Abstract
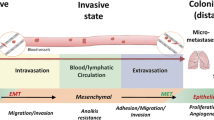
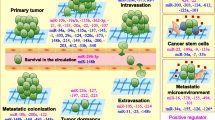
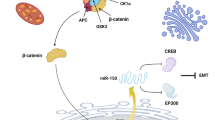
Metastasis is an important factor in predicting the prognosis of the patients with cancers and contributes to high cancer-related mortality. Recent studies indicated that microRNAs (miRNAs) played a functional role in the initiation and progression of human malignancies. MicroRNAs are small non-coding RNAs of about 22 nucleotides in length that can induce messenger RNA (mRNA) degradation or repress mRNA translation by binding to the 3′ untranslated region (3′-UTR) of their target genes. Overwhelming reports indicated that miRNAs could regulate cancer invasion and metastasis via epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related and/or non-EMT-related mechanisms. In this review, we concentrate on the underlying mechanisms of miRNAs in regulating cancer progression and metastasis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Le XF, Merchant O, Bast RC, Calin GA. The roles of microRNAs in the cancer invasion-metastasis cascade. Cancer microenvironment : official journal of the International Cancer Microenvironment Society. 2010;3(1):137–47. doi:10.1007/s12307-010-0037-4.
Gupta GP, Massague J. Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 2006;127(4):679–95. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.001.
Liu W, Vivian CJ, Brinker AE, Hampton KR, Lianidou E, Welch DR. Microenvironmental influences on metastasis suppressor expression and function during a metastatic cell’s journey. Cancer microenvironment : official journal of the International Cancer Microenvironment Society. 2014;7(3):117–31. doi:10.1007/s12307-014-0148-4.
Bonnomet A, Brysse A, Tachsidis A, Waltham M, Thompson EW, Polette M, et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions and circulating tumor cells. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2010;15(2):261–73. doi:10.1007/s10911-010-9174-0.
Eccles SA, Welch DR. Metastasis: recent discoveries and novel treatment strategies. Lancet. 2007;369(9574):1742–57. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60781-8.
He W, He S, Wang Z, Shen H, Fang W, Zhang Y, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer through activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. BMC Cancer. 2015;15(1):1124. doi:10.1186/s12885-015-1124-1.
Zang M, Zhang B, Zhang Y, Li J, Su L, Zhu Z, et al. CEACAM6 promotes gastric cancer invasion and metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e112908. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0112908.
Oneyama C, Okada M. MicroRNAs as the fine-tuners of Src oncogenic signaling. J Biochem. 2015. doi:10.1093/jb/mvv036.
Liu AN, Zhu ZH, Chang SJ, Hang XS. Twist expression associated with the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012;367(1–2):195–203. doi:10.1007/s11010-012-1333-8.
Kurahara H, Takao S, Maemura K, Mataki Y, Kuwahata T, Maeda K, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and mesenchymal-epithelial transition via regulation of ZEB-1 and ZEB-2 expression in pancreatic cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2012;105(7):655–61. doi:10.1002/jso.23020.
Deep G, Jain AK, Ramteke A, Ting H, Vijendra KC, Gangar SC, et al. SNAI1 is critical for the aggressiveness of prostate cancer cells with low E-cadherin. Mol Cancer. 2014;13:37. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-13-37.
Sun Y, Song GD, Sun N, Chen JQ, Yang SS. Slug overexpression induces stemness and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis. Oncol Lett. 2014;7(6):1936–40. doi:10.3892/ol.2014.2037.
Radisky ES, Radisky DC. Matrix metalloproteinase-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2010;15(2):201–12. doi:10.1007/s10911-010-9177-x.
Sheng S, Qiao M, Pardee AB. Metastasis and AKT activation. J Cell Physiol. 2009;218(3):451–4. doi:10.1002/jcp.21616.
Sun Y, Huang J, Yang Z. The roles of ADAMTS in angiogenesis and cancer. Tumour biology : the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine. 2015. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3461-8.
Tille JC, Nisato R, Pepper MS. Lymphangiogenesis and tumour metastasis. Novartis Found Symp. 2004;256:112–31 discussion 32-6, 259-69.
Gao P, Xing AY, Zhou GY, Zhang TG, Zhang JP, Gao C, et al. The molecular mechanism of microRNA-145 to suppress invasion-metastasis cascade in gastric cancer. Oncogene. 2013;32(4):491–501. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.61.
Zhang G, Zhou H, Xiao H, Liu Z, Tian H, Zhou T. MicroRNA-92a functions as an oncogene in colorectal cancer by targeting PTEN. Dig Dis Sci. 2014;59(1):98–107. doi:10.1007/s10620-013-2858-8.
Zhu Z, Zhang X, Wang G, Zheng H. Role of microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepat Mon. 2014;14(8):e18672. doi:10.5812/hepatmon.18672.
Paterson EL, Kazenwadel J, Bert AG, Khew-Goodall Y, Ruszkiewicz A, Goodall GJ. Down-regulation of the miRNA-200 family at the invasive front of colorectal cancers with degraded basement membrane indicates EMT is involved in cancer progression. Neoplasia. 2013;15(2):180–91.
Zhang Y, Takahashi S, Tasaka A, Yoshima T, Ochi H, Chayama K. Involvement of microRNA-224 in cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and anti-apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28(3):565–75. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2012.07271.x.
Liu LZ, Li C, Chen Q, Jing Y, Carpenter R, Jiang Y, et al. MiR-21 induced angiogenesis through AKT and ERK activation and HIF-1alpha expression. PLoS One. 2011;6(4):e19139. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019139.
Keklikoglou I, Hosaka K, Bender C, Bott A, Koerner C, Mitra D, et al. MicroRNA-206 functions as a pleiotropic modulator of cell proliferation, invasion and lymphangiogenesis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma by targeting ANXA2 and KRAS genes. Oncogene. 2014. doi:10.1038/onc.2014.408.
Huang J, Xiao D, Li G, Ma J, Chen P, Yuan W, et al. EphA2 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the wnt/beta-catenin pathway in gastric cancer cells. Oncogene. 2014;33(21):2737–47. doi:10.1038/onc.2013.238.
Iwai S, Yonekawa A, Harada C, Hamada M, Katagiri W, Nakazawa M, et al. Involvement of the wnt-beta-catenin pathway in invasion and migration of oral squamous carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 2010;37(5):1095–103.
Bhanot P, Brink M, Samos CH, Hsieh JC, Wang Y, Macke JP, et al. A new member of the Frizzled family from Drosophila functions as a wingless receptor. Nature. 1996;382(6588):225–30. doi:10.1038/382225a0.
Tamai K, Semenov M, Kato Y, Spokony R, Liu C, Katsuyama Y, et al. LDL-receptor-related proteins in wnt signal transduction. Nature. 2000;407(6803):530–5. doi:10.1038/35035117.
Clevers H, Nusse R. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease. Cell. 2012;149(6):1192–205. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.012.
Fu Y, Zheng S, An N, Athanasopoulos T, Popplewell L, Liang A, et al. Beta-catenin as a potential key target for tumor suppression. Int J Cancer J Int du Cancer. 2011;129(7):1541–51. doi:10.1002/ijc.26102.
Aberle H, Bauer A, Stappert J, Kispert A, Kemler R. Beta-catenin is a target for the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. EMBO J. 1997;16(13):3797–804. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.13.3797.
Cai J, Guan H, Fang L, Yang Y, Zhu X, Yuan J, et al. MicroRNA-374a activates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling to promote breast cancer metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(2):566–79. doi:10.1172/JCI65871.
Liu Y, Huang T, Zhao X, Cheng L. MicroRNAs modulate the wnt signaling pathway through targeting its inhibitors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;408(2):259–64. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.04.009.
Wang K, Wang X, Zou J, Zhang A, Wan Y, Pu P, et al. miR-92b controls glioma proliferation and invasion through regulating wnt/beta-catenin signaling via Nemo-like kinase. Neuro-Oncology. 2013;15(5):578–88. doi:10.1093/neuonc/not004.
Zhang X, Li M, Zuo K, Li D, Ye M, Ding L, et al. Upregulated miR-155 in papillary thyroid carcinoma promotes tumor growth by targeting APC and activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(8):E1305–13. doi:10.1210/jc.2012-3602.
Zhang Z, Liu S, Shi R, Zhao G. miR-27 promotes human gastric cancer cell metastasis by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer genetics. 2011;204(9):486–91. doi:10.1016/j.cancergen.2011.07.004.
Li Q, Shen K, Zhao Y, He X, Ma C, Wang L, et al. MicroRNA-222 promotes tumorigenesis via targeting DKK2 and activating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. FEBS Lett. 2013;587(12):1742–8. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2013.04.002.
Delic S, Lottmann N, Stelzl A, Liesenberg F, Wolter M, Gotze S, et al. MiR-328 promotes glioma cell invasion via SFRP1-dependent wnt-signaling activation. Neuro-Oncology. 2014;16(2):179–90. doi:10.1093/neuonc/not164.
Song MS, Salmena L, Pandolfi PP. The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(5):283–96. doi:10.1038/nrm3330.
Jiang H, Gao M, Shen Z, Luo B, Li R, Jiang X, et al. Blocking PI3K/Akt signaling attenuates metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through induction of mesenchymal-epithelial reverting transition. Oncol Rep. 2014;32(2):559–66. doi:10.3892/or.2014.3220.
Nicholson KM, Anderson NG. The protein kinase B/Akt signalling pathway in human malignancy. Cell Signal. 2002;14(5):381–95.
Zhao G, Cai C, Yang T, Qiu X, Liao B, Li W, et al. MicroRNA-221 induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance through PI3K/Akt pathway in human osteosarcoma. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53906. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0053906.
Ohta K, Hoshino H, Wang J, Ono S, Iida Y, Hata K, et al. MicroRNA-93 activates c-met/PI3K/Akt pathway activity in hepatocellular carcinoma by directly inhibiting PTEN and CDKN1A. Oncotarget. 2015;6(5):3211–24.
Zhang LY, Ho-Fun Lee V, Wong AM, Kwong DL, Zhu YH, Dong SS, et al. MicroRNA-144 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through repression of PTEN. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34(2):454–63. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgs346.
Jiang J, Zhang Y, Yu C, Li Z, Pan Y, Sun C. MicroRNA-492 expression promotes the progression of hepatic cancer by targeting PTEN. Cancer Cell Int. 2014;14(1):95. doi:10.1186/s12935-014-0095-7.
Samuels Y, Velculescu VE. Oncogenic mutations of PIK3CA in human cancers. Cell Cycle. 2004;3(10):1221–4.
Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, et al. High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science. 2004;304(5670):554. doi:10.1126/science.1096502.
Yu QQ, Wu H, Huang X, Shen H, Shu YQ, Zhang B, et al. MiR-1 targets PIK3CA and inhibits tumorigenic properties of A549 cells. Biomed Pharmacother Biomed Pharmacotherapie. 2014;68(2):155–61. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2014.01.005.
Wang Y, Tang Q, Li M, Jiang S, Wang X. MicroRNA-375 inhibits colorectal cancer growth by targeting PIK3CA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;444(2):199–204. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.01.028.
Cimino D, De Pitta C, Orso F, Zampini M, Casara S, Penna E, et al. miR148b is a major coordinator of breast cancer progression in a relapse-associated microRNA signature by targeting ITGA5, ROCK1, PIK3CA, NRAS, and CSF1. FASEB J: Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol. 2013;27(3):1223–35. doi:10.1096/fj.12-214692.
Fang Y, Xue JL, Shen Q, Chen J, Tian L. MicroRNA-7 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2012;55(6):1852–62. doi:10.1002/hep.25576.
Zhong M, Bian Z, miR- WZ. 30a suppresses cell migration and invasion through downregulation of PIK3CD in colorectal carcinoma. Cell Biochem: Int J Exp Cell Physiol, Biochem Pharmacol. 2013;31(2–3):209–18. doi:10.1159/000343362.
Cui F, Li X, Zhu X, Huang L, Huang Y, Mao C, et al. MiR-125b inhibits tumor growth and promotes apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase catalytic subunit delta. Cell Physiol Biochem: Int J Exp Cell Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;30(5):1310–8. doi:10.1159/000343320.
Shi Y, Chen C, Zhang X, Liu Q, Xu JL, Zhang HR, et al. Primate-specific miR-663 functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting PIK3CD and predicts the prognosis of human glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res: An Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2014;20(7):1803–13. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2284.
Que T, Song Y, Liu Z, Zheng S, Long H, Li Z, et al. Decreased miRNA-637 is an unfavorable prognosis marker and promotes glioma cell growth, migration and invasion via direct targeting Akt1. Oncogene. 2015. doi:10.1038/onc.2014.419.
Yu SH, Zhang CL, Dong FS, Zhang YM. miR-99a suppresses the metastasis of human non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting AKT1 signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(2):268–76. doi:10.1002/jcb.24965.
Pan SJ, Zhan SK, Pei BG, Sun QF, Bian LG, Sun BM. MicroRNA-149 inhibits proliferation and invasion of glioma cells via blockade of AKT1 signaling. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2012;25(4):871–81.
Cai N, Wang YD, Zheng PS. The microRNA-302-367 cluster suppresses the proliferation of cervical carcinoma cells through the novel target AKT1. RNA. 2013;19(1):85–95. doi:10.1261/rna.035295.112.
Zhang H, Cheng Y, Jia C, Yu S, Xiao Y, Chen J. MicroRNA-29 s could target AKT2 to inhibit gastric cancer cells invasion ability. Med Oncol. 2015;32(1):342. doi:10.1007/s12032-014-0342-8.
Liu LL, Lu SX, Li M, Li LZ, Fu J, Hu W, et al. FoxD3-regulated microRNA-137 suppresses tumour growth and metastasis in human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting AKT2. Oncotarget. 2014;5(13):5113–24.
Foley NH, Bray IM, Tivnan A, Bryan K, Murphy DM, Buckley PG, et al. MicroRNA-184 inhibits neuroblastoma cell survival through targeting the serine/threonine kinase AKT2. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:83. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-9-83.
Zhao HJ, Ren LL, Wang ZH, Sun TT, YN Y, Wang YC, et al. MiR-194 deregulation contributes to colorectal carcinogenesis via targeting AKT2 pathway. Theranostics. 2014;(12):1193–208. doi:10.7150/thno.8712.
Nassirpour R, Mehta PP, Yin MJ. miR-122 regulates tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting AKT3. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e79655. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0079655.
Ma Y, She XG, Ming YZ, Wan QQ, Ye QF. MicroRNA144 suppresses tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting AKT3. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(2):1378–83. doi:10.3892/mmr.2014.2844.
Boufraqech M, Zhang L, Jain M, Patel D, Ellis R, Xiong Y, et al. miR-145 suppresses thyroid cancer growth and metastasis and targets AKT3. Endocr-Relat Cancer. 2014;21(4):517–31. doi:10.1530/ERC-14-0077.
Ishizawar R, Parsons SJ. C-Src and cooperating partners in human cancer. Cancer Cell. 2004;6(3):209–14. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2004.09.001.
Irby RB, Yeatman TJ. Role of Src expression and activation in human cancer. Oncogene. 2000;19(49):5636–42. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203912.
Mandal M, Myers JN, Lippman SM, Johnson FM, Williams MD, Rayala S, et al. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in head and neck squamous carcinoma: association of Src activation with E-cadherin down-regulation, vimentin expression, and aggressive tumor features. Cancer. 2008;112(9):2088–100. doi:10.1002/cncr.23410.
Wang N, Liang H, Zhou Y, Wang C, Zhang S, Pan Y, et al. miR-203 suppresses the proliferation and migration and promotes the apoptosis of lung cancer cells by targeting SRC. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e105570. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0105570.
Majid S, Saini S, Dar AA, Hirata H, Shahryari V, Tanaka Y, et al. MicroRNA-205 inhibits Src-mediated oncogenic pathways in renal cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71(7):2611–21. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3666.
Sun V, Zhou WB, Nosrati M, Majid S, Thummala S, de Semir D, et al. Antitumor activity of miR-1280 in melanoma by regulation of Src. Mol Ther: J Am Soc Gene Ther. 2015;23(1):71–8. doi:10.1038/mt.2014.176.
Cance WG, Harris JE, Iacocca MV, Roche E, Yang X, Chang J, et al. Immunohistochemical analyses of focal adhesion kinase expression in benign and malignant human breast and colon tissues: correlation with preinvasive and invasive phenotypes. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2000;6(6):2417–23.
Beierle EA, Massoll NA, Hartwich J, Kurenova EV, Golubovskaya VM, Cance WG, et al. Focal adhesion kinase expression in human neuroblastoma: immunohistochemical and real-time PCR analyses. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2008;14(11):3299–305. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1511.
Owens LV, Xu L, Dent GA, Yang X, Sturge GC, Craven RJ, et al. Focal adhesion kinase as a marker of invasive potential in differentiated human thyroid cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 1996;3(1):100–5.
Taliaferro-Smith L, Oberlick E, Liu T, McGlothen T, Alcaide T, Tobin R, et al. FAK activation is required for IGF1R-mediated regulation of EMT, migration, and invasion in mesenchymal triple negative breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2015;6(7):4757–72.
Golubovskaya VM, Sumbler B, Ho B, Yemma M, Cance WG. MiR-138 and MiR-135 directly target focal adhesion kinase, inhibit cell invasion, and increase sensitivity to chemotherapy in cancer cells. Anti Cancer Agents Med Chem. 2014;14(1):18–28.
Wu DG, Wang YY, Fan LG, Luo H, Han B, Sun LH, et al. MicroRNA-7 regulates glioblastoma cell invasion via targeting focal adhesion kinase expression. Chin Med J. 2011;124(17):2616–21.
Kong X, Li G, Yuan Y, He Y, Wu X, Zhang W, et al. MicroRNA-7 inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast cancer cells via targeting FAK expression. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e41523. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041523.
Hao Z, Yang J, Wang C, Li Y, Zhang Y, Dong X, et al. MicroRNA-7 inhibits metastasis and invasion through targeting focal adhesion kinase in cervical cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(1):480–7.
Bing L, Hong C, Li-Xin S, Wei G. MicroRNA-543 suppresses endometrial cancer oncogenicity via targeting FAK and Twist1 expression. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014;290(3):533–41. doi:10.1007/s00404-014-3219-3.
Luedde T. MicroRNA-151 and its hosting gene FAK (focal adhesion kinase) regulate tumor cell migration and spreading of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2010;52(3):1164–6. doi:10.1002/hep.23854.
Bischoff A, Huck B, Keller B, Strotbek M, Schmid S, Boerries M, et al. miR149 functions as a tumor suppressor by controlling breast epithelial cell migration and invasion. Cancer Res. 2014;74(18):5256–65. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3319.
Ke TW, Hsu HL, Wu YH, Chen WT, Cheng YW, Cheng CW. MicroRNA-224 suppresses colorectal cancer cell migration by targeting cdc42. Dis Markers. 2014;2014:617150. doi:10.1155/2014/617150.
Li N, Tang A, Huang S, Li Z, Li X, Shen S, et al. MiR-126 suppresses colon cancer cell proliferation and invasion via inhibiting RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;380(1–2):107–19. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1664-0.
Pellegrino L, Krell J, Roca-Alonso L, Stebbing J, Castellano L. MicroRNA-23b regulates cellular architecture and impairs motogenic and invasive phenotypes during cancer progression. BioArchitecture. 2013;3(4):119–24.
Wang F, Chan LW, Law HK, Cho WC, Tang P, Yu J, et al. Exploring microRNA-mediated alteration of EGFR signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer using an mRNA:miRNA regression model supported by target prediction databases. Genomics. 2014;104(6 Pt B):504–11. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2014.09.004.
Scagliotti GV, Selvaggi G, Novello S, Hirsch FR. The biology of epidermal growth factor receptor in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2004;10(12 Pt 2):4227s–32s. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-040007.
Katakowski M, Zheng X, Jiang F, Rogers T, Szalad A, Chopp M. MiR-146b-5p suppresses EGFR expression and reduces in vitro migration and invasion of glioma. Cancer Investig. 2010;28(10):1024–30. doi:10.3109/07357907.2010.512596.
Rao SA, Arimappamagan A, Pandey P, Santosh V, Hegde AS, Chandramouli BA, et al. miR-219-5p inhibits receptor tyrosine kinase pathway by targeting EGFR in glioblastoma. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e63164. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063164.
Tao J, Wu D, Xu B, Qian W, Li P, Lu Q, et al. microRNA-133 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion in prostate cancer cells by targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. Oncol Rep. 2012;27(6):1967–75. doi:10.3892/or.2012.1711.
Xie J, Chen M, Zhou J, Mo MS, Zhu LH, Liu YP, et al. miR-7 inhibits the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells by suppressing epidermal growth factor receptor expression. Oncol Rep. 2014;31(4):1715–22. doi:10.3892/or.2014.3052.
Li Y, Vandenboom 2nd TG, Wang Z, Kong D, Ali S, Philip PA, et al. miR-146a suppresses invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010;70(4):1486–95. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2792.
Fang C, Zhao Y, Guo B. MiR-199b-5p targets HER2 in breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114(7):1457–63. doi:10.1002/jcb.24487.
Scott GK, Goga A, Bhaumik D, Berger CE, Sullivan CS, Benz CC. Coordinate suppression of ERBB2 and ERBB3 by enforced expression of micro-RNA miR-125a or miR-125b. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(2):1479–86. doi:10.1074/jbc.M609383200.
Shang C, Lu YM, Meng LR. MicroRNA-125b down-regulation mediates endometrial cancer invasion by targeting ERBB2. Med Sci Monit: Int Med J Exp Clin Res. 2012;18(4):BR149–55.
Epis MR, Giles KM, Barker A, Kendrick TS, Leedman PJ. miR-331-3p regulates ERBB-2 expression and androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(37):24696–704. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.030098.
Yan X, Chen X, Liang H, Deng T, Chen W, Zhang S, et al. miR-143 and miR-145 synergistically regulate ERBB3 to suppress cell proliferation and invasion in breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 2014;13:220. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-13-220.
Wu H, Zhu S, Mo YY. Suppression of cell growth and invasion by miR-205 in breast cancer. Cell Res. 2009;19(4):439–48. doi:10.1038/cr.2009.18.
Ling B, Wang GX, Long G, Qiu JH, Hu ZL. Tumor suppressor miR-22 suppresses lung cancer cell progression through post-transcriptional regulation of ErbB3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012;138(8):1355–61. doi:10.1007/s00432-012-1194-2.
Liang H, Liu M, Yan X, Zhou Y, Wang W, Wang X, et al. miR-193a-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in lung cancer by down-regulating ERBB4. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(2):926–40. doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.621409.
Zhang M, Yang Q, Zhang L, Zhou S, Ye W, Yao Q, et al. miR-302b is a potential molecular marker of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting ErbB4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res: CR. 2014;33:10. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-33-10.
Perl AK, Wilgenbus P, Dahl U, Semb H, Christofori GA. Causal role for E-cadherin in the transition from adenoma to carcinoma. Nature. 1998;392(6672):190–3. doi:10.1038/32433.
Peinado H, Olmeda D, Cano A. Snail, Zeb and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nature reviews. Cancer. 2007;7(6):415–28. doi:10.1038/nrc2131.
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell. 2009;139(5):871–90. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.11.007.
Burk U, Schubert J, Wellner U, Schmalhofer O, Vincan E, Spaderna S, et al. A reciprocal repression between ZEB1 and members of the miR-200 family promotes EMT and invasion in cancer cells. EMBO Rep. 2008;9(6):582–9. doi:10.1038/embor.2008.74.
Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Kolesnikoff N, Bert AG, Wang J, Shannon MF, et al. A double-negative feedback loop between ZEB1-SIP1 and the microRNA-200 family regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 2008;68(19):7846–54. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1942.
Majid S, Dar AA, Saini S, Deng G, Chang I, Greene K, et al. MicroRNA-23b functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating Zeb1 in bladder cancer. PLoS One. 2013;8(7):e67686. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0067686.
Guan H, Liang W, Xie Z, Li H, Liu J, Liu L, et al. Down-regulation of miR-144 promotes thyroid cancer cell invasion by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. Endocrine. 2015;48(2):566–74. doi:10.1007/s12020-014-0326-7.
Yokobori T, Suzuki S, Tanaka N, Inose T, Sohda M, Sano A, et al. MiR-150 is associated with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via targeting the EMT inducer ZEB1. Cancer Sci. 2013;104(1):48–54. doi:10.1111/cas.12030.
Zheng YB, Luo HP, Shi Q, Hao ZN, Ding Y, Wang QS, et al. miR-132 inhibits colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis via directly targeting ZEB2. World J Gastroenterol: WJG. 2014;20(21):6515–22. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6515.
Wu SM, Ai HW, Zhang DY, Han XQ, Pan Q, Luo FL, et al. MiR-141 targets ZEB2 to suppress HCC progression. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med. 2014;35(10):9993–7. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2299-9.
Xu Q, Sun Q, Zhang J, Yu J, Chen W, Zhang Z. Downregulation of miR-153 contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis in human epithelial cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34(3):539–49. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgs374.
Siemens H, Jackstadt R, Hunten S, Kaller M, Menssen A, Gotz U, et al. miR-34 and SNAIL form a double-negative feedback loop to regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Cell Cycle. 2011;10(24):4256–71. doi:10.4161/cc.10.24.18552.
Moes M, Le Bechec A, Crespo I, Laurini C, Halavatyi A, Vetter G, et al. A novel network integrating a miRNA-203/SNAI1 feedback loop which regulates epithelial to mesenchymal transition. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35440. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035440.
Ru P, Steele R, Newhall P, Phillips NJ, Toth K, Ray RB. miRNA-29b suppresses prostate cancer metastasis by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(5):1166–73. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0100.
Zhang J, Zhang H, Liu J, Tu X, Zang Y, Zhu J, et al. miR-30 inhibits TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocyte by targeting Snail1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;417(3):1100–5. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.12.121.
Osaka E, Yang X, Shen JK, Yang P, Feng Y, Mankin HJ, et al. MicroRNA-1 (miR-1) inhibits chordoma cell migration and invasion by targeting slug. J Orthop Res: Off Publ Orthopaedic Res Soc. 2014;32(8):1075–82. doi:10.1002/jor.22632.
Liang YJ, Wang QY, Zhou CX, Yin QQ, He M, Yu XT, et al. MiR-124 targets slug to regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34(3):713–22. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgs383.
Li W, Jiang G, Zhou J, Wang H, Gong Z, Zhang Z, et al. Down-regulation of miR-140 induces EMT and promotes invasion by targeting slug in esophageal cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem: Int J Exp Cell Physiol, Biochem Pharmacol. 2014;34(5):1466–76. doi:10.1159/000366351.
Qiu YH, Wei YP, Shen NJ, Wang ZC, Kan T, Yu WL, et al. miR-204 inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting slug in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem: Int J Exp Cell Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2013;32(5):1331–41. doi:10.1159/000354531.
Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL, Ramaswamy S, Itzykson RA. Come C et al. Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell. 2004;117(7):927–39. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.06.006.
Li Y, Wang W, Wang W, Yang R, Wang T, Su T, et al. Correlation of Twist2 up-regulation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition during tumorigenesis and progression of cervical carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 2012;124(1):112–8. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.09.003.
Long L, Huang G, Zhu H, Guo Y, Liu Y, Huo J. Down-regulation of miR-138 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis via directly targeting Twist2. J Transl Med. 2013;11:275. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-11-275.
Dong P, Kaneuchi M, Watari H, Sudo S, Sakuragi N. MicroRNA-106b modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting Twist1 in invasive endometrial cancer cell lines. Mol Carcinog. 2014;53(5):349–59. doi:10.1002/mc.21983.
Li B, Han Q, Zhu Y, Yu Y, Wang J, Jiang X. Down-regulation of miR-214 contributes to intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma metastasis by targeting Twist. FEBS J. 2012;279(13):2393–8. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08618.x.
Yu J, Xie F, Bao X, Chen W, Xu Q. miR-300 inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition and metastasis by targeting Twist in human epithelial cancer. Mol Cancer. 2014;13:121. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-13-121.
Hernandez JM, Elahi A, Clark CW, Wang J, Humphries LA, Centeno B, et al. miR-675 mediates downregulation of Twist1 and Rb in AFP-secreting hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(Suppl 3):S625–35. doi:10.1245/s10434-013-3106-3.
Li LZ, Zhang CZ, Liu LL, Yi C, Lu SX, Zhou X, et al. miR-720 inhibits tumor invasion and migration in breast cancer by targeting Twist1. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35(2):469–78. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgt330.
Vihinen P, Kahari VM. Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer: prognostic markers and therapeutic targets. Int J Cancer J Int du Cancer. 2002;99(2):157–66. doi:10.1002/ijc.10329.
Hadler-Olsen E, Winberg JO, Uhlin-Hansen L. Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer: their value as diagnostic and prognostic markers and therapeutic targets. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med. 2013;34(4):2041–51. doi:10.1007/s13277-013-0842-8.
Deryugina EI, Quigley JP. Matrix metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006;25(1):9–34. doi:10.1007/s10555-006-7886-9.
Liu X, Yu J, Jiang L, Wang A, Shi F, Ye H, et al. MicroRNA-222 regulates cell invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP1) and manganese superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) in tongue squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Genom Proteomics. 2009;6(3):131–9.
Vaisanen A, Tuominen H, Kallioinen M, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T. matrix metalloproteinase-2 (72 kD type IV collagenase) expression occurs in the early stage of human melanocytic tumour progression and may have prognostic value. J Pathol. 1996;180(3):283–9. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199611)180:3<283::AID-PATH662>3.0.CO;2-3.
Chen Q, Zhao X, Zhang H, Yuan H, Zhu M, Sun Q, et al. MiR-130b suppresses prostate cancer metastasis through down-regulation of MMP2. Mol Carcinog. 2014. doi:10.1002/mc.22204.
Wang H, Zhu Y, Zhao M, Wu C, Zhang P, Tang L, et al. miRNA-29c suppresses lung cancer cell adhesion to extracellular matrix and metastasis by targeting integrin beta1 and matrix metalloproteinase2 (MMP2. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e70192. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070192.
Fang JH, Zhou HC, Zeng C, Yang J, Liu Y, Huang X, et al. MicroRNA-29b suppresses tumor angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis by regulating matrix metalloproteinase 2 expression. Hepatology. 2011;54(5):1729–40. doi:10.1002/hep.24577.
Tang R, Cui ZM, Lou YH. MicroRNA-16 regulates the proliferation, invasion and apoptosis of ovarian epithelial carcinoma cells in vitro. Zhonghua fu chan ke za zhi. 2012;47(11):846–50.
Jin J, Cai L, Liu ZM, Zhou XS. miRNA-218 inhibits osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion by down-regulating of TIAM1, MMP2 and MMP9. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev: APJCP. 2013;14(6):3681–4.
Zhang C, Li C, Zhu M, Zhang Q, Xie Z, Niu G, et al. Meta-analysis of MMP2, MMP3, and MMP9 promoter polymorphisms and head and neck cancer risk. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e62023. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062023.
Wang W, Lin H, Zhou L, Zhu Q, Gao S, Xie H, et al. MicroRNA-30a-3p inhibits tumor proliferation, invasiveness and metastasis and is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol: J Eur Soc Surg Oncol Br Assoc Surg Oncol. 2014;40(11):1586–94. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2013.11.008.
Zhao ZG, Jin JY, Zhang AM, Zhang LP, Wang XX, Sun JG, et al. MicroRNA profile of tumorigenic cells during carcinogenesis of lung adenocarcinoma. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(3):458–66. doi:10.1002/jcb.24999.
Groblewska M, Siewko M, Mroczko B, Szmitkowski M. The role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their inhibitors (TIMPs) in the development of esophageal cancer. Folia Histochem et Cytobiol/Pol Acad Sci Pol Histochem Cytochemical Soc. 2012;50(1):12–9. doi:10.2478/18691.
Zhou Y, Li Y, Ye J, Jiang R, Yan H, Yang X, et al. MicroRNA-491 is involved in metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibitions of matrix metalloproteinase and epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Liver international : official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver. 2013;33(8):1271–80. doi:10.1111/liv.12190.
Yang TQ, Lu XJ, Wu TF, Ding DD, Zhao ZH, Chen GL, et al. MicroRNA-16 inhibits glioma cell growth and invasion through suppression of BCL2 and the nuclear factor-kappaB1/MMP9 signaling pathway. Cancer Sci. 2014;105(3):265–71. doi:10.1111/cas.12351.
Wang F, Xiao W, Sun J, Han D, Zhu Y. MiRNA-181c inhibits EGFR-signaling-dependent MMP9 activation via suppressing Akt phosphorylation in glioblastoma. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med. 2014;35(9):8653–8. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2131-6.
Wang Q, Cai J, Wang J, Xiong C, Zhao J. MiR-143 inhibits EGFR-signaling-dependent osteosarcoma invasion. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med. 2014;35(12):12743–8. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2600-y.
Liu P, Wilson MJ. miR-520c and miR-373 upregulate MMP9 expression by targeting mTOR and SIRT1, and activate the Ras/Raf/MEK/Erk signaling pathway and NF-kappaB factor in human fibrosarcoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 2012;227(2):867–76. doi:10.1002/jcp.22993.
Wu D, Li M, Wang L, Zhou Y, Zhou J, Pan H, et al. microRNA145 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting matrix metallopeptidase-11 in renal cell carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 2014;10(1):393–8. doi:10.3892/mmr.2014.2149.
Han HB, Gu J, Zuo HJ, Chen ZG, Zhao W, Li M, et al. Let-7c functions as a metastasis suppressor by targeting MMP11 and PBX3 in colorectal cancer. J Pathol. 2012;226(3):544–55. doi:10.1002/path.3014.
Siragam V, Rutnam ZJ, Yang W, Fang L, Luo L, Yang X, et al. MicroRNA miR-98 inhibits tumor angiogenesis and invasion by targeting activin receptor-like kinase-4 and matrix metalloproteinase-11. Oncotarget. 2012;3(11):1370–85.
Bi Q, Tang S, Xia L, Du R, Fan R, Gao L, et al. Ectopic expression of MiR-125a inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting MMP11 and VEGF. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e40169. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0040169.
Xu N, Zhang L, Meisgen F, Harada M, Heilborn J, Homey B, et al. MicroRNA-125b down-regulates matrix metallopeptidase 13 and inhibits cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(35):29899–908. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.391243.
Yang Z, Zhang Y, Wang L. A feedback inhibition between miRNA-127 and TGFbeta/c-Jun cascade in HCC cell migration via MMP13. PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e65256. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0065256.
Li T, Xie J, Shen C, Cheng D, Shi Y, Wu Z, et al. miR-150-5p inhibits hepatoma cell migration and invasion by targeting MMP14. PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e115577. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0115577.
Xu M, Wang YZ. miR133a suppresses cell proliferation, migration and invasion in human lung cancer by targeting MMP14. Oncol Rep. 2013;30(3):1398–404. doi:10.3892/or.2013.2548.
Hong L, Han Y, Zhou Y, Nita A. Angiogenesis-related microRNAs in colon cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013;13(1):77–84. doi:10.1517/14712598.2013.727391.
Zhang X, Tang J, Zhi X, Xie K, Wang W, Li Z, et al. miR-874 functions as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting angiogenesis through STAT3/VEGF-A pathway in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6(3):1605–17.
Danza K, De Summa S, Pinto R, Pilato B, Palumbo O, Merla G, et al. MiR-578 and miR-573 as potential players in BRCA-related breast cancer angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 2015;6(1):471–83.
Du C, Lv Z, Cao L, Ding C, Gyabaah OA, Xie H, et al. MiR-126-3p suppresses tumor metastasis and angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting LRP6 and PIK3R2. J Transl Med. 2014;12:259. doi:10.1186/s12967-014-0259-1.
Zheng Y, Li S, Ding Y, Wang Q, Luo H, Shi Q, et al. The role of miR-18a in gastric cancer angiogenesis. Hepato-Gastroenterology. 2013;60(127):1809–13.
He T, Qi F, Jia L, Wang S, Song N, Guo L, et al. MicroRNA-542-3p inhibits tumour angiogenesis by targeting angiopoietin-2. J Pathol. 2014;232(5):499–508. doi:10.1002/path.4324.
Yang X, Zhang XF, Lu X, Jia HL, Liang L, Dong QZ, et al. MicroRNA-26a suppresses angiogenesis in human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting hepatocyte growth factor-cMet pathway. Hepatology. 2014;59(5):1874–85. doi:10.1002/hep.26941.
Yin Y, Yan ZP, Lu NN, Xu Q, He J, Qian X, et al. Downregulation of miR-145 associated with cancer progression and VEGF transcriptional activation by targeting N-RAS and IRS1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1829(2):239–47. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.11.006.
Zhu K, Pan Q, Zhang X, Kong LQ, Fan J, Dai Z, et al. MiR-146a enhances angiogenic activity of endothelial cells in hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting PDGFRA expression. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34(9):2071–9. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgt160.
Lee DY, Deng Z, Wang CH, Yang BB. MicroRNA-378 promotes cell survival, tumor growth, and angiogenesis by targeting SuFu and Fus-1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(51):20350–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.0706901104.
Anand S, Majeti BK, Acevedo LM, Murphy EA, Mukthavaram R, Scheppke L, et al. MicroRNA-132-mediated loss of p120RasGAP activates the endothelium to facilitate pathological angiogenesis. Nat Med. 2010;16(8):909–14. doi:10.1038/nm.2186.
Christiansen A, Detmar M. Lymphangiogenesis and cancer. Genes Cancer. 2011;2(12):1146–58. doi:10.1177/1947601911423028.
Sasahira T, Kurihara M, Bhawal UK, Ueda N, Shimomoto T, Yamamoto K, et al. Downregulation of miR-126 induces angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis by activation of VEGF-A in oral cancer. Br J Cancer. 2012;107(4):700–6. doi:10.1038/bjc.2012.330.
Hu J, Cheng Y, Li Y, Jin Z, Pan Y, Liu G, et al. microRNA-128 plays a critical role in human non-small cell lung cancer tumourigenesis, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis by directly targeting vascular endothelial growth factor-C. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(13):2336–50. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2014.06.005.
Jiang L, Wang Y, Rong Y, Xu L, Chu Y, Zhang Y, et al. miR-1179 promotes cell invasion through SLIT2/ROBO1 axis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(1):319–27.
Yang FQ, Zhang HM, Chen SJ, Yan Y, Zheng JH. MiR-506 is down-regulated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and inhibits cell growth and metastasis via targeting FLOT1. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0120258. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0120258.
Liu T, Zhang X, Sha K, Liu X, Zhang L, Wang B. miR-709 up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, promotes proliferation and invasion by targeting GPC5. Cell Prolif. 2015. doi:10.1111/cpr.12181.
Chen B, Hou Z, Li C, Tong Y. MiRNA-494 inhibits metastasis of cervical cancer through Pttg1. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med. 2015. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3440-0.
Yang X, Zang W, Xuan X, Wang Z, Liu Z, Wang J, et al. miRNA-1207-5p is associated with cancer progression by targeting stomatin-like protein 2 in esophageal carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2015;46(5):2163–71. doi:10.3892/ijo.2015.2900.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81172351 and 81372856) and the Taishan Scholars Programme of Shandong Province (Grant No. ts201511096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, HT., Gao, P. The roles of microRNAs related with progression and metastasis in human cancers. Tumor Biol. 37, 15383–15397 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5436-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5436-9