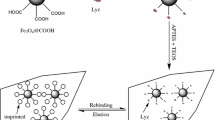
Abstract
Molecular imprinting has shown significant advances in the recognition and separation of small molecules. This technology has been proposed for different applications, including solid-phase extraction, stationary phases in HPLC, chemical sensing, drug-delivery systems, passive sampling, among others. However, imprinting of biological macromolecules with increased structural complexity is still challenging. In this work, CaCO3 microparticles were synthesized using a precipitation method and employed as a novel support for the preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) towards a model protein (bovine serum albumin, BSA), through the polymerization of dopamine. Microparticles exhibited a rhombohedral morphology and a narrow size distribution (2.5 ± 0.4 µm). Reaction times showed to increase the polydopamine coating thickness, the MIP adsorption capacities, and the impression efficiency, reaching values of 5.1 nm, 50.2 ± 5.9 mg BSA/g sample, and 8.1 after 24 h, respectively. In addition, lower adsorption capacities were observed against proteins with similar physicochemical properties, such as ovalbumin (25.07 ± 2.5 mg/g) and casein (19.62 ± 7.01 mg/g). The adsorption kinetic assay indicated that MIPs present the highest BSA adsorption capacity after 1 h. In this regard, a methodology that offers a simple approach for the synthesis of materials designed for the specific recognition and separation of biological molecules is presented. The microparticles developed represent a potential use for protein separation in applications such as stationary phase in liquid chromatography.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Should any data files be needed they are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Rico Yuste A, Carrasco S (2019) Molecularly imprinted polymer-based hybrid materials for the development of optical sensors. Polymers 11:1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/POLYM11071173
Belbruno JJ (2019) Molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem Rev 119:94–119. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00171
Liu G, Huang X, Li L, Xu X, Zhang Y, Lv J, Xu D (2019) Recent advances and perspectives of molecularly imprinted polymer-based fluorescent sensors in food and environment analysis. Nanomaterials 9:1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/NANO9071030
Mostafa AM, Barton SJ, Wren SP, Barker J (2022) Development of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the extraction of salivary pepsin prior to analysis by a novel HPLC-SEC method. Polymer 261:125417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2022.125417
Lu W, Liu J, Li J, Wang X, Lv M, Cui R, Chen L (2019) Dual-template molecularly imprinted polymers for dispersive solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones in water samples coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. Analyst 144:1292–1302. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AN02133C
Olcer YA, Demirkurt M, Demir MM, Eroglu AE (2017) Development of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) as a solid phase extraction (SPE) sorbent for the determination of ibuprofen in water. RSC Adv 7:31441–31447. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA05254E
Madikizela LM, Tavengwa NT, Chimuka L (2018) Applications of molecularly imprinted polymers for solid-phase extraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics from environmental waters and biological samples. J Pharm Biomed Anal 147:624–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2017.04.010
Kalogiouri NP, Tsalbouris A, Kabir A, Furton KG, Samanidou VF (2020) Synthesis and application of molecularly imprinted polymers using sol–gel matrix imprinting technology for the efficient solid-phase extraction of BPA from water. Microchem J 157:104965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.104965
Nematollahzadeh A, Shojaei A, Abdekhodaie MJ, Sellergren B (2013) Molecularly imprinted polydopamine nano-layer on the pore surface of porous particles for protein capture in HPLC column. J Colloid Interface Sci 404:117–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.04.004
Hroboňová K, Lomenova A (2018) Molecularly imprinted polymer as stationary phase for HPLC separation of phenylalanine enantiomers. Monatshefte für Chemie Chem Mon 149:939–946. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-018-2155-5
Podjava A, Šilaks A (2021) Study of chromatographic properties of catecholamines and their acidic metabolites using novel molecularly imprinted polymers as stationary phases. Key Eng Mater 903:15–21. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.903.15
Yang F, Wang R, Na G, Yan Q, Lin Z, Zhang Z (2018) Preparation and application of a molecularly imprinted monolith for specific recognition of domoic acid. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:1845–1854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0843-3
Zare EN, Fallah Z, Le VT, Doan VD, Mudhoo A, Joo SW, Vasseghian Y, Tajbakhsh M, Moradi O, Sillanpää M, Varma RS (2022) Remediation of pharmaceuticals from contaminated water by molecularly imprinted polymers: a review. Environ Chem Lett 20:2629–2664
Heidari G, Afruzi FH, Zare EN (2023) Molecularly imprinted magnetic nanocomposite based on carboxymethyl dextrin for removal of ciprofloxacin antibiotic from contaminated water. Nanomaterials 13:489. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030489
Casis N, Busatto C, Fidalgo de Cortalezzi MM, Ravaine S, Estenoz DA (2015) Molecularly imprinted hydrogels from colloidal crystals for the detection of progesterone. Polym Int 64:773–779. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.4851
Kadhem A, Xiang S, Nagel S, Lin CH, Fidalgo de Cortalezzi M (2018) Photonic molecularly imprinted polymer film for the detection of testosterone in aqueous samples. Polymers 10:349. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040349
Gao M, Gao Y, Chen G, Huang X, Xu X, Lv J, Wang J, Xu D, Liu G (2020) Recent advances and future trends in the detection of contaminants by molecularly imprinted polymers in food samples. Front Chem 8:616326. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.616326
Zaidi SA (2020) Molecular imprinting: a useful approach for drug delivery. Mater Sci Energy Technol 3:72–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2019.10.012
Liu R, Poma A (2021) Advances in molecularly imprinted polymers as drug delivery systems. Molecules 26:3589. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123589
Sanadgol N, Wackerlig J (2020) Developments of smart drug-delivery systems based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for targeted cancer therapy: a short review. Pharmaceutics 12:831. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12090831
Khulu S, Ncube S, Nuapia Y, Madikizela LM, Mavhunga E, Chimuka L (2022) Development and application of a membrane assisted solvent extraction-molecularly imprinted polymer based passive sampler for monitoring of selected pharmaceuticals in surface water. Water Res 225:119145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.119145
Garnier A, Montigny C, Causse L, Spinelli S, Avezac M, Otazaghine B, Gonzalez C (2022) Synthesis of an organotin specific molecularly imprinted polymer for organotin passive sampling in seawater. Water 14:1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111786
Mostafa AM, Barton SJ, Wren SP, Barker J (2021) Review on molecularly imprinted polymers with a focus on their application to the analysis of protein biomarkers. Trend Anal Chem 144:116431. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TRAC.2021.116431
Pupin RR, Foguel MV, Gonçalves LM, del Sotomayor M, PT, (2020) Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers obtained by photopolymerization for selective recognition of penicillin G. J Appl Polym Sci 137:48496. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.48496
Wei X, Yu M, Guo J (2019) A core-shell spherical silica molecularly imprinted polymer for efficient selective recognition and adsorption of dichlorophen. Fiber Polym 20:459–465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-019-8822-2
Qasim S, Hsu SY, Rossi E, Salahshoor Z, Lin CH, Parada LP, Fidalgo M (2022) Detection of progesterone in aqueous samples by molecularly imprinted photonic polymers. Microchim Acta 189:174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05290-w
Malik AA, Nantasenamat C, Piacham T (2017) Molecularly imprinted polymer for human viral pathogen detection. Mater Sci Eng C 77:1341–1348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.209
Nahhas AF, Webster TJ (2021) The promising use of nano-molecular imprinted templates for improved SARS-CoV-2 detection, drug delivery and research. J Nanobiotechnol 19:305. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-021-01032-x
Dar KK, Shao S, Tan T, Lv Y (2020) Molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective recognition of microorganisms. Biotechnol Adv 45:107640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2020.107640
El-Schich Z, Zhang Y, Feith M, Beyer S, Sternbæk L, Ohlsson L, Stollenwerk M, Wingren AG (2020) Molecularly imprinted polymers in biological applications. Biotechniques 69:406–419. https://doi.org/10.2144/btn-2020-0091
Zhang Z, Niu D, Li Y, Shi J (2018) Magnetic, core-shell structured and surface molecularly imprinted polymers for the rapid and selective recognition of salicylic acid from aqueous solutions. Appl Surf Sci 435:178–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.033
Cui F, Zhou Z, Zhou HS (2020) Molecularly imprinted polymers and surface imprinted polymers based electrochemical biosensor for infectious diseases. Sensors 20:996. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20040996
Zhang W, Zhang Y, Wang R, Zhang P, Zhang Y, Randell E, Zhang M, Jia Q (2022) A review: development and application of surface molecularly imprinted polymers towards amino acids, peptides, and proteins. Anal Chem Acta 1234:340319. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACA.2022.340319
Wang Y, Zhou J, Wu C, Tian L, Zhang B, Zhang Q (2018) Fabrication of micron-sized BSA-imprinted polymers with outstanding adsorption capacity based on poly(glycidyl methacrylate)/polystyrene (PGMA/PS) anisotropic microspheres. J Mater Chem B 6:5860–5866. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB01423J
Babou-Kammoe R, Hamoudi S, Larachi F, Belkacemi K (2012) Synthesis of CaCO3 nanoparticles by controlled precipitation of saturated carbonate and calcium nitrate aqueous solutions. Can J Chem Eng 90:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.20673
Boyjoo Y, Pareek VK, Liu J (2014) Synthesis of micro and nano-sized calcium carbonate particles and their applications. J Mater Chem A 2:14270–14288. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA02070G
Mirzayi B, Nematollahzadeh A, Seraj S (2015) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic maghemite/catecholamine core/shell nanoparticles. Powder Technol 270:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2014.10.022
Kato T, Sugawara A, Hosoda N (2002) Calcium carbonate-organic hybrid materials. Adv Mater 14:869. https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-4095(20020618)14:12%3c869::AID-ADMA869%3e3.0.CO;2-E
Islam KN, Bakar MZBA, Ali ME, Bin HMZ, Noordin MM, Loqman MY, Miah G, Wahid H, Hashim U (2013) A novel method for the synthesis of calcium carbonate (aragonite) nanoparticles from cockle shells. Powder Technol 235:70–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2012.09.041
Luo H, Gu C, Zheng W, Dai F, Wang X, Zheng Z (2015) Facile synthesis of novel size-controlled antibacterial hybrid spheres using silver nanoparticles loaded with polydopamine spheres. RSC Adv 5:13470–13477. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra16469e
Kusuktham B (2011) Spinning of PET fibres mixed with calcium carbonate. Asian J Text 1:106–113. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajt.2011.106.113
Lazarevic A, Pokrajac D, Marcano A, Melikechi N (2009) Support vector machine based classification of fast Fourier transform spectroscopy of proteins. Adv Biomed Clin Diag Syst 7169:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.809964
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the financial support from CONICET, MINCyT, and UNL. The authors would also like to express their sincere gratitude to Lic. Malen Menegon for her valuable support in the gel electrophoresis assays.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Citta, M.d., Fookes, F., Busatto, C. et al. Molecularly imprinted CaCO3/polydopamine hybrid composite for selective protein recognition. Iran Polym J 32, 1111–1122 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-023-01189-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-023-01189-2