Abstract
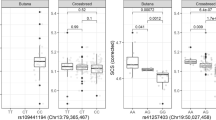
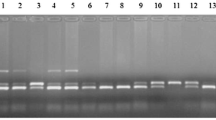
Mastitis is a major source of economic loss in dairy herds. The objective of this research was to evaluate the association between genotypes within SLC11A1 and CXCR1 candidate genes and clinical mastitis in Holstein dairy cattle using the selective genotyping method. The data set contained clinical mastitis records of 3,823 Holstein cows from two Holstein dairy herds located in two different regions in Iran. Data included the number of cases of clinical mastitis per lactation. Selective genotyping was based on extreme values for clinical mastitis residuals (CMR) from mixed model analyses. Two extreme groups consisting of 135 cows were formed (as cases and controls), and genotyped for the two candidate genes, namely, SLC11A1 and CXCR1, using polymerase chain reaction-single strand conformation polymorphism (PCR-SSCP) and polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP), respectively. Associations between single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) genotypes with CMR and breeding values for milk and protein yield were carried out by applying logistic regression analyses, i.e. estimating the probability of the heterogeneous genotype in the dependency of values for CMR and breeding values (BVs). The sequencing results revealed a novel mutation in 1139 bp of exon 11 of the SLC11A1 gene and this SNP had a significant association with CMR (P < 0.05). PCR-RFLP analysis leads to three banding patterns for CXCR1c.735C>G and these genotypes had significant relationships with CMR. Overall, the results showed that SLC11A1 and CXCR1 are valuable candidate genes for the improvement of mastitis resistance as well as production traits in dairy cattle populations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagheri M, Miraie-Ashtiani R, Moradi-Sharhrbabak M, Nejati-Javaremi A, Pakdel A, von Borstel UU, Pimentel ECG, König S (2013) Selective genotyping and logistic regression analyses to identify favorable SNP-genotypes for clinical mastitis and production traits in Holstein dairy cattle. Livest Sci 151:140–151
Beecher C, Daly M, Childs S, Berry DP, Magee DA, McCarthy TV, Giblin L (2010) Polymorphisms in bovine immune genes and their associations with somatic cell count and milk production in dairy cattle. BMC Genet 11:99
Capparelli R, Alfano F, Amoroso MG, Borriello G, Fenizia D, Bianco A, Roperto S, Roperto F, Iannelli D (2007) Protective effect of the Nramp1 BB genotype against Brucella abortus in the water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). Infect Immun 75:988–996
Chen R, Yang Z, Ji D, Mao Y, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Hamza, Wang X, Li Y (2011) SNPs of CXCR1 gene and its associations with somatic cell score in Chinese Holstein Cattle. Anim Biotechnol 22:133–142
Fleischer RC, Perry EA, Muralidharan K, Stevens EE, Wemmer CM (2001) Phylogeography of the Asian elephant (Elephas maximus) based on mitochondrial DNA. Evolution 55:1882–1892
Galvão KN, Pighetti GM, Cheong SH, Nydam DV, Gilbert RO (2011) Association between interleukin-8 receptor-α (CXCR1) polymorphism and disease incidence, production, reproduction, and survival in Holstein cows. J Dairy Sci 94:2083–2091
Gernand E, Rehbein P, von Borstel UU, König S (2012) Incidences of and genetic parameters for mastitis, claw disorders, and common health traits recorded in dairy cattle contract herds. J Dairy Sci 95:2144–2156
Goertz I, Baes C, Weimann C, Reinsch N, Erhardt G (2009) Association between single nucleotide polymorphisms in the CXCR1 gene and somatic cell score in Holstein dairy cattle. J Dairy Sci 92:4018–4022
Grosse WM, Kappes SM, Laegreid WW, Keele JW, Chitko-McKown CG, Heaton MP (1999) Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) discovery and linkage mapping of bovine cytokine genes. Mamm Genome 10:1062–1069
Henshall JM, Goddard ME (1999) Multiple-trait mapping of quantitative trait loci after selective genotyping using logistic regression. Genetics 151(2):885–894
Heringstad B, Klemetsdal G, Steine T (2007) Selection responses for disease resistance in two selection experiments with Norwegian red cows. J Dairy Sci 90:2419–2426
Hinrichs D, Stamer E, Junge W, Kalm E (2005) Genetic analyses of mastitis data using animal threshold models and genetic correlation with production traits. J Dairy Sci 88:2260–2268
König S, Sharifi AR, Wentrot H, Landmann D, Eise M, Simianer H (2005) Genetic parameters of claw and foot disorders estimated with logistic models. J Dairy Sci 88:3316–3325
Leyva-Baca I, Schenkel F, Martin J, Karrow NA (2008) Polymorphisms in the 5′ upstream region of the CXCR1 chemokine receptor gene, and their association with somatic cell score in Holstein cattle in Canada. J Dairy Sci 91:407–417
Martínez R, Dunner S, Barrera G, Cañon J (2008) Novel variants within the coding regions of the SLC11A1 gene identified in Bos taurus and Bos indicus breeds. J Anim Breed Genet 125:57–62
Miglior F, Muir BL, Van Doormaal BJ (2005) Selection indices in Holstein cattle of various countries. J Dairy Sci 88:1255–1263
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1215
Moe M, Lien S, Aasmundstad T, Meuwissen THE, Hansen MHS, Bendixen C, Grindflek E (2009) Association between SNPs within candidate genes and compounds related to boar taint and reproduction. BMC Genet 10:32
Murphy PM, Tiffany HL (1991) Cloning of complementary DNA encoding a functional human interleukin-8 receptor. Science 253:1280–1283
Paape MJ, Shafer-Weaver K, Capuco AV, Van Oostveldt K, Burvenich C (2000) Immune surveillance of mammary tissue by phagocytic cells. Adv Exp Med Biol 480:259–277
Rambeaud M, Pighetti GM (2007) Differential calcium signaling in dairy cows with specific CXCR1 genotypes potentially related to interleukin-8 receptor functionality. Immunogenetics 59:53–58
SAS (2004) SAS/STAT 9.1 user’s guide. SAS Institute Inc., Cary
Schabenberger O (2007) Growing up fast: SAS 9.2 enhancements to the GLIMMIX procedure. SAS Global Forum, Citeseer
Sharma BS, Jansen GB, Karrow NA, Kelton D, Jiang Z (2006) Detection and characterization of amplified fragment length polymorphism markers for clinical mastitis in Canadian Holsteins. J Dairy Sci 89:3653–3663
Shivanand DM, Ahlawat SPS, Bhusan B, Tiwari AK, Sonawane A, Kumar P, Inamdar B, Dutt T (2011) PCR-SSCP and sequencing of CXCR2 receptor gene in Vrindavani cattle. J Adv Vet Res 1:52–56
Verbeke J, Van Poucke M, Peelman L, Piepers S, De Vliegher S (2014) Associations between CXCR1 polymorphisms and pathogen-specific incidence rate of clinical mastitis, test-day somatic cell count, and test-day milk yield. J Dairy Sci 97(12):7927–7939
Vidal S, Tremblay ML, Govoni G, Gauthier S, Sebastiani G, Malo D, Skamene E, Olivier M, Jothy S, Gros P (1995) The Ity/Lsh/Bcg locus: natural resistance to infection with intracellular parasites is abrogated by disruption of the Nramp1 gene. J Exp Med 182:655–666
Youngerman SM, Saxton AM, Pighetti GM (2004a) Novel single nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotypes within the bovine CXCR2 gene . Immunogenetics 56:355–359
Youngerman SM, Saxton AM, Oliver SP, Pighetti GM (2004b) Association of CXCR2 polymorphisms with subclinical and clinical mastitis in dairy cattle. J Dairy Sci 87:2442–2448
Zhang CL, Wang YH, Chen H, Gu CW, Fang XT (2009) SLC11A1 gene polymorphisms are not associated to somatic cell score and milk yield in Chinese Holstein. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 127:389–392
Acknowledgements
Data and blood samples were kindly obtained from two dairy cattle farms (Foka and Taliseh). The authors are thankful for the help of these farms’ owners and staff.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Maciej Szydlowski
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bagheri, M., Moradi-Sharhrbabak, M., Miraie-Ashtiani, R. et al. Case–control approach application for finding a relationship between candidate genes and clinical mastitis in Holstein dairy cattle. J Appl Genetics 57, 107–112 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-015-0299-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-015-0299-0