Abstract
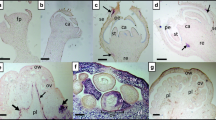
Pantoea agglomerans is an important bacterial symbiont of insects. Despite its frequent discovery in various insects, little is known of its strain diversity and quantitative dynamics. In this study, we investigated these aspects of the bacterium in the rice water weevil, Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus Kuschel (Coleoptera: Curculionidae), a serious pest of rice in North America and East Asia. Based on the cloning and sequencing of a bacterial 16S rRNA gene, we identified three novel P. agglomerans strains from different weevil populations, with each population harboring only one strain. In female adults, gut was the dominant tissue harboring P. agglomerans. This bacterium was also present in the ovary, but its density was very low there. The bacterium was maintained at a low density across all immature stages (from egg to pupa); however, the density increased substantially as adults emerged. Its density was low in the overwintering stage, but increased stepwise after the overwintered adults were allowed to feed on host plants, i.e., when they developed from early to actively reproducing stages. The infection density returned to a low level in the adults at a late reproductive stage. In conclusion, each of the L. oryzophilus populations we investigated was probably infected by a single P. agglomerans strain, and the gut of adults is the major tissue/developmental stage to harbor this bacterium, with actively reproducing adults attaining a high level of infection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumann L, Baumann P (1994) Growth-kinetics of the endosymbiont Buchnera aphidicola in the aphid Schizaphis gramizum. Appl Environ Microb 60:3440–3443
Bisi DC, Lampe DJ (2011) Secretion of anti-Plasmodium effector proteins from a natural Pantoea agglomerans isolate by using pelB and hlyA secretion signals. Appl Environ Microb 77:4669–4675
Blackburn MB, Gundersen-Rindal DE, Weber DC, Martin PAW Jr, Farrar RR (2008) Enteric bacteria of field-collected Colorado potato beetle larvae inhibit growth of the entomopathogens Photorhabdus temperata and Beauveria bassiana. Biol Control 46:434–441
Bridges JR (1981) Nitrogen-fixing bacteria associated with bark beetles. Microb Ecol 7:131–137
Chavshin AR, Oshaghi MA, Vatandoost H, Yakhchali B, Raeisi A, Zarenejad F (2013) Escherichia coli expressing a green fluorescent protein (GFP) in Anopheles stephensi: a preliminary model for paratransgenesis. Symbiosis 60:17–24
Chen H, Chen ZM, Zhou YS (2005) Rice water weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in mainland China: Invasion, spread and control. Crop Prot 24:695–702
Crippen TL, Zheng L, Sheffield CL, Tomberlin JK, Beier RC, Yu Z (2012) Transient gut retention and persistence of Salmonella through metamorphosis in the lesser mealworm, Alphitobius diaperinus (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). J Appl Microb 112:920–926
Delétoile A, Decré D, Courant S, Passet V, Audo J, Grimont P, Arlet G, Brisse S (2009) Phylogeny and identification of Pantoea species and typing of Pantoea agglomerans strains by multilocus gene sequencing. J Clin Microbiol 47:300–310
Dillon RJ, Charnley AK (1995) Chemical barriers to gut infection in the desert locust-in vivo production of antimicrobial phenols associated with the bacterium Pantoea agglomerans. J Invertebr Pathol 66:72–75
Dillon RJ, Charnley AK (1996) Colonization of the guts of germ-free desert locusts, Schistocerca gregaria, by the bacterium Pantoea agglomerans. J Invertebr Pathol 67:11–14
Dillon RJ, Vennard CT, Charnley AK (2002) A note: gut bacteria produce components of a locust cohesion pheromone. J Appl Microbiol 92:759–763
Dossi FCA, Da Silva EP, Consoli FL (2014) Population dynamics and growth rates of endosymbionts during Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera, Liviidae) ontogeny. Microb Ecol 68:881–889
Duan J, Yi T, Lu Z, Shen D, Feng Y (2007) Rice endophyte Pantoea agglomerans YS19 forms multicellular symplasmata via cell aggregation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 270:220–226
Fang HW, Zhang BW, Fang XQ, Chen CQ, Li QL, Yao CY, Yu HB (2003) Bionomics of Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus in Tongcheng, Anhui province. Entomol Knowl 40:546–549 (in Chinese with English summary)
Fukatsu T, Nikoh N (1998) Two intracellular symbiotic bacteria from the mulberry psyllid Anomoneura mori (Insecta, Homoptera). Appl Environ Microb 64:3599–3606
Gavini F, Mergaert J, Beji A, MielcarekC Izard D, Kersters K, De Ley J (1989) Transfer of Enterobacter agglomerans (Beijerinck 1888) Ewing and Fife 1972 to Pantoea gen. nov. as Pantoea agglomerans comb. nov. and description of Pantoea dispersa sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:337–345
Gravgaard JC, Turnbull MW, McNealy TL (2010) A novel technique for feeding and confirming uptake of bacteria in larvae of the southern house mosquito, Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae). Fla Entomol 93:577–583
Greenberg B (1959) Persistence of bacteria in the developmental stages of the housefly. III. Quantitative distribution in prepupae and pupae. Am J Trop Med Hyg 8:613–617
Gusmão DS, Santos AV, Marini DC Jr, Bacci M, Berbert-Molina MA, Lemos FJA (2010) Culture-dependent and culture-independent characterization of microorganisms associated with Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) (L.) and dynamics of bacterial colonization in the midgut. Acta Trop 115:275–281
Heerman M, Weng J, Hurwitz I, Durvasula R, Ramalho-Ortigao M (2015) Bacterial infection and immune responses in Lutzomyia longipalpis sand fly larvae midgut. PLoS Neglect Trop D 9:e0003923
Hosokawa T, Hironaka M, Inadomi K, Mukai H, Nikoh N, Fukatsu T (2013) Diverse strategies for vertical symbiont transmission among subsocial stinkbugs. PLoS One 8:e65081
Hunt J, Charnley AK (1981) Abundance and distribution of the gut flora of the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. J Invertebr Pathol 38:378–385
Jiang MX, Cheng JA (2003) Effects of starvation and absence of free water on the oviposition of overwintered adult rice water weevil, Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus Kuschel (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Int J Pest Manage 49:89–94
Jiang CG, Baehrecke EH, Thummel CS (1997) Steroid regulated programmed cell death during Drosophila metamorphosis. Development 124:4673–4683
Jiang MX, Zhang WJ, Cheng JA (2004) Termination of reproductive diapause in the rice water weevil with particular reference to the effects of temperature. Appl Entomol Zool 39:683–689
Jiang M, Way MO, Yoder R, Zhang W, Cheng J (2006) Elytral color dimorphism in rice water weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): occurrence in spring populations and relationship to female reproductive development. Ann Entomol Soc Am 99:1127–1132
Kaltenpoth M, Goettler W, Koehler S, Strohm E (2010) Life cycle and population dynamics of a protective insect symbiont reveal severe bottlenecks during vertical transmission. Evol Ecol 24:463–477
Komaki K, Ishikawa H (2000) Genomic copy number of intracellular bacterial symbionts of aphids varies in response to developmental stage and morph of their host. Insect Biochem Mol 30:253–258
Lauzon CR, Sjogren RE, Prokopy RJ (2000) Enzymatic capabilities of bacteria associated with apple maggot flies: a postulated role in attraction. J Chem Ecol 26:953–967
Lauzon CR, Potter SE, Prokopy RJ (2003) Degradation and detoxification of the dihydrochalcone phloridzin by Enterobacter agglomerans, a bacterium associated with the apple pest, Rhagoletis pomonella (Walsh) (Diptera: Tephritidae). Environ Entomol 32:953–962
Lauzon CR, McCombs SD, Potter SE, Peabody NC (2009) Establishment and vertical passage of Enterobacter (Pantoea) agglomerans and Klebsiella pneumoniae through all life stages of the Mediterranean fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 102:85–95
Loncaric I, Heigl H, Licek E, Moosbeckhofer R, Busse H, Rosengarten R (2009) Typing of Pantoea agglomerans isolated from colonies of honey bees (Apis mellifera) and culturability of selected strains from honey. Apidologie 40:40–54
Lu F, Kang X, Jiang C, Lou B, Jiang M, Way MO (2013a) Isolation and characterization of bacteria from midgut of the rice water weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Environ Entomol 42:874–881
Lu F, Zhang WJ, Jiang MX, Way MO (2013b) Southern cutgrass, Leersia hexandra Swartz, allows rice water weevils to avoid summer diapause. Southwest Entomol 38:153–162
Lu F, Kang X, Lorenz G, Espino L, Jiang M, Way MO (2014) Culture-Independent analysis of bacterial communities in the gut of rice water weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 107:592–600
Moll RM, Romoser WS, Modrzakowski MC, Moncayo AC, Lerdthusnee K (2001) Meconial peritrophic membranes and the fate of midgut bacteria during mosquito (Diptera: Culicidae) metamorphosis. J Med Entomol 38:29–32
Moro CV, Tran FH, Raharimalala FN, Ravelonandro P, Mavingui P (2013) Diversity of culturable bacteria including Pantoea in wild mosquito Aedes albopictus. BMC Microbiol 13:70
Nadarasah G, Stavrinides J (2014) Quantitative evaluation of the host-colonizing capabilities of the enteric bacterium Pantoea using plant and insect hosts. Microbiology 160:602–615
Nishikori K, Morioka K, Kubo T, Morioka M (2009) Age- and morph-dependent activation of the lysosomal system and Buchnera degradation in aphid endosymbiosis. J Insect Physiol 55:351–357
Ohkuma M, Noda S, Usami R, Horikoshi K, Kudo T (1996) Diversity of nitrogen fixation genes in the symbiotic intestinal microflora of the termite Reticulitermes speratus. Appl Environ Microb 62:2747–2752
Potrikus CJ, Breznak JA (1977) Nitrogen-fixing Enterobacter agglomerans isolated from guts of wood-eating termites. Appl Environ Microb 33:392–399
Radvan R (1960) Persistence of bacteria during development in flies. III. Localization of the bacteria and transmission after emergence of the fly. Folia Microbiol 5:149–156
Rochon K, Lysyk TJ, Selinger LB (2005) Retention of Escherichia coli by house fly and stable fly (Diptera: Muscidae) during pupal metamorphosis and eclosion. J Med Entomol 42:397–403
Saito T, Hirai K, Way MO (2005) The rice water weevil, Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus Kuschel (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Appl Entomol Zool 40:31–39
Schloss PD, Handelsman J (2005) Introducing DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl Environ Microb 71:1501–1506
Shi W, Syrenne R, Sun J, Yuan JS (2010) Molecular approaches to study the insect gut symbiotic microbiota at the ‘omics’ age. Insect Sci 17:199–219
Stoll S, Gadau J, Gross R, Feldhaar H (2007) Bacterial microbiota associated with ants of the genus Tetraponera. Biol J Linn Soc 90:399–412
Straif SC, Mbogo C, Toure AM, Walker ED, Kaufman M, Toure YT, Beier JC (1998) Midgut bacteria in Anopheles gambiae and An. funestus (Diptera: Culicidae) from Kenya and Mali. J Med Entomol 35:222–226
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Vorwerk S, Martinez-Torres D, Forneck A (2007) Pantoea agglomerans-associated bacteria in grape phylloxera (Daktulosphaira vitifoliae, Fitch). Agric For Entomol 9:57–64
Waku Y, Endo Y (1987) Ultrastructure and life cycle of the symbionts in a homopteran insect, Anomoneura mori Schwartz (Psyllidae). Appl Entomol Zool 22:630–637
Wolschin F, Holldobler B, Gross R, Zientz E (2004) Replication of the endosymbiotic bacterium Blochmannia floridanus is correlated with the developmental and reproductive stages of its ant host. Appl Environ Microb 70:4096–4102
Wright ES, Yilmaz LS, Noguera DR (2012) Decipher, a search-based approach to chimera identification for 16S rRNA sequences. Appl Environ Microb 78:717–725
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 31372001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Huang, Y., Huang, X. et al. Infection state of Pantoea agglomerans in the rice water weevil Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Appl Entomol Zool 51, 561–569 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-016-0433-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-016-0433-4