Abstract
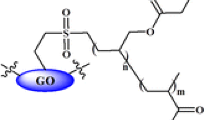
A facial and novel method for removal of Pb+2 based on the appealing interaction between thiosemicarbazide-modified graphene oxide nanosheets and Pb+2 is reported in this work. Textural and chemical characterization of graphite, graphene oxide, esterified graphene oxide and thiosemicarbazide-modified graphene oxide nanosheets was investigated using thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), nitrogen adsorption at − 196 °C, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Adsorption of Pb+2 was confirmed by Langmuir model with maximum adsorption capacity of 192.7 mg/g for thiosemicarbazide-modified graphene oxide nanosheets at 27 °C and initial pH value of 5.0. Kinetic studies showed that the adsorption of lead ions on the solid adsorbents follows pseudo-first order and Elovich kinetic models. Regeneration of graphene oxide, esterified graphene oxide and thiosemicarbazide-modified graphene oxide nanosheets was studied using different eluents (H2O, 0.1 M HCl, 0.1 M EDTA) at different pH values. Both of disodium salt of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and HCl solutions (0.1 M) are efficient eluents to desorb lead cations from the solid adsorbent surface. Desorption efficiency of HCl solution decreases with increasing its pH value.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghdam K, Omayon H, Panahi A, Alaei E, Hasani AH, Moniri E (2016) Preparation of functionalized graphene oxide and its application as a nanoadsorbent for Hg2+ removal from aqueous solution. Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5226-2
Ahmed SA (2008) Alumina physically loaded by thiosemicarbazide for selective preconcentration of mercury (II) ion from natural water samples. J Hazard Mater 156:521–529
Alok PS, Chauhan Komal C (2016) Comparative studies on graphite and carbon black powders, and their dispersions. J Mol Liq 221:292–297
Becerril HA, Mao J, Liu Z, Stoltenberg RM, Bao Z, Chen Y (2008) Evaluation of solution-recessed reduced graphene oxide films as transparent conductors. ACS Nano 2:463–470
Ciesielczyk F, Bartczak P, Jesionowski T (2015) A comprehensive study of Cd(II) ions removal utilizing high surface-area binary Mg–Si hybrid oxide adsorbent. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:3613–3626
Ciesielczyk F, Bartczak P, Jesionowski T (2016) Removal of cadmium(II) and lead(II) ions from model aqueous solutions using sol–gel-derived inorganic oxide adsorbent. Adsorption 22(4):445–458
El-Metwally NM, Al-Hazmi GAA (2013) Spectroscopic evaluation for VO(II), Ni(II), Pd(II) and Cu(II) complexes derived from thiosemicarbazide: a special emphasis on EPR study and DNA cleavage. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 107:289–295
Fan L, Luo C, Sun M, Qiu H (2012) Synthesis of graphene oxide decorated with magnetic cyclodextrin for fast chromium removal. J Mater Chem 22(47):24577
Fan L, Luo C, Sun M, Li X, Qiu H (2013) Highly selective adsorption of lead ions by water-dispersible magnetic chitosan/graphene oxide composites. Colloids Surf B 103:523–529
Golbad S, Khoshnoud P, Abu-Zahra N (2016) Hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxy sodalite from fly ash for the removal of lead ions from water. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1133-x
Kosynkin DV, Higginbotham AL, Sinitskii A, Lomeda JR, Dimiev A, Price BK, Tour JM (2009) Longitudinal unzipping of carbon nanotubes to form graphene nanoribbons. Nature 458:872–876
Li L, Fan L, Sun M, Qiu H, Li X, Duan H, Luo C (2013) Adsorbent for chromium removal based on graghene oxide functionalized with magnetic cyclodextrin-chitosan. Colloids Surf B 107:76–83
Liu L, Li C, Bao C, Jia Q, Xiao P, Liu X, Zhang Q (2012) Preparation and characterization of chitosan/graphene oxide composites for the adsorption of Au(III) and Pd(II). Talanta 93:350–357
Liu Z, Zhou H, Huang Z, Wang W, Zeng F, Kuang Y (2013) Graphene covalently functionalized with poly(pphenylenediamine) as high performance electrode material for supercapacitors. J Mater Chem A 1(10):3454–3462
Lv M, Wang X, Li J, Yang X, Zhang C, Yang HuH (2013) Cyclodextrin-reduced graphene oxide hybrid nanosheets for the simultaneous determination of lead(II) and cadmium(II) using square wave anodic stripping voltammetry. Electrochim Acta 108:412–420
Mohamed A, Ahamed R, Jeyakumar D, Burkanudeen AR (2013) Removal of cations using ion-binding terpolymer involving 2-amino-6-nitro-benzothiazole and thiosemicarbazide with formaldehyde by batch equilibrium technique. J Hazard Mat 248–249:59–68
Mohamed EM, Gehan MN, Nabila ME, Heba IB, Sandeep K, Tarek MA (2016) Kinetics, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies of the adsorption of reactive red 195 A dye from water by modified Switchgrass Biochar adsorbent. J Ind Eng Chem 37:156–167
Moharram MA, Tohami T, El Hotaby WM, Bakr AM (2016) Graphene oxide porous crosslinked cellulose nanocomposite microspheres for lead removal: kinetic study. React Funct Polym 101:9–19
Mukherjee R, Bhunia P, De S (2016) Impact of graphene oxide on removal of heavy metals using mixed matrix membrane. Chem Eng J 292:284–297
Murugan VA, Muraliganth T, Manthiram A (2009) Rapid, facial microwave-solvothermal synthesis of grapheme nanosheets and their polyaniline nanocomposites for energy storage. Chem Mater 21:5004–5006
Pourjavadi A, Abedin-Moghanaki A, Hosseini SH (2016) Synthesis of poly(amidoamine)-graft- poly(methyl acrylate) magnetic nanocomposite for removal of lead contaminant from aqueous media. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:2437–2448
Pumera M (2013) Electrochemistry of graphene, graphene oxide and other graphenoids. Electrochem Commun 36:14–18
Ramezanzadeh B, Haeri Z, Ramezanzadeh M (2016) A facile route of making silica nanoparticles-covered graphene oxide nanohybrids (SiO2–GO); fabrication of SiO2–GO/epoxy composite coating with superior barrier and corrosion protection performance. Chem Eng J 303:511–528
Salvatore C, Antonio G, Demetrio M, Nicola M, Alberto P (2016) Pb(II) adsorption by a novel activated carbon–alginate composite material: kinetic and equilibrium study. Int J Biol Macromol 92:769–778
Wang S, Gong W, Liu X, Yao Y, Gao B, Yue Q (2007) Removal of lead(II) from aqueous solution by adsorption onto manganese oxide-coated carbon nanotubes. Sep Purif Technol 58:17–23
Wang Z, Yue B, Teng J, Jiao F, Jiang X, Yu J, Zhong M, Chen X (2016) Tartaric acid modified graphene oxide as a novel adsorbent for high-efficiently removal of Cu(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solutions. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 66:181–190
Wu W, Yang Y, Zhou H, Ye T, Huang Z, Liu R, Kuang Y (2013) Highly efficient removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solution by using graphene oxide. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1372–1379
Yan X, Qun G, Hongqin L, Kangsheng Z (2016) Effects of functional graphene oxide on the properties of phenyl silicone rubber composites. Polym Test 54:168–175
Yang X, Li Y, Du Q, Sun J, Chen L, Hu S, Wang Z, Yanzhi X, Linhua X (2015) Highly effective removal of basic fuchsin from aqueous solutions by anionic polyacrylamide/graphene oxide aerogels. J Colloid Interface Sci 453:107–114
Yari M, Rajab M, Moradi O, Yari A, Asif M, Agarwal S, Gupta VK (2015) Kinetics of the adsorption of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions by graphene oxide and thiol functionalized graphene oxide. J Mol Liq 209:50–57
Yu B, Xu J, Liu J, Yang S, Luo J, Zhou Q, Wan J, Liao R, Wang H (2013) Adsorption behavior of copper ions on graphene oxide–chitosan aerogel. J Environ Chem Eng 1:1044–1050
Zhu C, Dong X, Chen Z, Naidu R (2016) Adsorption of aqueous Pb(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) ions by amorphous tin(VI) hydrogen phosphate: an excellent inorganic adsorbent. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:1257–1268
Acknowledgements
This research was financed by the Research Sector of Damanhour University, Egypt and partially supported the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic (Institutional Project No. RVO: 68081723).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Josef Trögl.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, A.F., Bulánek, R. Preparation and characterization of thiosemicarbazide functionalized graphene oxide as nanoadsorbent sheets for removal of lead cations. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 6207–6216 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2002-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2002-6