Abstract
Background
In this study, we used phenotypic and genetic analysis to investigate Double haploid (DH) lines derived from normal corn parents (HF1 and 11S6169). DH technology offers an array of advantages in maize genetics and breeding as follows: first, it significantly shortens the breeding cycle by development of completely homozygous lines in two or three generations; and second, it simplifies logistics, including requiring less time, labor, and financial resources for developing new DH lines compared with the conventional RIL population development process.
Objectives
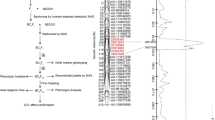
In our study, we constructed a maize genetic linkage map using SSR markers and a DH population derived from a cross of normal corn (HF1) and normal corn (11S6169).
Methods
The DH population used in this study was developed by the following methods: we crossed normal corn (HF1) and normal corn (11S6169), which are parent lines of a normal corn cultivar, in 2014; and the next year, the F1 hybrids were crossed with a tropicalized haploid inducer line (TAIL), which is homozygous for the dominant marker gene R1-nj (Nanda and Chase in Crop Sci 6:213–215, 1966), and we harvested seeds of the haploid lines.
Results
A total of 200 SSR markers were assigned to 10 linkage groups that spanned 1145.4 cM with an average genetic distance between markers of 5.7 cM. 68 SSR markers showed Mendelian segregation ratios in the DH population at a 5% significance threshold. A total of 15 quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for plant height (PH), ear height (EH), ear height ratio (ER), leaf length (LL), ear length (EL), set ear length (SEL), set ear ratio (SER), ear width (EW), 100 kernel weight (100 KW), and cob color (CC) were found in the 121 lines in the DH population.
Conclusion
The results of this study may help to improve the detection and characterization of agronomic traits and provide great opportunities for maize breeders and researchers using a DH population in maize breeding programs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi H, Yokozaki Y, Inagaki A, Fujimura T (1997) Highly polymorphic microsatellites of rice consist of AT repeats, and a classification of closely related cultivars with these microsatellite loci. Theor Appl Genet 94:61–67
Ali ML, Taylor JH, Jie L, Sun G, William M, Kasha KJ, Reid LM, Pauls KP (2005) Molecular mapping of QTLs for resistance to Gibberella ear rot, in corn, caused by Fusarium graminearum. Genome 48:521–533
Almeida GD, Makumbi D, Magorokosho C, Nair S, Borém A, Ribaut JM, Bänziger M, Prasanna BM, Crossa J, Babu R (2013) QTL mapping in three tropical maize populations reveals a set of constitutive and adaptive genomic regions for drought tolerance. Theor Appl Genet 126:583–600
Alvi S, Tuberosa R (2005) To clone or not to clone plant QTL: present and future challenges. Trends in Plant Sci 10:297–304
Beavis WD, Grant D, Albertsen M, Fincher R (1991) Quantitative trait loci for plant height in four maize populations and their associations with qualitative genetic loci. Theor Appl Genet 83:141–145
Cai H, Chu Q, Gu R, Yuan L, Liu J, Zhang X, Chen F, Mi G, Zhang F (2012) Identification of QTLs for plant height, ear height and grain yield in maize (Zea mays L.) in response to nitrogen and phosphorus supply. Plant Breed 131:502–510
Chang MT, Coe EH (2009) Doubled haploids. In: Kriz AL, Larkins BA (eds) Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry. Vol. 63. molecular genetic approaches to maize improvement, vol 63. Springer, Berlin, pp 127–142
Choe ES, Rocheford TR (2012) Genetic and QTL analysis of pericarp thickness and ear architecture traits of Korean waxy corn germplasm. Euphytica 183:243–260
Collard BCY, Jahufer MZZ, Brouwer JB, Pang ECK (2005) An introduction to markers, quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping and marker-assisted selection for crop improvement: the basic concepts. Euphytica 142:169–196
Cui TT, He KH, Chang LG, Zhang XH, Xue JQ, Liu JC (2017) QTL mapping for leaf area in maize (Zea mays L.) under multi-environments. J Integ Agri 16:800–808
Danson J, Lagat M, Kimani M, Kuria A (2008) Quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for resistance to gray leaf spot and common rust diseases of maize. Afr J Biotech 7:3247–3254
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A simple and rapid method for plant DNA preparation, Version II. Plant Mol Bio Rep 1:19–21
Ding D, Li W, Song G, Qi H, Liu J, Tang J (2011a) Identification of QTLs for arsenic accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.) using a RIL population. PLoS One 6:e25646
Ding JQ, Ma JL, Zhang CR, Dong HF, Xi ZY, Xia ZL, Wu JY (2011b) QTL mapping for test weight by using F2:3 population in maize. J Genet 90:75–80
Duvick DN (2005) The contribution of breeding to yield advances in maize (Zea mays L.). Adv Agron 86:83–145
Duvick DN, Smith JSC, Cooper RM (2004) Long-term selection in a commercial hybrid maize breeding program. Plant Breed Rev 24:109–151
Forster BP, Thomas WTB (2005) Doubled haploids in genetics and plant breeding. Plant Breed Rev 25:57–88
Frascaroli E, Canè MA, Landi P, Pea G, Gianfranceschi L, Villa M, Morgante M, Pè ME (2007) Classical genetic and quantitative trait loci analyses of heterosis in a maize hybrid between two elite inbred lines. Genetics 176:625–644
Gardiner JM, Coe EH, Melia-Hancock S, Hoisington DA, Chao S (1993) Development of a core RFLP map in maize using an immortalized F2 population. Genetics 134:917–930
Geiger HH (2009) Doubled haploids. In: Bennetzen JL, Hake S (eds) Maize handbook-volume II; genetics and genomics. Springer, New York, pp 641–657
Geiger HH, Gordillo GA (2009) Doubled haploids in hybrid maize breeding. Maydica 54:485–499
Guo Y, Yang X, Chander S, Yan J, Zhang J, Song T, Li J (2013) Identification of unconditional and conditional QTL for oil, protein and starch content in maize. Crop J 1:34–42
Jiang L, Ge M, Zhao H, Zhang T (2015) Analysis of heterosis and quantitative trait loci for kernel shape related traits using triple testcross population in maize. PLoS One 10:e0124779
Kosambi D (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Landi P, Albrecht B, Giuliani MM, Sanguineti MC (1998) Seedling characteristics in hydroponic culture and field performance of maize genotypes with different resistance to root lodging. Maydica 43:111–116
Lechelt C, Peterson T, Laird A, Chen J, Dellaporta SL, Dennis E, Peacock W, Starlinger P (1989) Isolation and molecular analysis of the maize P locus. Mol Gene Genet 219:225–234
Lee JK, Park JY, Kim JH, Kwon SJ, Shin JH, Hong SK, Min HK, Kim NS (2006) Genetic mapping of the Isaac-CACTA transposon in maize. Theor Appl Genet 113:16–22
Li YL, Li XH, Li JZ, Fu JF, Wang YZ, Wei MG (2009) Dent corn genetic background influences QTL detection for grain yield and yield components in high-oil maize. Euphytica 169:273–284
Li JZ, Zhang ZW, Li YL, Wang QL, Zhou YG (2011a) QTL consistency and meta-analysis for grain yield components in three generations in maize. Theor Appl Genet 122:771–782
Li Y, Ma XL, Wang TY, Li YX, Liu C, Liu ZZ, Sun BC, Shi YS, Song YC, Carlone M, Bubeck D, Bhardwaj H, Whitaker D, Wilson W, Jones E, Wright K, Sun SK, Niebur W, Smith S (2011b) Increasing maize productivity in China by planting hybrids with germplasm that responds favorably to higher planting densities. Crop Sci 51:2391–2400
Lu GH, Tang JH, Yan JB, Ma XQ, Li JS, Chen SJ, Ma JC, Liu ZX, Zhang YR, Dai JR (2006) Quantitative trait loci mapping of maize yield and its components under different water treatments at flowering time. J Integr Plant Biol 48:1233–1243
Liu G, Bernhardt JL, Jia MH, Wamishe YA, Jia Y (2008) Molecular characterization of the recombinant inbred line population derived from a japonica–indica rice cross. Euphytica 159:73–82
Liu XH, He SL, Zheng ZP, Huang YB, Tan ZB, Wu X (2010) QTL identification for row number per ear and grain number per row in maize. Maydica 55:127–133
Liu ZH, Ji HQ, Cui ZT, Wu X, Duan LJ, Feng XX, Tang JH (2011) QTL detected for grain-filling rate in maize using a RIL population. Mol Breed 27:25–36
Liu Y, Wang L, Sun C, Zhang Z, Zheng Y, Qiu F (2014) Genetic analysis and major QTL detection for maize kernel size and weight in multi-environments. Theor Appl Genet 127:1019–1037
Liu R, Meng Q, Zheng F, Kong L, Yuan J, Lübberstedt T (2017) Genetic mapping of QTL for maize leaf width combining RIL and IF2 populations. PLoS One 12:e0189441
Lombard V, Delourme R (2001) A consensus linkage map for rapeseed (Brassica napus L.): construction and integration of three individual maps from DH population. Theor Appl Genet 103:491–507
Lu B, Xie K, Yang C, Zhang L, Wu T, Li L, Liu X, Jiang L, Wan J (2011) Efficient QTL detection for heading date in backcross inbred line and F2 population derived from the same rice cross. Afr J Agri Res 6:2372–2378
Lübberstedt T, Melchinger AE, Fahr S, Klein D, Dally A, Westhoff P (1998) QTL mapping in testcrosses of flint lines of maize: III. Comparison across populations for forage traits. Crop Sci 38:1278–1289
Mclntyre CL, Mathews KL, Rattey A, Chapman SC, Drenth J, Ghaderi M, Reynolds M, Shorter R (2010) Molecular detection of genomic regions associated with grain yield and yield-related components in an elite bread wheat cross evaluated under irrigated and rainfed conditions. Theor Appl Genet 120:527–541
Meyer J, Snook M, Houchins K, Rector B, Widstrom N, McMullen M (2007) Quantitative trait loci for maysin synthesis in maize (Zea mays L.) lines selected for high silk maysin content. Theor Appl Genet 115:119–128
Nanda DK, Chase SS (1966) An embryo marker for detecting monoploids of maize (Zea mays L.). Crop Sci 6:213–215
Park YJ, Lee JK, Kim NS (2009) Simple sequence repeat polymorphisms (SSRPs) for evaluation of molecular diversity and germplasm classification of minor crops. Molecules 14:4546–4569
Park KJ, Sa KJ, Kim BY, Koh HJ, Lee JK (2014) Genetic mapping and QTL analysis for yield and agronomic traits with an F2:3 population derived from a waxy corn x sweet corn cross. Genes Genomics 36:179–189
Prasanna BM, Chaikam V, Mahuku G (eds) (2012) Doubled haploid technology in maize breeding: theory and practice. CIMMYT, Mexico, D.F.
Prigge V, Xu X, Li L, Babu R, Chen S, Atlin GN, Melchinger AE (2012) New insights into the genetics of in vivo induction of maternal haploids, the backbone of doubled haploid technology in maize. Genetics 190:781–793
Qiu F, Zheng Y, Zhang Z, Xu S (2007) Mapping of QTL associated with waterlogging tolerance during the seedling stage in maize. Anna Botany 99:1067–1081
Röber FK, Gordillo GA, Geiger HH (2005) In vivo haploid induction in maize-performance of new inducers and significance of doubled haploid lines in hybrid breeding. Maydica 50:275–283
Ryu SH, Park JY, Huh NK, Min HK (2001) Relationship between genetic distance and hybrid performance of black waxy corn (Zea mays L.). Korean J Breed Sci 33:95–103
Sa KJ, Park JY, Park KC, Lee JK (2012) Analysis of genetic mapping in a waxy/dent maize RIL population using SSR and SNP markers. Genes Genomics 34:157–164
Sa KJ, Park JY, Woo SY, Ramekar RV, Jang CS, Lee JK (2015) Mapping of QTL traits in corn using a RIL population derived from a cross of dent corn x waxy corn. Genes Genomics 37:1–14
Sabadin PK, Souza JCL, Souza AP, Garcia AAF (2008) QTL mapping for yield components in a tropical maize population using microsatellite markers. Hereditas 145:194–203
Salvi S, Corneti S, Bellotti M, Carraro N, Sanguineti MC, Castelletti S, Tuberosa R (2011) Genetic dissection of maize phenology using an intraspecific introgression library. BMC Plant Biol 11:4
Semagn K, Bjørnstad Å, Ndjiondjop MN (2006) Principle, requirements and prospects of genetic mapping in plants. Afr J Biotech 5:2569–2587
Tang JH, Teng WT, Yan JB, Ma XQ, Meng YJ, Dai JR, Li JS (2007) Genetic dissection of plant height by molecular markers using a population of recombinant inbred lines in maize. Euphytica 155:117–124
Tanksley SD, Grandillo S, Fulton TM, Zamir D, Eshed Y, Petiard V, Lopez J, Beck-Bunn T (1996) Advanced backcross QTL analysis in a cross between an elite processing line of tomato and its wild relative L. pimpinellifolium. Theor Appl Genet 92:213–224
Troyer AF, Larkins JR (1985) Selection for early flowering in corn: 10 late synthetics. Crop Sci 25:695–697
Wang DL, Zhu J, Li ZK, Paterson AH (1999) User manual for QTL mapper version 1.0, pp 1–57
Wang C, Chen Y, Ku L, Wang T, Sun Z, Cheng F, Wu L (2010) Mapping QTL associated with photoperiod sensitivity and assessing the importance of QTL × environment interaction for flowering time in maize. PLoS One 5:e14068
Wang TY, Ma XL, Li Y, Bai DP, Liu C, Liu ZZ, Tan XJ, Shi YS, Song YC, Carlone M, Bubeck D, Bhardwaj H, Jones E, Wright K, Smith S (2011) Changes in yield and yield components of single-cross maize hybrids released in China between 1964 and 2000. Crop Sci 51:512–525
Wang G, He QQ, Xu ZK, Song RT (2012) High segregation distortion in maize B73 x teosinte crosses. Genet Mol Res 11:693–706
Wang H, Liang Q, Li K, Hu X, Wu Y, Wang H, Liu Z, Huang C (2017) QTL analysis of ear leaf traits in maize (Zea mays L.) under different planting densities. Crop J 5:387–395
Wei M, Fu J, Li X, Wang Y, Li Y (2009) Influence of dent corn genetic backgrounds on QTL detection for plant-height traits and their relationships in high-oil maize. J Appl Genet 50:225–234
Yamagishi M, Takeuchi Y, Tanaka I, Kono I, Murai K, Yano M (2010) Segregation distortion in F2 and doubled haploid populations of temperate japonica rice. J Genet 89:237–241
Yang DE, Jin DM, Wang B, Zhang DS, Nguyen HT, Zhang CL, Chen SJ (2005) Characterization and mapping of Rpi1, a gene that confers dominant resistance to stalk rot in maize. Mol Genet Genet 274:229–234
Yang G, Li Y, Wang Q, Zhou Y, Zhou Q, Shen B, Zhang F, Liang X (2012) Detection and integration of quantitative trait loci for grain yield components and oil content in two connected recombinant inbred line populations of high-oil maize. Mol Breed 29:313–333
Young ND (1995) Isolation and cloning of plant disease resistance genes. In: Singh RP, Singh US (eds) Molecular methods in plant pathology. Lewis, Boca Raton, pp 221–234
Yu J, Arbelbide M, Bernardo R (2005) Power of in silico QTL mapping from phenotypic, pedigree, and marker data in a hybrid breeding program. Theor Appl Genet 110:1061–1067
Zhang ZM, Zhao MJ, Ding HP, Rong TZ, Pan GT (2006) Quantitative trait loci analysis of plant height and ear height in maize (Zea mays L.). Rus J Genet 42:306–310
Zhang X, Tang B, Liang W, Zheng Y, Qiu F (2011a) Quantitative genetic analysis of flowering time, leaf number and photoperiod sensitivity in maize (Zea mays L.). J Plant Breed Crop Sci 3:168–184
Zhang Y, Li Y, Wang Y, Peng B, Liu C, Liu Z, Tan W, Wang D, Shi Y, Sun B, Song Y, Wang T, Li Y (2011b) Correlations and QTL detection in maize family per se and testcross progenies for plant height and ear height. Plant Breed 130:617–624
Zhao X, Peng Y, Zhang J, Fang P, Wu B (2018) Identification of QTLs and meta-QTLs for seven agronomic traits in multiple maize populations under well-watered and water-stressed conditions. Crop Sci 58:507–520
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project title #PJ013157012018, Project #PJ013308012018), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea, and the Golden Seed Project (No. 213009-05-1-WT821, PJ012650012017), Ministry of Agriculture, Food, and Rural Affairs (MAFRA), Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries (MOF), Rural Development Administration (RDA), and Korea Forest Service (KFS), Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Jae-Keun Choi declares that he has no conflict of interest. Kyu Jin Sa declares that he has no conflict of interest. Dae Hyun Park declares that he has no conflict of interest. Su Eun Lim declares that she has no conflict of interest. Si-Hwan Ryu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Jong Yeol Park declares that he has no conflict of interest. Ki Jin Park declares that he has no conflict of interest. Hae-Ik Rhee declares that he has no conflict of interest. Mijeong Lee declares that she has no conflict of interest. Ju Kyong Lee declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human subjects or animals performed by any of the above authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, JK., Sa, K.J., Park, D.H. et al. Construction of genetic linkage map and identification of QTLs related to agronomic traits in DH population of maize (Zea mays L.) using SSR markers. Genes Genom 41, 667–678 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00813-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00813-x