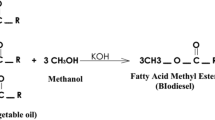
Abstract
Engine component design optimization plays an important role in enhancing the performance and emission characteristics of internal combustion engines. It has already been demonstrated that biodiesel-fueled compression ignition engines emit lower levels of emissions. The present work involves optimizing toroidal piston bowl geometry, in order to improve performance, emission, and combustion characteristics in dual fuel mode using diesel-acetylene and biodiesel-acetylene. The turbulence-creating tendency is utilized for optimizing piston bowl geometry to induce homogeneous mixture creation in the combustion chamber. To optimize the piston geometry physically is a time- and cost-consuming process, so the ANSYS-FLUENT CFD code is used to simulate the modified piston bowl geometries, where 1-, 1.5-, and 2-mm-diameter helical holes are placed in the surface of the crown to induce turbulence in the combustion chamber. Furthermore, 3, 4, and 5 holes are drilled in the crown surface for each diameter. The selection of optimum number of holes is carried out based on the analysis of turbulent intensity contours and the optimum hole diameter selection is based on the turbulent kinetic energy distribution. The results of the simulations show that the piston bowl of a diesel-acetylene fueled dual fuel engine with 5 holes of 1-mm-diameter piston geometry induces more turbulence than the other piston bowl geometries. Moreover, when compared to the other piston bowl geometries, the biodiesel-acetylene fueled dual fuel engine piston bowl with 5 holes of 2-mm-diameter piston geometry induces more turbulence.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- aTDC:
-
After top dead center
- BTE:
-
Brake thermal efficiency
- bTDC:
-
Before top dead center
- CAD:
-
Computer-aided design
- CI:
-
Compression ignition
- CFD:
-
Computational fluid dynamics
- CO:
-
Carbon monoxide
- CNG:
-
Compressed Natural Gas
- EFI:
-
End of the fuel injection
- HC:
-
Hydrocarbon
- HCC:
-
Hemispherical combustion chamber
- IVC:
-
Intake valve close
- IC:
-
Internal combustion
- LPH:
-
Liters per hour
- LPG:
-
Liquefied petroleum gas
- LPM:
-
Liters per minute
- MAB:
-
Microalgae biodiesel
- NOx:
-
Oxides of nitrogen
- RNG:
-
Re-Normalized Group
- SCC:
-
Shallow depth combustion chamber
- SFI:
-
Start of the fuel injection
- SI:
-
Spark ignition
- TCC:
-
Toroidal combustion chamber
- TKE:
-
Turbulent kinetic energy
- TDC:
-
Top dead center
- ⍴ :
-
Density
- c d :
-
Nozzle's discharge coefficient
- D d,stable :
-
Stable droplet diameter
- D d :
-
Instantaneous droplet diameter
- e :
-
Specific internal energy
- k :
-
Turbulent kinetic energy
- K c :
-
Form loss coefficient
- K ε :
-
Empirical coefficient
- L :
-
Hole length
- p :
-
Pressure
- q i :
-
Diffusive heat flux
- Q H :
-
Heat source or sink per unit volume
- S i :
-
Mass-distributed external force per unit mass
- t b :
-
Characteristics time scale
- U :
-
Average injection velocity
- u :
-
Fluid velocity
- ε :
-
Turbulence dissipation rate
- μ t :
-
Turbulent viscosity
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- τ ij :
-
Viscous shear stress tensor
- h :
-
Thermal enthalpy
References
Akkoli, K.M.; Banapurmath, N.R.; Shivashimpi, M.M.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Badruddin, I.A.; Alazwari, M.A.; Venu, H.: Effect of injection parameters and producer gas derived from redgram stalk on the performance and emission characteristics of a diesel engine. Alex. Eng. J. 60(3), 3133–3142 (2021)
Bai, C.,; Gosman, A. D: Development of methodology for spray impingement simulation. SAE Trans., 550–568 (1995)
Banapurmath, N.R.; Chandrashekar, T.K.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Anqi, A.E.; Mujtaba, M.A.; Goodarzi, M.; Ali, M.A.: Effect of parameters behavior of simarouba methyl ester operated diesel engine. Energies 14(16), 4973 (2021)
Bari, S.; Hossain, S.N.; Saad, I.: A review on improving airflow characteristics inside the combustion chamber of CI engines to improve the performance with higher viscous biofuels. Fuel 264, 116769 (2020)
Chiodi, M.; Berner, H. J.; Bargende, M.: Investigation on mixture formation and combustion process in a CNG-engine by using a fast response 3D-CFD-simulation (No. 2004–01–3004). SAE Technical Paper, (2004)
Dasrath, D.K.; Biwalkar, R.; Singh, S.; Northrop, W.F.: Bowl piston geometry as an alternative to enlarged crevice pistons for rapid compression machines. Proc. Combust. Inst. 38(4), 5723–5731 (2021)
Deivajothi, P.; Manieniyan, V.; Sivaprakasam, S.: An impact of ethyl esters of groundnut acid oil (vegetable oil refinery waste) used as emerging fuel in DI diesel engine. Alex. Eng. J. 57(4), 2215–2223 (2018)
Ganji, P.R.; Singh, R.N.; Raju, V.R.K.; Rao, S.S.: Design of piston bowl geometry for better combustion in direct-injection compression ignition engine. Sādhanā 43(6), 1–9 (2018)
Ge, S.; Brindhadevi, K.; Xia, C.; Elesawy, B.H.; Elfasakhany, A.; Unpaprom, Y.; Van Doan, H.: Egg shell catalyst and chicken waste biodiesel blends for improved performance, combustion and emission characteristics. Fuel 306, 121633 (2021)
Han, Z.; Reitz, R.D.: Turbulence modeling of internal combustion engines using RNG κ-ε models. Combust. Sci. Technol. 106(4–6), 267–295 (1995)
Hara, S.; Tsukahara, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.: Experimental investigation of streamwise velocity fluctuation based on the Reynolds-number dependency in turbulent viscoelastic-fluid flow. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 68, 281–289 (2017)
Harari, P.A.; Banapurmath, N.R.; Yaliwal, V.S.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Khan, T.Y.; Mujtaba, M.A.; EL-Seesy, A.I.: Experimental investigation on compression ignition engine powered with pentanol and thevetia peruviana methyl ester under reactivity controlled compression ignition mode of operation. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 25, 100921 (2021)
Heywood, J. G. Viscous incompressible fluids: mathematical theory (2006)
Huh, K. Y. (1991). A phenomenological model of diesel spray atomization. In Proc. of The International Conf. on Multiphase Flows' 91-Tsukuba
Jemni, M.A.; Kantchev, G.; Abid, M.S.: Influence of intake manifold design on in-cylinder flow and engine performances in a bus diesel engine converted to LPG gas fuelled, using CFD analyses and experimental investigations. Energy 36(5), 2701–2715 (2011)
Karthickeyan, V.: Effect of combustion chamber bowl geometry modification on engine performance, combustion and emission characteristics of biodiesel fuelled diesel engine with its energy and exergy analysis. Energy 176, 830–852 (2019)
Khan, H.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Kumar, R.H.; Safaei, M.R.; Farooq, M.; Khidmatgar, A.; Taqui, S.N.: Effect of nano-graphene oxide and n-butanol fuel additives blended with diesel–Nigella sativa biodiesel fuel emulsion on diesel engine characteristics. Symmetry 12(6), 961 (2020)
Khan, S.; Panua, R.; Bose, P.K.: Combined effects of piston bowl geometry and spray pattern on mixing, combustion and emissions of a diesel engine: a numerical approach. Fuel 225, 203–217 (2018)
Kumar, M.V.; Babu, A.V.; Kumar, P.R.: Experimental investigation on the effects of diesel and mahua biodiesel blended fuel in direct injection diesel engine modified by nozzle orifice diameters. Renew. Energy 119, 388–399 (2018)
Lakshmanan, T.; Nagarajan, G.: Experimental investigation on dual fuel operation of acetylene in a DI diesel engine. Fuel Process. Technol. 91(5), 496–503 (2010)
Miles, P.; Megerle, M.; Hammer, J.; Nagel, Z.; Reitz, R. D.; Sick, V.: Late-cycle turbulence generation in swirl-supported, direct-injection diesel engines. SAE Trans. 1510–1529 (2002)
Montoya, J.P.G.; Arrieta, A.A.A.: Effect of the turbulence intensity on knocking tendency in a SI engine with high compression ratio using biogas and blends with natural gas, propane and hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 44(33), 18532–18544 (2019)
Muthuswamy, S.; Veerasigamani, M.:Impact of secondary fuel injector in various distance on direct injection diesel engine using acetylene-bio diesel in reactivity controlled compression ignition mode. Energy Sour. Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Effects, 1–15 (2020)
Muthuswamy, S.; Veerasigamani, M; Comparative experimental analysis on dual fuel with biodiesel-acetylene in reactivity controlled compression ignition engine. Int. J. Ambient Energy, 1–12 (2021)
Oni, B.A.; Sanni, S.E.; Daramola, M.; Olawepo, A.V.: Effects of oxy-acetylation on performance, combustion and emission characteristics of Botryococcus braunii microalgae biodiesel-fuelled CI engines. Fuel 296, 120675 (2021)
Prabhakaran, P.; Ramesh, P.; Saravanan, C.G.; Loganathan, M.; Gunasekaran, E.J.: Experimental and numerical investigation of swirl enhancing grooves on the flow and combustion characteristics of a DI diesel engine. Energy 115, 1234–1245 (2016)
Prabhakaran, P.; Saravanan, C.G.; Vallinayagam, R.; Vikneswaran, M.; Muthukumaran, N.; Ashok, K.: Investigation of swirl induced piston on the engine characteristics of a biodiesel fueled diesel engine. Fuel 279, 118503 (2020)
Prasad, B.V.V.S.U.; Sharma, C.S.; Anand, T.N.C.; Ravikrishna, R.V.: High swirl-inducing piston bowls in small diesel engines for emission reduction. Appl. Energy 88(7), 2355–2367 (2011)
Rahmanian, B.; Safaei, M.R.; Kazi, S.N.; Ahmadi, G.; Oztop, H.F.; Vafai, K.: Investigation of pollutant reduction by simulation of turbulent non-premixed pulverized coal combustion. Appl. Therm. Eng. 73(1), 1222–1235 (2014)
Rajak, U.; Nashine, P.; Dasore, A.; Verma, T. N.: Utilization of renewable and sustainable microalgae biodiesel for reducing the engine emissions in a diesel engine. Fuel, 122498 (2021)
Ranganatha Swamy, L.; Banapurmath, N. R.; Chandrashekar, T. K.; Soudagar, M. E. M.; Gul, M.; Nik-Ghazali, N. N.; Goodarzi, M.: Effect of injection timing and duration on the performance of diesel engine fueled with port injection of oxygenated fuels.Chem. Eng. Commun., 1–13 (2021)
Reitz, R. D., & Diwakar, R. (1986). Effect of drop breakup on fuel sprays. SAE transactions, 218–227.
Gavhane, R S.; Kate, A M.; Pawar, A.; Safaei, M. R., Soudagar M; Mujtaba Abbas M. E; Shahapurkar K M.: Effect of zinc oxide nano-additives and soybean biodiesel at varying loads and compression ratios on VCR diesel engine characteristics. Symmetry, 12(6), 1042 (2020)
Sadeghinezhad, E.; Kazi, S.N.; Sadeghinejad, F.; Badarudin, A.; Mehrali, M.; Sadri, R.; Safaei, M.R.: A comprehensive literature review of bio-fuel performance in internal combustion engine and relevant costs involvement. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 30, 29–44 (2014)
Samir Naje, A,; Yuvarajan, D.; abed Al-Ridah, Z.; Sandeep, H.; Nagarajan, A: Ignition study of neat biodiesel in dual fueled research engine. Fuel, 281, 118673 (2020)
Sateesh, K.A.; Yaliwal, V.S.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Banapurmath, N.R.; Fayaz, H.; Safaei, M.R.; El-Seesy, A.I.: Utilization of biodiesel/Al2O3 nanoparticles for combustion behavior enhancement of a diesel engine operated on dual fuel mode. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 147(10), 5897–5911 (2022)
Sener, R.; Yangaz, M.U.; Gul, M.Z.: Effects of injection strategy and combustion chamber modification on a single-cylinder diesel engine. Fuel 266, 117122 (2020)
Sharma, S.; Sharma, D.; Soni, S. L.; & Singh, D.: Experimental investigation on spark-ignition (SI) engine fuelled with acetylene in dual-fuel mode. Int. J. Ambient Energy, 1–7 (2020)
Shen, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Lin, Bo.; Shen, Y.; Yang, J.: Numerical investigation of natural gas-diesel dual-fuel engine with different piston geometries and radial clearances. Energy 220, 119706 (2021)
Shi, Y.; Ge, H.W.; Reitz, R.D.: Computational optimization of internal combustion engines. Springer Science & Business Media (2011)
Sonachalam, M.; Manieniyan, V.: Optimization of critical angle, distance and flow rate of secondary fuel injection in DI diesel engine using computational fluid dynamics. SN Appl. Sci. 3(1), 1–13 (2021)
Sonachalam, M.; PaulPandian, P.; Manieniyan, V.: Emission reduction in diesel engine with acetylene gas and biodiesel using inlet manifold injection. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 22(10), 2177–2191 (2020)
Soudagar, M. E. M.; Afzal, A.; Safaei, M. R.; Manokar, A. M.; EL-Seesy, A. I.; Mujtaba, M. A.; Goodarzi, M: Investigation on the effect of cottonseed oil blended with different percentages of octanol and suspended MWCNT nanoparticles on diesel engine characteristics. J. Therm. Anal. Calorimetry, 1–18 (2020)
Soudagar, M.E.M.; Khan, H.M.; Khan, T.M.; Razzaq, L.; Asif, T.; Mujtaba, M.A.; Safaei, M.R.: Experimental analysis of engine performance and exhaust pollutant on a single-cylinder diesel engine operated using moringa oleifera biodiesel. Appl. Sci. 11(15), 7071 (2021)
Soudagar, M.E.M.; Mujtaba, M.A.; Safaei, M.R.; Afzal, A.; Ahmed, W.; Banapurmath, N.R.; Taqui, S.N.: Effect of Sr@ ZnO nanoparticles and Ricinus communis biodiesel-diesel fuel blends on modified CRDI diesel engine characteristics. Energy 215, 119094 (2021)
Sukumar, V.; Manieniyan, V.; Sivaprakasam, S.: Experimental studies on DI diesel engine fueled in sweet lime pyrolysis oil with biodiesel. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 14(5), 1145–1150 (2019)
Sukumar, V.; Manieniyan, V.; Senthilkumar, R.; Sivaprakasam, S.: Production of bio oil from sweet lime empty fruit bunch by pyrolysis. Renew. Energy 146, 309–315 (2020)
Uyumaz, A.: Experimental evaluation of linseed oil biodiesel/diesel fuel blends on combustion, performance and emission characteristics in a DI diesel engine. Fuel 267, 117150 (2020)
Wategave, S.P.; Banapurmath, N.R.; Sawant, M.S.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Mujtaba, M.A.; Afzal, A.; Sajjan, A.M.: Clean combustion and emissions strategy using reactivity controlled compression ignition (RCCI) mode engine powered with CNG-Karanja biodiesel. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 124, 116–131 (2021)
Wise, D. M.; Olsen, D. B.; Kim, M: Development of a lean burn methane number measurement technique for alternative gaseous fuel evaluation. In Internal Combustion Engine Division Fall Technical Conference (Vol. 56109, p. V002T02A014). American Society of Mechanical Engineers (2013)
Wulff, J. W.; Hulett, M.; Lee, S.: (2000).U.S. Patent No. 6,076,487. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office
Zhang, Y.; Jia, M.; Liu, H.; Xie, M.; Wang, T.; Zhou, L.: (2014). Development of a new spray/wall interaction model for diesel spray under PCCI-engine relevant conditions. Atomization Sprays, 24(1)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G. Babusankar carried out the design of the work and Data collection; V. Manieniyan has done the data analysis, interpretation and drafting of the article; S. Sivaprakasam was involved in the critical revision of the article and Final approval of the version to be published.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Babusankar, G., Manieniyan, V. & Sivaprakasam, S. Numerical Investigation of a Dual Fuel Engine Fueled by Diesel-Acetylene and Biodiesel-Acetylene with Modified Piston Bowl Geometry. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 3783–3795 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07254-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07254-x