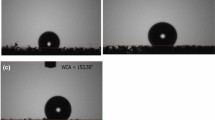
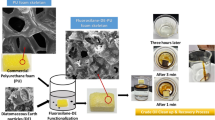
Abstract
Cost-effective oil absorbents for the remediation of oil spills have been developed following a facile process involving the modification of polyurethane foam surfaces with mixtures of silicon oxide nanoparticles and polydimethylsiloxane. Polyurethane foams with different pore sizes and connectivity are tested, and it was found that the proposed treatment, applied by dip coating and spray coating, strongly improves the intrinsic foams’ performance in terms of selectivity and oil absorption capacity. The modified foams reach oil absorption capacities up to 60 g/g and simultaneous negligible water uptake. The treatment is stable after multiple absorption cycles, and therefore, the foams can be reused without significant decrease in their performance, being possible, after five cycles of absorption and recovery of oil, to reach overall oil absorption capacities up to 250 g/g.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramoff MD, Magalhães PJ, Ram SJ (2004) Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Inter 11:36–42
Adebajo MO, Frost RL, Kloprogge JT, Carmody O, Kokot S (2003) Porous materials for oil spill cleanup: a review of synthesis and absorbing properties. J Porous Mater 10:159–170
Bi H, Xie X, Yin K, Zhou Y, Wan S, He L, Xu F, Banhart F, Sun L, Ruoff RS (2012) Spongy graphene as a highly efficient and recyclable sorbent for oils and organic solvents. Adv Funct Mater 22:4421–4425
Calcagnile P, Fragouli D, Bayer IS, Anyfantis GC, Martiradonna L, Cozzoli PD, Cingolani R, Athanassiou A (2012) Magnetically driven floating foams for the removal of oil contaminants from water. ACS Nano 6:5413–5419
Ceseracciu L, Heredia-Guerrero JA, Dante S, Athanassiou A, Bayer IS (2015) Robust and biodegradable elastomers based on corn starch and polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:3742–3753
Chen X, Weibel JA, Garimella SV (2016) Continuous oil–water separation using polydimethylsiloxane-functionalized melamine sponge. Ind Eng Chem Res 55:3596–3602
Choi SJ, Kwon TH, Im H, Moon DI, Baek DJ, Seol ML, Duarte JP, Choi YK (2011) A polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sponge for the selective absorption of oil from water. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:4552–4556
Eni (2015) Incident statistics [online]. http://www.eni.com/en_NG/sustainability/environment/response-to-oil-spills/spill-incident-statistics/spill-incident-statistics.shtml
Feng L, Zhang Z, Mai Z, Ma Y, Liu B, Jiang L, Zhu D (2004) A super-hydrophobic and super-oleophilic coating mesh film for the separation of oil and water. Angew Chem Int Edit 116:2046–2048
Fingas M (2013) The basics of oil spill cleanup, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Ge J, Ye Y-D, Yao H-B, Zhu X, Wang X, Wu L, Wang J-L, Ding H, Yong N, He L-H, Yu S-H (2014) Pumping through porous hydrophobic/oleophilic materials: an alternative technology for oil spill remediation. Angew Chem Int Edit 53:3612–3616
Ge B, Men X, Li Y, Zhang Z (2016) One-step foaming method to functional polyurethane absorbents foam. Sep Sci Technol 51:1299–1306
He Y, Liu Y, Wu T, Ma J, Wang X, Gong Q, Kong W, Xing F, Liu Y, Gao J (2013) An environmentally friendly method for the fabrication of reduced graphene oxide foam with a super oil absorption capacity. J Hazard Mater 260:796–805
Husseien M, Amer AA, El-Maghraby A, Taha NA (2009) Availability of barley straw application on oil spill clean up. Int J Environ Sci Technol 6:123–130
Hussein M, Amer AA, Sawsan II (2008) Oil spill sorption using carbonized pith bagasse: trial for practical application. Int J Environ Sci Technol 5:233–242
Jiang G, Hu R, Xi X, Wang X, Wang R (2013) Facile preparation of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic sponge for fast removal of oils from water surface. J Mater Res 28:651–656
Keshavarz A, Zilouei H, Abdolmaleki A, Asadinezhad A (2015a) Enhancing oil removal from water by immobilizing multi-wall carbon nanotubes on the surface of polyurethane foam. J Environ Manag 157:279–286
Keshavarz A, Zilouei H, Abdolmaleki A, Asadinezhad A, Nikkhah AA (2015b) Impregnation of polyurethane foam with activated carbon for enhancing oil removal from water. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:699–710
Li H, Boufadel MC (2010) Long-term persistence of oil from the Exxon Valdez spill in two-layer beaches. Nat Geosci 3:96–99
Li H, Liu L, Yang F (2013) Oleophilic polyurethane foams for oil spill cleanup. Procedia Environ Sci 18:528–533
Li B, Liu X, Zhang X, Zou J, Chai W, Lou Y (2015) Rapid adsorption for oil using superhydrophobic and superoleophilic polyurethane sponge. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 90:2106–2112
Lin J, Shang Y, Ding B, Yang J, Yu J, Al-Deyab SS (2012) Nanoporous polystyrene fibers for oil spill cleanup. Mar Pollut Bull 64:347–352
Liu Y, Ma J, Wu T, Wang X, Huang G, Liu Y, Qiu H, Li Y, Wang W, Gao J (2013) Cost-effective reduced graphene oxide-coated polyurethane sponge as a highly efficient and reusable oil-absorbent. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:10018–10026
Liu H-D, Gu B, Jia F, Li Y, Ying Q, Yuan WF, Chen B, He Q (2016) Facile fabrication of hydrophobic octadecylamine-functionalized polyurethane foam for oil spill cleanup. J Macromol Sci A 53:196–200
Medjahdi M, Benderdouche N, Bestani B, Duclaux L, Reinert L (2016) Modeling of the sorption of crude oil on a polyurethane foam-powdered activated carbon composite. Desalin Water Treat 57:22311–22320
Napierska D, Thomassen LC, Lison D, Martens JA, Hoet PH (2010) The nanosilica hazard: another variable entity. Part Fibre Toxicol 7:39
Nikkhah AA, Zilouei H, Asadinezhad A, Keshavarz A (2015) Removal of oil from water using polyurethane foam modified with nanoclay. Chem Eng J 262:278–285
NRC (2005) Oil spill dispersants: efficacy and effects. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC
Peacock EE, Nelson RK, Solow AR, Warren JD, Baker JL, Reddy CM (2005) The West Falmouth oil spill: ∼100 kg of oil found to persist decades later. Environ Forensics 6:273–281
Peng L, Yuan S, Yan G, Yu P, Luo Y (2014) Hydrophobic sponge for spilled oil absorption. J Appl Polym Sci 131:40886
Pinto J, Solorzano E, Rodriguez-Perez MA, De Saja JA (2013) Characterization of the cellular structure based on user-interactive image analysis procedures. J Cell Plast 49:555–575
Pinto J, Athanassiou A, Fragouli D (2016) Effect of the porous structure of polymer foams on the remediation of oil spills. J Phys D Appl Phys 49:145601–145608
Pintor AM, Ferreira CI, Pereira JC, Correia P, Silva SP, Vilar VJ, Botelho CM, Boaventura RA (2012) Use of cork powder and granules for the adsorption of pollutants: a review. Water Res 46:3152–3166
Rengasamy RS, Das D, Karan CP (2011) Study of oil sorption behavior of filled and structured fiber assemblies made from polypropylene, kapok and milkweed fibers. J Hazard Mater 186:526–532
Shell-Oil-Company (2015) Oil spills in the Niger Delta—monthly data. http://www.shell.com.ng/sustainability/environment/oil-spills.html. Accessed 20 Dec 2016
Shi H, Shi D, Yin L, Yang Z, Luan S, Gao J, Zha J, Yin J, Li RK (2014) Ultrasonication assisted preparation of carbonaceous nanoparticles modified polyurethane foam with good conductivity and high oil absorption properties. Nanoscale 6:13748–13753
Su C (2009) Highly hydrophobic and oleophilic foam for selective absorption. Appl Surf Sci 256:1413–1418
Tjandra R, Lui G, Veilleux A, Broughton J, Chiu G, Yu A (2015) Introduction of an enhanced binding of reduced graphene oxide to polyurethane sponge for oil absorption. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:3657–3663
Wang CF, Lin SJ (2013) Robust superhydrophobic/superoleophilic sponge for effective continuous absorption and expulsion of oil pollutants from water. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:8861–8864
Wang J, Zheng Y, Wang A (2012) Superhydrophobic kapok fiber oil-absorbent: preparation and high oil absorbency. Chem Eng J 213:1–7
Wang B, Li J, Wang G, Liang W, Zhang Y, Shi L, Guo Z, Liu W (2013a) Methodology for robust superhydrophobic fabrics and sponges from in situ growth of transition metal/metal oxide nanocrystals with thiol modification and their applications in oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:1827–1839
Wang H, Lin KY, Jing B, Krylova G, Sigmon GE, Mcginn P, Zhu Y, Na C (2013b) Removal of oil droplets from contaminated water using magnetic carbon nanotubes. Water Res 47:4198–4205
Wang J, Zheng Y, Wang A (2013c) Coated kapok fiber for removal of spilled oil. Mar Pollut Bull 69:91–96
Wu J, Wang N, Wang L, Dong H, Zhao Y, Jiang L (2012) Electrospun porous structure fibrous film with high oil adsorption capacity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:3207–3212
Wu D, Yu Z, Wu W, Fang L, Zhu H (2014) Continuous oil–water separation with surface modified sponge for cleanup of oil spills. RSC Adv 4:53514–53519
Wu L, Li L, Li B, Zhang J, Wang A (2015) Magnetic, durable, and superhydrophobic polyurethane@Fe3O4@SiO2@fluoropolymer sponges for selective oil absorption and oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:4936–4946
Yu L, Hao G, Zhou S, Jiang W (2016) Durable and modified foam for cleanup of oil contaminations and separation of oil–water mixtures. RSC Adv 6:24773–24779
Zhou X, Zhang Z, Xu X, Guo F, Zhu X, Men X, Ge B (2013a) Robust and durable superhydrophobic cotton fabrics for oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:7208–7214
Zhou X, Zhang Z, Xu X, Men X, Zhu X (2013b) Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic sponge with selective absorption and collection of oil from water. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:9411–9416
Zhu Q, Pan Q (2014) Mussel-inspired direct immobilization of nanoparticles and application for oil–water separation. ACS Nano 8:1402–1409
Zhu H, Qiu S, Jiang W, Wu D, Zhang C (2011a) Evaluation of electrospun polyvinyl chloride/polystyrene fibers as sorbent materials for oil spill cleanup. Environ Sci Technol 45:4527–4531
Zhu Q, Pan Q, Liu F (2011b) Facile removal and collection of oils from water surfaces through superhydrophobic and superoleophilic sponges. J Phys Chem C 115:17464–17470
Zhu Q, Chu Y, Wang Z, Chen N, Lin L, Liu F, Pan Q (2013) Robust superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge as a highly reusable oil-absorption material. J Mater Chem A 1:5386–5393
Acknowledgements
This study was supported financially by EDISON (Italy). Recticel Flexible Foams Inc. is gratefully acknowledged for providing one of the pristine PU foams characterized in this work. The authors kindly acknowledge the assistance of Alice Scarpellini (Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia) for the TEM study of the nanoparticles.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Josef Trögl.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pinto, J., Heredia-Guerrero, J.A., Athanassiou, A. et al. Reusable nanocomposite-coated polyurethane foams for the remediation of oil spills. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 14, 2055–2066 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1310-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1310-6