Abstract
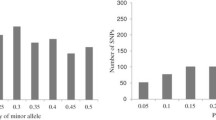
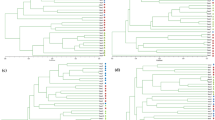
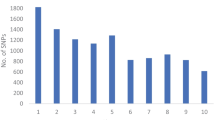
Maize has been domesticated in diverse environments ranging from low latitudes in tropical countries to high latitudes in Canada. Because maize breeding programs primarily focus on hybrid vigor by selectively crossing inbred lines to maximize recombination, we collected a diverse array of commercial hybrid and inbred lines from southern Asia, China, and Canada and analyzed them by amplified length fragment polymorphism (AFLP), sequence-specific amplified polymorphism (SSAP), and CACTA-transposon display (TD) analyses. Cluster analyses using these molecular marker systems clearly differentiated these maize lines into three groups: southern Asian lines, northern Asian lines, and Canadian lines. However, principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) based on Nei’s distances grouped them into two groups: Asian and Canadian lines. Thus, groupings by cluster dendrograms and PCoA showed that geographic origin was a more dominant factor than growing seasonal differences resulting from different latitudes. The overall genetic diversity (Ht) was found to be high (more than 80 % molecular variations) among the maize lines by all three of the marker systems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barata C, Carena MJ (2006) Classification of North Dakota maize inbred lines into heterotic groups based on molecular and testcross data. Euphytica 151:339–349
Baucom RS, Estill JC, Chaparro C, Upshaw N, Jogi A, Deragon JM, Westerman RP, Sanmiguel PJ, Bennetzen JL (2009) Exceptional diversity, non-random distribution, and rapid evolution of retroelements in the B73 maize genome. PLoS Genet 5:e1000732
Buckler ES, Stevens NM (2006) Maize origins, domestication, and selection. Darwin’s Harvest. Columbian University Press, New York
Dao A, Sanou J, Mitchell SE, Gracen V, Danquah EY (2014) Genetic diversity among INERA maize inbred lines with single nuculeotide polymorphism (SNP) markers and their relationship with CIMMYT, IITA, and temperate lines. BMC Genet 15:127
Fedoroff N, Bennetzen JL (2013) Transposons, genomic shock, and genome evolution. In: Fedorff N (ed) Plant transposons and genome dynamics in evolution, 1st edn. Wiley, pp 181–201
Finnegen DJ (1989) Eukaryotic transposable elements and genome evolution. Trends Genet 5:103–107
Hirano R, Naito K, Fukunaga K, Watanabe KN, Ohsawa R, Kawase M (2011) Genetic structure of landraces in foxtail millet (Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.) revealed with transposon display and interpretation to crop evolution of foxtail millet. Genome 54:498–506
Il Lee S, Park KC, Ha MW, Kim KS, Jang YS, Kim NS (2012) CACTA transposon-derived Ti-SCARs for cultivar fingerprinting in rapeseed. Genes Genomics 34:575–579
Kalendar R, Flavell AJ, Ellis T, Sjakste T, Moisy C, Schulman A (2011) Analysis of plant diversity with retrotransposon-based molecular markers. Heredity 106:520–530
Kwon SJ, Park KC, Kim JH, Lee JK, Kim NS (2005) Rim 2/Hipa CACTA transposon display: a new genetic marker technique in Oryza species. BMC Genet 6:15
Loarce Y, Gallego R, Ferrer E (1996) A comparative analysis of the genetic relationships between rye cultivars using RFLP and RAPD markers. Euphytica 88:107–115
Lou Q, Chen J (2007) Ty1-copia retrotransposon-based SSAP marker development and its potential in the genetic study of cucurbits. Genome 50:802–810
Mardi M, Naghavi MR, Pirseyedi SM, Alamooti MK, Monfared SR, Ahkami AH, Omidbakhsh MA, Alavi NS, Shanjani PS, Katsiotis A (2011) Comparative assessment of SSAP, AFLP and SSR markers for evaluation of genetic diversity of durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var. durum). J Agric Sci Technol 13:905–920
Matsuoka Y, Vigouroux Y, Gooman MM, Sanchez GJJ, Buckler E, Doebley J (2002) A single domestication for maize shown by multilocus microsatellite genotyping. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:6080–6084
McClintock B (1950) The origin and behavior of mutable loci in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 36:344–355
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Nagaraju J, Reddy KD, Nagaraja GM, Sethuraman BN (2001) Comparison of multilocus RFLPs and PCR-based marker systems for genetic analysis of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Heredity 86:588–597
Peakall R, Smouse P (2005) Appendix 1—methods and statistics in GenAlEx 6 by Rod Peakall and Peter Smouse. Statistics (Ber) 5:1–23
Phumichai C, Dougchan W, Puddlanon P, Jampatong S, Gruloyma P, Kirdsri C, Chungwonse J, Pulam Y (2008) SSR-based and grain yield-based diversity of hybrid maize in Thailand. Field Crop Res 108:157–162
Porceddu A, Albertini E, Barcaccia G, Bertoli F, Vereonesi F (2002) Development of S-SAP markers based on an LTR-like sequence from Medicago sativa L. Mol Genet Genomics 267:107–114
Powell W, Morgante M, Andre C, Hanafey M, Vogel J, Tingey S, Rafalski A (1996) The comparison of RFLP, RAPD, AFLP and SSR (microsatellite) markers for germplasm analysis. Mol Breed 2:225–238
Prasanna BM (2012) Diversity in global maize germplasm: characterization and utilization. J Biosci 37:1–13
Prigge V, Melchinger AE (2012) Production of haploids and doubled haploids in maize. Methods Mol Biol 877:161–172
Ranum P, Peña-Rosas JP, Garcia-Casal MN (2014) Global maize production, utilization, and consumption. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1312:105–112
Reid LM, Xiang K, Zhu X, Baum BR, Molnar SJ (2011) Genetic diversity analysis of 119 Candian maize inbred lines based on pedigree and simple sequence repeat markers. Can J Plant Sci 91:651–661
Roy N, Choi JY, Lee SI, Kim NS (2015a) Marker utility of transposable elements for plant genetics, breeding, and ecology: a review. Genes Genomics 37:141–151
Roy N, Choi JY, Lim MJ, Lee SI, Choi HJ, Kim NS (2015b) Genetic and epigenetic diversity among dent, waxy, and sweet corns. Genes Genomics 37:865–874
Sánchez GJJ, Stuber CW, Goodman M (2000) Isozymatic diversity in the races of maize in Americas. Maydica 45:185–203
Sánchez GJJ, Goodman M, Stuber CW (2007) Racial diversity of mazie in Brazil and adjacenty areas. Maydica 52:13–30
Sanmiguel P, Vitte C (2009) The LTR-retrotransposons of maize. Maize handbook, vol 2. Springer, Berlin, pp 307–327
Sanz AM, Gonzalez SG, Syed NH, Suso MJ, Saldana CC, Flavell AJ (2007) Genetic diversity analysis in Vicia species using retrotransposon-based SSAP markers. Mol Genet Genomics 278:433–441
Schnable PS, Warer D, Fulton RS, Stein JC, Wei F, Pasternak S, Liang C, Zhang J, Fulton L, Graves TA et al (2009) The B73 maize genome: compexity, diversity, and dinamics. Science 326:1112–1115
Syed NH, Flavell AJ (2006) Sequence-specific amplification polymorphisms (SSAPs): a multi-locus approach for analyzing transposon insertions. Nat Protoc 1:2746–2752
Tam SM, Mhiri C, Vogelaar A, Kerkveld M, Pearce SR, Grandbastien (2005) Comparative analyses of genetic diversities within tomato and pepper collections detected by retrotransposon-based SSAP, AFLP and SSR. Theor Appl Genet 110:819–831
Tenallion MI, Sawkins MC, Long AD, Gaut RL, Doebly JF, Gaut BS (2001) Patterns of DNA sequence polymorphism along chromosome 1 of maize (Zea mays ssp. Mays L.). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9161–9166
Vigouroux Y, Glaubitz JC, Matusoka Y, Goodman MM, Sanchez H, Doebley J (2008) Population structure and genetic diversity of new world maize races assessed by DNA microsatellites. Am J Bot 95:1240–1253
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van der Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Wang Q, Dooner HK (2006) Remarkable variation in maize genome structure inferred from haplotype diversity at the bz locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 21:17644–17649
Wicker T, Sabot F, Hua-Van A, Bennetzen JL, Capy P, Chalhoub B, Flavell A, Leroy P, Morgante M, Panaud O et al (2007) A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements. Nat Rev Genet 8:973–982
Yeh FC, Yang RC, Boyle T, Freeware MW (1999) Popgene version 1.31. University of Alberta and Tim Boyle Center for International Forestry Research, Alberta, pp 1–29
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by a grant from the Golden Seed Project, Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA), Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries (MOF), Rural Development of Korea (RDA), and the Korea Forest Service (Project Number: ATIS-PJ00994003, FRIS-213001-04-3-SBA20), as well as a 2015 research grant from Kangwon National University (Grant No. 520159395).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Neha Roy declares that she does not have conflict of interest. Nam-Soo Kim declares that he does not have conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human subjects or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, N.S., Kim, NS. Genetic diversity analysis of maize lines using AFLP and TE-based molecular marker systems. Genes Genom 38, 1005–1012 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0461-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0461-z