient removal of radionuclides. Sci China Chem 62(8):933–967
Wang X, Feng J, Zhang Z, Zeng W, Gao M, Lv Y, Wei T, Ren Y, Fan Z (2020) Pt enhanced the photo-Fenton activity of ZnFe2O4/α-Fe2O3 heterostructure synthesized via one-step hydrothermal method. J Colloid Interface Sci 561:793–800
Xiong XH, Yu ZW, Gong LL, Tao Y, Gao Z, Wang L, Yin WH, Yang LX, Luo F (2019) Ammoniating covalent organic framework (COF) for high-performance and selective extraction of toxic and radioactive uranium ions. Adv Sci 6(16):1900547
Xu J, Zhou L, Jia Y, Liu Z, Adesina AA (2015) Adsorption of thorium (IV) ions from aqueous solution by magnetic chitosan resins modified with triethylene-tetramine. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 303(1):347–356
Yang Y, Liu J, Zhang B, Liu F (2017) Mechanistic studies of mercury adsorption and oxidation by oxygen over spinel-type MnFe2O4. J Hazard Mater 321:154–161
Yezi H, Chaofeng Z et al (2018) Combining batch technique with theoretical calculation studies to analyze the highly efficient enrichment of U(VI) and Eu(III) on magnetic MnFe2O4 nanocubes. Chem Eng J 349:347–357
Zhang Y, Yan L, Xu W, Guo X, Cui L, Gao L, Wei Q, Du B (2014) Adsorption of Pb(II) and Hg(II) from aqueous solution using magnetic CoFe2O4-reduced graphene oxide. J Mol Liq 191:177–182
Zhang C, Li X, Chen Z, Wen T, Huang S, Hayat T, Alsaedi A, Wang X (2018) Synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbonaceous materials and their highly efficient capture of uranium from solutions. Sci China Chem 61(3):281–293
Zhang L, Guo J, Huang X, Wang W, Sun P, Li Y, Han J (2019) Functionalized biochar-supported magnetic MnFe2O4 nanocomposite for the removal of Pb(ii) and Cd(ii). RSC Adv 9:365–376
Zhang Yakun Yan Liangguo XW (2014) Adsorption of Pb(II) and Hg(II) from aqueous solution using magnetic CoFe2O4—reduced graphene oxide. J Mol Liq 191(193):177–182
Zhu S, Ho SH, Huang X, Wang D, Yang F, Wang L, Wang C, Cao X, Ma F (2017) Magnetic nanoscale zerovalent iron assisted biochar: interfacial chemical behaviors and heavy metals remediation performance. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(11):9673–9682
Acknowledgements
This work has been partially supported by the Inner Mongolia Natural Science Foundation (2016BS0511,2020MS02015,2019LH02006). The authors also thank the anonymous reviewers for their invaluable insight and helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Fatih Şen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W.D., Cui, Y.X., Zhang, L.K. et al. Synthesis of a novel ZnFe2O4/porous biochar magnetic composite for Th(IV) adsorption in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 18, 2733–2746 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-03023-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-03023-1