Abstract
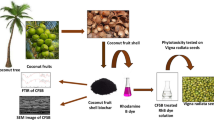
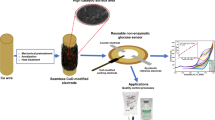
Hexavalent chromium is a toxic heavy metal getting discharged into the environment and water bodies through various industrial processes. Conventional analysis methods call for expensive equipment and complicated sample pretreatment that made unsuitable for onsite detection. Paper is used as an enzyme immobilization platform because of its property to wick the liquid by capillary action; lightweight, cheap and can be easily patterned or cut according to the requirements for developing biosensor. In this study, enzyme immobilization of glucose oxidase (GOx) on filter paper were examined using three polysaccharides such as chitosan, sodium alginate and dextran for entrapment efficiency, activity and stability of the immobilized enzyme. Among the three, chitosan proved efficient for enzyme entrapment with about 90% efficiency at 0.3% (w/v) chitosan. The stability was checked after 1 week at 4 °C and room temperature, where the chitosan entrapped enzyme retained nearly 97% stability at 4 °C. Enzyme inhibition study of GOx and Cr(VI) was carried out using chronoamperometry shown uncompetitive type of inhibition. A paper-based electrochemical biosensor strip was developed by immobilizing GOx enzyme on filter paper using chitosan as an entrapping agent and associating it with a screen-printed carbon electrode for amperometric measurements. The linear range of detection was obtained as 0.05–1 ppm with the limit of detection as 0.05 ppm for Cr(VI), which is the standard permissible limit in potable water. The relative standard deviation (5.6%) indicates good reproducibility of the fabricated biosensor.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amatatongchai M, Sitanurak J, Sroysee W, Sodanat S, Chairam S, Jarujamrus P, Nakapricha D, Lieberzeit PA (2019) Highly sensitive and selective electrochemical paper-based device using a graphite screen-printed electrode modified with molecularly imprinted polymers coated Fe3O4@ Au@ SiO2 for serotonin determination. Anal Chim Acta 1077:255–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.05.047
Amine A, Arduini F, Moscone D, Palleschi G (2016) Recent advances in biosensors based on enzyme inhibition. Biosens Bioelectron 76:180–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.07.010
Attar A, Ghicaa ME, Amine A, Brett CM (2014) Poly (neutral red) based hydrogen peroxide biosensor for chromium determination by inhibition measurements. J Hazard Mater 279:348–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.07.019
Ayenimo JG, Adeloju SB (2016) Rapid amperometric detection of trace metals by inhibition of an ultrathin polypyrrole-based glucose biosensor. Talanta 148:502–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.11.024
Banchhor A, Pandey M, Pandey PK (2017) A review of hexavalent chromium contamination in India. Res J Chem Sci 7:39–44
Bankar SB, Bule MV, Singhal RS, Ananthanarayan L (2009) Glucose oxidase-an overview. Biotechnol Adv 27:489–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.04.003
Bansod B, Kumar T, Thaur R, Rana S, Sing I (2017) A review on various electrochemical techniques for heavy metal ions detection with different sensing platforms. Biosens Bioelectron 94:443–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.03.031
Beppu MM, Vieira RS, Aimoli CG, Santana CC (2007) Crosslinking of chitosan membranes using glutaraldehyde: Effect on ion permeability and water absorption. J Membr Sci 301:126–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2007.06.015
Bezerra CS, de Farias Lemos CMG, de Sousa M, Gonçalves LRB (2015) Enzyme immobilization onto renewable polymeric matrixes: past, present, and future trends. J Appl Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.42125
Biswas P, Karn AK, Balasubramanian P, Kale PG (2017) Biosensors for detection of dissolved chromium in potable water: a review. Biosens Bioelectron 94:589–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.03.043
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Calvo-Perez A, Domínguez-Renedo O, Alonso-Lomillo M, Arcos-Martínez M (2014) Speciation of chromium using chronoamperometric biosensors based on screen-printed electrodes. Anal Chim Acta 833:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2014.05.006
Cao R, Guan L, Li M, Tian J, Shen W (2015) A zero-step functionalization on paper-based biosensing platform for covalent biomolecule immobilization. Sens Biosens Res 6:13–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2015.09.002
Chen C, Xie Q, Wang L, Qin C, Xie F, Yao S, Chen J (2011) Experimental platform to study heavy metal ion-enzyme interactions and amperometric inhibitive assay of Ag+ based on solution state and immobilized glucose oxidase. Anal Chem 83:2660–2666. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac1031435
Cinti S, Mazzaracchio V, Cacciotti I, Moscone D, Arduini F (2017) Carbon black-modified electrodes screen-printed onto paper towel, waxed paper and parafilm M®. Sensors 17:2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102267
Cornish-Bowden A (1974) A simple graphical method for determining the inhibition constants of mixed, uncompetitive and non-competitive inhibitors. Biochem J 137:143. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj1370143
da Silva W, Ghica ME, Brett CM (2020) Biotoxic trace metal ion detection by enzymatic inhibition of a glucose biosensor based on a poly (brilliant green)-deep eutectic solvent/carbon nanotube modified electrode. Talanta 208:120427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120427
DesMarais TL, Costa M (2019) Mechanism of chromium induced toxicity. Curr Opin Toxicol 14:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cotox.2019.05.003
Dhanekar S, Jain S (2013) Porous silicon biosensor: current status. Biosens Bioelectron 41:54–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.09.045
Dungchai W, Chailapakul O, Henry CS (2009) Electrochemical detection for paper-based microfluidics. Anal Chem 81:5821–5826. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac9007573
Dungchai W, Chailapakul O, Henry CS (2011) A low-cost, simple, and rapid fabrication method for paper-based microfluidics using wax screen-printing. Analyst 136:77–82. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0AN00406E
Fenton K, Apblett C, Atanassov P (2008) Rapid electrochemical assay of glucose oxidase activity within electrophoresis gels. In: ECS meeting abstracts 7:202–202. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/https://doi.org/10.1149/MA2009-01/41/1425/meta
Fopase R, Nayak S, Mohanta M, Kale P, Balasubranian P (2019) Inhibition assays of free and immobilized urease for detecting hexavalent chromium in water samples. 3 Biotech 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1661-4
Fopase R, Paramasivam S, Kale P, Balasubramanian P (2020) Strategies, challenges and opportunities of enzyme immobilization on porous silicon for biosensing applications. J Environ Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104266
Ghica EM, Carvalho RC, Amine A, Brett CM (2013) Glucose oxidase enzyme inhibition sensor for heavy metals at carbon film electrodes modified with cobalt or copper hexacyanoferrate. Sens Actuators B 178:270–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.12.113
Gunda NSK, Singh M, Norman L, Kaur K, Mitra SK (2014) Optimization and characterization of biomolecule immobilization on silicon substrates using (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane (APTES) and glutaraldehyde linker. Appl Surf Sci 305:522–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.03.130
Hughes G, Pemberton RM, Nicholas P, Hart JP (2018) Fabrication of miniaturised screen-printed glucose biosensors, using a water-based ink, and the evaluation of their electrochemical behaviour. Electroanalysis 30:1616–1620. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201800104
Juang YJ, Li WS, Chen PS (2017) Fabrication of microfluidic paper-based analytical devices by filtration-assisted screen printing. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 80:71–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.08.007
Karyakin AA, Gitelmatcher OV, Karyakina EE (1995) Prussian blue-based first generation biosensor: a sensitive amperometric electrode for glucose. Anal Chem 67:2419–2423. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00110a016
Kildeeva NR, Perminov PA, Vladimirov LV, Novikov VV, Mikhailov SN (2009) About mechanism of chitosan cross-linking with glutaraldehyde. Russ J Bioorg Chem 35:360–369. https://doi.org/10.1134/S106816200903011X
Krajewska B (2004) Application of chitin-and chitosan-based materials for enzyme immobilizations: a review. Enzyme Microb Technol 35:126–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2003.12.013
Lace A, Ryan D, Bowkett MM, Cleary J (2019) Chromium monitoring in water by colorimetry using optimied 1,5-diphenycarbazide method. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101803
Lasmi K, Derder H, Kermad A, Sam S, Boukhalfa-Abib H, Belhousse S, Tighilt FZ, Hamdani K, Gabouze N (2018) Tyrosinase immobilization on functionalized porous silicon surface for optical monitoring of pyrocatechol. Appl Surf Sci 446:3–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.03.037
Lei CX, Hu SQ, Shen GL, Yu RQ (2003) Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase to a nano-Au monolayer modified chitosan-entrapped carbon paste electrode for the detection of hydrogen peroxide. Talanta 59:981–988. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(02)00641-0
Letant SE, Hart BR, Kane SR, Hadi MZ, Shields SJ, Reynolds JG (2004) Enzyme immobilization on porous silicon surfaces. Adv Mater 16:689–693
Liana DD, Raguse B, Gooding JJ, Chow E (2012) Recent advances in paper-based sensors. Sensors 12:11505–11526. https://doi.org/10.3390/s120911505
Libertino S, Aiello V, Scandurra A, Renis M, Sinatra F (2008) Immobilization of the enzyme glucose oxidase on both bulk and porous SiO2 surfaces. Sensors 8:5637–5648. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8095637
Liu S, Su W, Ding X (2016) A review on microfluidic paper-based analytical devices for glucose detection. Sensors 16:2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16122086
Liu L, Chen C, Chen C, Kang X, Zhang H, Tao Y, Xie Q, Yao S (2019) Poly (noradrenalin) based bi-enzyme biosensor for ultrasensitive multianalyte determination. Talanta 194:343–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.10.055
Lopez-Gallego F, Guisán JM, Betancor L (2013) Glutaraldehyde-mediated protein immobilization. Immobilization of enzymes and cells. Springer, Totowa, pp 33–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-550-7_3
Moretta R, De Stefano L, Terracciano M, Rea I (2021) Porous silicon optical devices: recent advances in biosensing applications. Sensors 21:1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041336
Nayak S, Rangabhashiyam S, Balasubramanian P, Kale P (2020a) A review of chromite mining in Sukinda Valley of India: impact and potential remediation measures. Int J Phytorem. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2020.1717432
Nayak S, Kale P, Balasubramanian P (2020b) Inhibition assays of horseradish peroxidase by hexavalent chromium and other heavy metals. Int J Environ Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1776864
Nery EW, Kubota LT (2016) Evaluation of enzyme immobilization methods for paper-based devices-a glucose oxidase study. J Pharm Biomed Anal 117:551–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2015.08.041
Noiphung J, Songjaroen T, Dungchai W, Henry CS, Chailapakul O, Laiwattanapaisal W (2013) Electrochemical detection of glucose from whole blood using paper-based microfluidic devices. Anal Chim Acta 788:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.06.021
Osorio-Gonzalez CS, Hegde K, Brar SK, Delgado-Cano B, Gomez-Falcon N, Avalos-Ramirez A (2019) Advancesin protein/enzyme-based biosensors for detection of metal contaminants in the environment. Tools, techniques and protocols for monitoring environmental contaminants. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 245–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814679-8.00012-1
Prabhakaran DC, Ramamurthy PC, Sivry Y, Subramian S (2020) Electrochemical detection of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) ions present in aqueous solutions using bio-modified carbon paste electrode: a voltammetric study. Int J Environ Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2015.08.041
Rodrigues RC, Virgen-Ortiz JJ, Dos Santos JC, Berenguer-Murcia A, Alcantara AR, Barbosa O, Ortiz C, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2019) Immobilization of lipases on hydrophobic supports: immobilization mechanism, advantages, problems, and solutions. Biotechnol Adv 37:746–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.04.003
Sekar NC, Shaegh SAM, Ng SH, Ge L, Tan SN (2014) A paper-based amperometric glucose biosensor developed with Prussian Blue-modified screen-printed electrodes. Sens Actuators B Chem 204:414–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.07.103
Shuler ML, Kargi F (2002) Bioprocess Engineering: Basic Concepts, 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall of India pvt ltd, New Delhi, pp 79–91
Song JH, Sailor MJ (1999) Chemical modification of crystalline porous silicon surfaces. Comments Inorg Chem 21:69–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/02603599908020416
WHO (1998) Guidelines for drinking-water quality. Heal Criteria Other Support Inf 2(1930128):1–283
Wilbur SB, Abdin H, Fay M, Yu D, Tencza B, Ingerman L,Klotzbach J, James S (2012) Toxicological profile for chromium. US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24049864
Wilson R, Turner APF (1992) Glucose oxidase: an ideal enzyme. Biosens Bioelectr 7:165–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-5663(92)87013-F
Yang Y, Noviana E, Nguyen MP, Geiss BJ, Dandy DS, Henry CS (2017) Based microfluidic devices: emerging themes and applications. Anal Chem 89:71–91. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04581
Yang Y, Fang Z, Yu YY, Wang YZ, Naraginti S, Yong YC (2019) A mediator-free whole-cell electrochemical biosensing system for sensitive assessment of heavy metal toxicity in water. Water Sci Technol 79:1071–1080. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2019.101
Zeng GM, Tang L, Shen GL, Huang GH, Niu CG (2004) Determination of trace chromium (VI) by an inhibition-based enzyme biosensor incorporating an electropolymerized aniline membrane and ferrocene as electron transfer mediator. Int J Environ Anal Chem 84:761–774. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067310410001730619
Zhang Q, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2006) Glucose microfluidic biosensors based on immobilizing glucose oxidase in poly (dimethylsiloxane) electrophoretic microchips. J Chromatogr A 1135:122–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.09.052
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Department of Biotechnology and Medical Engineering of National Institute of Technology Rourkela for providing the research facility. The authors greatly acknowledge the Ministry of Human Resources Development (MHRD) of the Government of India (GoI) for sponsoring the Master’s programme of the first author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AD: conception and design, data curation, writing- original draft preparation, final approval of the article; SJ: supervision, methodology, writing- reviewing and editing; BP: conceptualization, supervision, writing- reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dabhade, A., Jayaraman, S. & Paramasivan, B. Development of glucose oxidase-chitosan immobilized paper biosensor using screen-printed electrode for amperometric detection of Cr(VI) in water. 3 Biotech 11, 183 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02736-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02736-5