Abstract
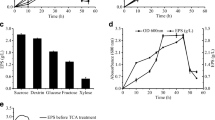
This work engrosses the production and further chemical modifications of EPS produced by Lactobacillus plantarum BR2 and subsequent evaluation of their biological properties showed greater antioxidant properties for the derivatives compared to its native unmodified form. Of the three derivatives, acetylated EPS (a-EPS), carboxymethylated EPS (Cm-EPS), and sulphated EPS (s-EPS), a-EPS exhibited the highest DPPH radical scavenging and total antioxidant activity in a dose-dependent manner. At all tested concentrations, a-EPS showed higher scavenging activity, and a maximum activity of 73.81% at 2 mg/mL. Meanwhile, s-EPS showed the highest reducing power potential and hydroxyl radical scavenging activities. At 2 mg/mL concentration, the order of reducing power was observed to be s-EPS (41.39%) > a-EPS (37.43%) > Cm-EPS (24.02) > BR2 control EPS (16%) and the hydroxyl radical scavenging activity for the s-EPS was 54.43%. The highest reducing power activity exhibited by s-EPS is 2.6-fold higher and a 1.5-fold increase in the scavenging activity of native BR2 EPS after the sulphonyl group addition was observed. The increase in these activities is due to the addition of various functional groups that contributes largely to the scavenging abilities of different free radicals. The s-EPS and Cm-EPS derivatives also exhibited increased cholesterol-lowering activity of 40 and 34.5%, respectively, than the native EPS. Interestingly, there were hardly any inhibitions on cell growth and viability of normal L929 fibroblast cell lines upon treatment with these EPSes. The improved antioxidant properties resulting from chemical modification opened better avenues for EPS application in the food and pharma sectors. Thus, the potentiality of chemically modified EPS may be explored further in the development of functional foods.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article (and its supplementary information files).
Abbreviations
- EPS:
-
Exopolysaccharides
- LAB:
-
Lactic acid bacteria
- a-EPS:
-
Acetylated EPS
- Cm-EPS:
-
Carboxymethylated EPS
- s-EPS:
-
Sulphated EPS
- DS:
-
Degree of substitution
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulphoxide
- DPPH:
-
1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl
- H3PO4 :
-
Phosphoric acid
- SO3⋅Py:
-
Sulphur trioxide pyridine complex
- kDa:
-
Kilo dalton
- Vc:
-
Vitamin C equivalents
- CTAB:
-
Hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
- nm:
-
Nanometer
- LD:
-
Lethal dose
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- HSR %:
-
Hydroxyl radical scavenging activity percentage
References
Adebayo-tayo B, Fashogbon R (2020) Heliyon in vitro antioxidant, antibacterial, in vivo immunomodulatory, antitumor and hematological potential of exopolysaccharide produced by wild type and mutant Lactobacillus delbureckii subsp. bulgaricus. Heliyon 6:e03268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03268
Alam MN, Bristi NJ, Rafiquzzaman M (2013) Review on in vivo and in vitro methods evaluation of antioxidant activity. Saudi Pharm J 21:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2012.05.002
Ayyash M, Abu-Jdayil B, Olaimat A et al (2020) Physicochemical, bioactive and rheological properties of an exopolysaccharide produced by a probiotic Pediococcus pentosaceus M41. Carbohydr Polym 229:115462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115462
Bhat B, Bajaj BK (2019) Hypocholesterolemic potential and bioactivity spectrum of an exopolysaccharide from a probiotic isolate Lactobacillus paracasei M7. Bioact Carbohydr Diet Fibre 19:100191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcdf.2019.100191
Bintsis T (2018) Lactic acid bacteria: their applications in foods. J Bacteriol Mycol Open Access. https://doi.org/10.15406/jbmoa.2018.06.00182
Chen Y, Zhang H, Wang Y et al (2014) Acetylation and carboxymethylation of the polysaccharide from Ganoderma atrum and their antioxidant and immunomodulating activities. Food Chem 156:279–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.01.111
Chen Y, Zhang H, Wang Y et al (2015) Sulfated modification of the polysaccharides from Ganoderma atrum and their antioxidant and immunomodulating activities. Food Chem 186:231–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.10.032
Chouchane H, Najjari A, Cherif H et al (2020) Carboxymethylated sulfated heteroexopolysaccharide from a haloarchaeal strain as potential biomolecule for harmless adjuvant therapy in cancer treatment. J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8907958
Dilna SV, Surya H, Aswathy RG et al (2015) Characterization of an exopolysaccharide with potential health-benefit properties from a probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum RJF4. LWT Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.07.040
Fujiike AY, Lee CYAL, Rodrigues FST et al (2022) Anticancer effects of carboxymethylated (1→3)(1→6)-β-d-glucan (botryosphaeran) on multicellular tumor spheroids of MCF-7 cells as a model of breast cancer. J Toxicol Environ Health Part A Curr Issues 85:521–537. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2022.2048153
Gao H, Wen JJ, Hu JL et al (2018) Polysaccharide from fermented Momordica charantia with Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116 ameliorates type 2 diabetes in rats. Carbohydr Polym 201:624–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.08.075
Guo Y, Pan D, Sun Y et al (2013) Antioxidant activity of phosphorylated exopolysaccharide produced by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Carbohydr Polym 97:849–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.06.024
Ismail B, Nampoothiri KM (2010) Production, purification and structural characterization of an exopolysaccharide produced by a probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum MTCC 9510. Arch Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-010-0636-y
Ismail B, Nampoothiri KM (2013) Exposition of antitumour activity of a chemically characterized exopolysaccharide from a probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum MTCC 9510. Biology. https://doi.org/10.1002/zamm.201500180
Jin M, Lu Z, Huang M et al (2011) Sulfated modification and antioxidant activity of exopolysaccahrides produced by Enterobacter cloacae Z0206. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2011.01.023
Jin M, Wang Y, Wang Y et al (2014) Sulphation can enhance the antioxidant activity of polysaccharides produced by Enterobacter cloacae Z0206. Carbohydr Polym 99:624–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.08.072
Li S, Shah NP (2014) Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of sulphated polysaccharides from Pleurotus eryngii and Streptococcus thermophilus ASCC 1275. Food Chem 165:262–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.05.110
Li S, Xiong Q, Lai X et al (2016) Molecular modification of polysaccharides and resulting bioactivities. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 15:237–250. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12161
Liu J, Luo J, Ye H, Zeng X (2012) Preparation, antioxidant and antitumor activities in vitro of different derivatives of levan from endophytic bacterium Paenibacillus polymyxa EJS-3. Food Chem Toxicol 50:767–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2011.11.016
Liu Z, Dong L, Jia K et al (2019) Sulfonation of Lactobacillus plantarum WLPL04 exopolysaccharide amplifies its antioxidant activities in vitro and in a Caco-2 cell model. J Dairy Sci 102:5922–5932. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2018-15831
Lobo RE, Gómez MI, De VGF, Torino MI (2019) Physicochemical and antioxidant properties of a gastroprotective exopolysaccharide produced by Streptococcus thermophilus CRL1190. Food Hydrocoll. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.05.036
Prete R, Alam MK, Perpetuini G et al (2021) Lactic acid bacteria exopolysaccharides producers: a sustainable tool for functional foods. Foods 10:1–27. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071653
Radhakrishnan M, Gopikrishnan V, Vijayalakshmi G, Kumar V (2016) In vitro antioxidant activity and antimicrobial activity against biofilm forming bacteria by the pigment from Desert soil Streptomyces sp D25. J Appl Pharm Sci 6(6):148–150. https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2016.60626
Sasikumar K, Kozhummal Vaikkath D, Devendra L, Nampoothiri KM (2017) An exopolysaccharide (EPS) from a Lactobacillus plantarum BR2 with potential benefits for making functional foods. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.075
Soh H, Kim C, Lee S (2003) A new in vitro assay of cholesterol adsorption by food and microbial polysaccharides. J Food Sci 6:225–230. https://doi.org/10.1089/10966200360716643
Soumya MP, Sasikumar K, Pandey A, Nampoothiri KM (2019) Cassava starch hydrolysate as sustainable carbon source for exopolysaccharide production by Lactobacillus plantarum. Bioresour Technol Rep 6:85–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2019.02.012
Surayot U, Wang J, Seesuriyachan P et al (2014) Exopolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria: structural analysis, molecular weight effect on immunomodulation. Int J Biol Macromol 68:233–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.05.005
Talarico LB, Zibetti RGM, Faria PCS et al (2004) Anti-herpes simplex virus activity of sulfated galactans from the red seaweeds Gymnogongrus griffithsiae and Cryptonemia crenulata. Int J Biol Macromol 34:63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2004.03.002
Tao Y, Zhang L, Cheung PCK (2006) Physicochemical properties and antitumor activities of water-soluble native and sulfated hyperbranched mushroom polysaccharides. Carbohydr Res 341:2261–2269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2006.05.024
Terho TT, Hartiala K (1971) Method for determination of the sulfate content of glycosaminoglycans. Anal Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(71)90167-9
Tsai CC, Lin PP, Hsieh YM et al (2014) Cholesterol-lowering potentials of lactic acid bacteria based on bile-salt hydrolase activity and effect of potent strains on cholesterol metabolism in vitro and in vivo. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/690752
van Casteren W (1998) Characterisation and modification of the exopolysaccharide produced by Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris B40. Carbohydr Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(98)00044-7
Wang J, Zhao X, Yang Y et al (2015a) Characterization and bioactivities of an exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus plantarum YW32. Int J Biol Macromol 74:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.12.006
Wang K, Li W, Rui X et al (2015b) Chemical modification, characterization and bioactivity of a released exopolysaccharide (r-EPS1) from Lactobacillus plantarum 70810. Glycoconj J 32:17–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-014-9567-1
Xie L, Shen M, Hong Y et al (2020) Chemical modifications of polysaccharides and their anti-tumor activities. Carbohydr Polym 229:115436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115436
Xu Y, Wu Y, Sun P et al (2019) Chemically modified polysaccharides: synthesis, characterization, structure activity relationships of action. Int J Biol Macromol 132:970–977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.213
Ye M, Yuan RY, He YL et al (2013) Phosphorylation and anti-tumor activity of exopolysaccharide from Lachnum YM120. Carbohydr Polym 97:690–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.05.033
Yuan H, Zhang W, Li X et al (2005) Preparation and in vitro antioxidant activity of κ-carrageenan oligosaccharides and their oversulfated, acetylated, and phosphorylated derivatives. Carbohydr Res 340:685–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2004.12.026
Zak B, Epstein E (1961) Clin Chim Acta 6:72–78
Zhang J, Cao Y, Wang J et al (2016a) Physicochemical characteristics and bioactivities of the exopolysaccharide and its sulphated polymer from Streptococcus thermophilus GST-6. Carbohydr Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.03.063
Zhang Z, Liu Z, Tao X, Wei H (2016b) Characterization and sulfated modification of an exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus plantarum ZDY2013 and its biological activities. Carbohydr Polym 153:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.07.084
Zheng LP, Zou T, Ma YJ et al (2016) Antioxidant and DNA damage protecting activity of exopolysaccharides from the endophytic bacterium Bacillus Cereus SZ1. Molecules 21:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21020174
Acknowledgements
Research fellowships from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India are greatly appreciated by Soumya MP and acknowledge Academy of Scientific and Innovative Research (AcSIR) Ghaziabad for the enrolment for doctoral program. Corresponding author acknowledges the grant from CSIR under FBR MLP0052. The authors sincerely acknowledge the technical help provided by Mr. Anoop Puthiyamadam and Ms Reeba Parameswaran of the MPTD Division, CSIR NIIST for the characterization and biochemical studies. ACCESSION No.: MN176402.
Funding
The Funding was provided by CSIR New Delhi (Grant nos. MLP0052, SRF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MPS: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal experimental analysis, Investigation and Writing of the original draft manuscript. KMN: Provided general guidance on the content and made the critical reading and editing of the manuscript. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Both authors agreed to the submission of the manuscript to the Journal, and there is no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Soumya, M.P., Nampoothiri, K.M. Evaluation of improved biological properties of chemically modified exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus plantarum BR2. 3 Biotech 13, 308 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03718-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03718-5