Abstract
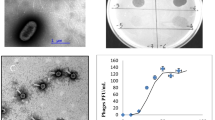
Wetlands have unique characteristics and play a number of roles in the environment, principally in water purification, flood control, and the maintenance of shoreline stability. In this work, a lytic cold-active bacteriophage designated VNPH-1 was isolated from the Napahai wetland in China together with Aeromonas sobria NPH-1 cells, and a preliminary characterization of this bacteriophage was carried out. Electron microscopy revealed that VNPH-1 had an icosahedral head (116.7 nm) and a contractile tail (10 nm in width, 166.7 nm in length). Bacteriophage VNPH-1 was classified as Myoviridae and had an approximate genome size of 110 to 120 kb. One-step growth curve revealed that the latent and burst periods were 20 and 10 min, respectively, with an average burst size of 80 bacteriophage particles per infected cell. The pH and thermal stability of bacteriophage VNPH-1 were also investigated. The maximum stability of the bacteriophage was observed at an optimal pH of 9.0, and the phage was comparatively stable at pH 5.0-10.0. The specificity of this bacteriophage for its host makes it an attractive candidate for phage therapy of A. sobria infections. As VNPH-1 is a cold-active bacteriophage with a low production temperature, it would be worthwhile to characterize it further and to deepen knowledge of its interaction with A. sobria in future studies.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackermann HW (2007) 5500 phages examined in the electron microscope. Arch Virol 152:227–243
Adams MH (1959) Bacteriophages. Interscience Publishers, Inc., New York
Anesio AM, Bellas CM (2011) Are low temperature habitats hot spots of microbial evolution driven by viruses? Trends Microbiol 19:52–57
Anesio AM, Hodson AJ, Andreas F, Psenner R, Sattler B (2009a) High microbial activity on glaciers: importance to the global carbon cycle. Glob Chang Biol 15:955–960
Anesio AM, Hodson AJ, Andreas F, Psenner R, Sattler B (2009b) High diversity of the viral community from an Antarctic lake. Science 326:858–861
Atlas RM (2004) Handbook of microbiological media. CRC Press 1455, Boca Raton London New York
Beilstein F, Dreiseikelmann B (2008) Temperate bacteriophage PhiO18P from an Aeromonas media isolate: characterization and complete genome sequence. Virology 373:25–29
Breitbart M, Rohwer F (2005) Here a virus, there a virus, everywhere the same virus? Trends Microbiol 13:278–284
Casjens SR (2008) Diversity among the tailed-bacteriophages that infect the Enterobacteriaceae. Res Microbiol 159:340–348
Castillo D, Higuera G, Villa M, Middelboe M, Dalsgaard I, Madsen L, Espejo RT (2012) Diversity of Flavobacterium psychrophilum and the potential use of its phages for protection against bacterial cold water disease in salmonids. J Fish Dis 35:193–201
Castillo D, Christiansen RH, Espejo R, Middelboe M (2014) Diversity and geographical distribution of Flavobacterium psychrophilum isolates and their phages: patterns of susceptibility to phage infection and phage host range. Microb Ecol 67:748–757
Chow MS, Rouf MA (1983) Isolation and partial characterization of two Aeromonas hydrophila bacteriophages. Appl Environ Microbiol 45:1670–1676
Danovaro R, Dell’Anno A, Corinaldesi C, Magagnini M, Noble R, Tamburini C, Weinbauer M (2008) Major viral impact on the functioning of benthic deep-sea ecosystems. Nature 454:1084–1087
Haq Ul, Chaudhry WN, Andleeb S, Qadri I (2012) Isolation and partial characterization of a virulent bacteriophage IHQ1 specific for Aeromonas punctata from stream water. Microb Ecol 63:954–963
Hermoso JA, Garcia JL, Garcia P (2007) Taking aim on bacterial pathogens: from phage therapy to enzybiotics. Curr Opin Microbiol 10:461–472
Imbeault S, Parent S, Lagace M, Uhland CF, Blais JF (2006) Using bacteriophages to prevent furunculosis caused by Aeromonas salmonicida in farmed brook trout. J Aquat Anim Health 18:203–214
Kim JH, Son JS, Choi YJ, Choresca CH, Shin SP, Han JE, Jun JW, Kang DH, Oh C, Heo SJ, Park SC (2012a) Isolation and characterization of a lytic Myoviridae bacteriophage PAS-1 with broad infectivity in Aeromonas salmonicida. Curr Microbiol 64:418–426
Kim JH, Son JS, Choresca CH, Shin SP, Han JE, Jun JW, Kang DH, Oh C, Heo SJ, Park SC (2012b) Complete genome sequence of bacteriophage phiAS7, a T7-like virus that infects Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida. J Virol 86:2894–2895
Li P, Chen B, Song Z, Song Y, Yang Y, Ma P, Wang H, Ying J, Ren P, Yang L, Gao G, Jin S, Bao Q, Yang H (2012) Bioinformatic analysis of the Acinetobacter baumannii phage AB1 genome. Gene 507:125–134
Lin LL, Han J, Ji XL, Hong W, Huang L, Wei YL (2011) Isolation and characterization of a new bacteriophage MMP17 from Meiothermus. Extremophiles 15:253–258
Liu B, Wu SJ, Song Q, Zhang XB, Xie LH (2006) Two novel bacteriophages of thermophilic bacteria isolated from deep-sea hydrothermal fields. Curr Microbiol 53:163–166
Lu Z, Breidt F, Fleming HP, Altermann E, Klaenhammer TR (2003) Isolation and characterization of a Lactobacillus plantarum bacteriophage, phiJL-1, from a cucumber fermentation. Int J Food Microbiol 84:225–235
Madsen L, Bertelsen SK, Dalsgaard I, Middelboe M (2013) Dispersal and survival of Flavobacterium psychrophilum phages in vivo in rainbow trout and in vitro under laboratory conditions: implications for their use in phage therapy. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:4853–4861
Merino S, Camprubi S, Tomas JM (1990) Isolation and characterization of bacteriophage PM2 from Aeromonas hydrophila. FEMS Microbiol Lett 56:239–244
Rex MA, Etter RJ, Morris JS, Crouse J, McClain CR, Johnson NA, Stuatr CT, Deming JW, Thies R, Avery R (2006) Global bathymetric pattern of standing stock and body size in the deep-sea benthos. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 317:1–8
Rohwer F, Thurber RV (2009) Viruses manipulate the marine environment. Nature 459:207–212
Sawstrom C, Lisle J, Anesio AM, Priscu JC, Laybourn-Parry J (2008a) Bacteriophage in polar inland waters. Extremophiles 12:167–175
Sawstrom C, Pearce I, Davidson AT, Rosen P, Laybourn-Parry J (2008b) Influence of environmental conditions, bacterial activity and viability on the viral component in 10 Antarctic lakes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 63:12–22
Shen CJ, Liu YJ, Lu CP (2012a) Complete genome sequence of Aeromonas hydrophila phage CC2. J Virol 86:10900
Shen GH, Wang JL, Wen FS, Chang KM, Kuo CF, Lin CH, Luo HR, Hung CH (2012b) Isolation and characterization of phikm18p, a novel lytic phage with therapeutic potential against extensively drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. PLoS One 7:e46537
Sime-Ngando T, Colombet J (2009) Virus and prophages in aquatic ecosystems. Can J Microbiol 55:95–109
Suttle CA (2005) Viruses in the sea. Nature 437:356–361
Xiang XY, Chen LM, Huang XX, Luo YM, She QX, Huang L (2005) Sulfolobus tengchongensis spindle-shaped virus STSV1: virus-host interactions and genomic features. J Virol 79:8677–8686
Acknowledgments
This research was supported the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31160121), Yunnan Provincial Education Fund project (2013Z138) and funded by Open Research Fund Program of the State Key Laboratory of Virology of China (2013002).
Ethical standards
The authors declare that all the experiments were conducted according to the current laws of the country in which they were performed.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no substantial financial or commercial conflicts of interest with the current work or its publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, X., Yu, H., Zhang, Q. et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel lytic cold-active bacteriophage VNPH-1 from the Napahai wetland in China. Ann Microbiol 65, 1789–1796 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-1018-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-1018-5