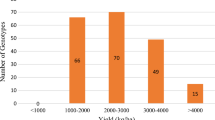
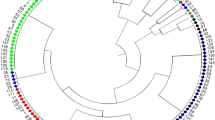
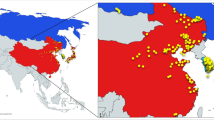
Abstract
Genetic diversity is the foundation for any breeding program. The present study analyzed the genetic base of 163 soybean genotypes from three continents viz. Africa, America and Asia using 68 trait-linked simple sequence repeats (SSR) markers. The average number of alleles among the germplasm from the three continents followed the trend as Asia (9) > America (8) > Africa (7). Similar trends were observed for gene diversity (0.76 > 0.74 > 0.71) and polymorphism information content (PIC) (0.73 > 0.71 > 0.68). These findings revealed that soybean germplasm from Asia has wider genetic base followed by America, and least in Africa. The 163 genotypes were grouped into 4 clusters by phylogenetic analysis, whereas model-based population structure analysis also divided them into 4 subpopulations comprising 80.61% pure lines and 19.39% admixtures. The genotypes from Africa were easily distinguished from those of other two continents using phylogenetic analysis, indicating important role of geographyical differentiation for this genetic variability. Our results indicated that soybean germplasm has moved from Asia to America, and from America to Africa. Analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) showed 8.41% variation among the four subpopulations, whereas 63.12% and 28.47% variation existed among and within individuals in the four subpopulations, respectively. Based on the association mapping, a total of 21 SSR markers showed significant association with days to flowering (DoF) and 100-seed weight (HSW). Two markers Satt365 and Satt581 on chromosome 6 and 10, respectively, showed pleiotropic effect or linkage on both traits. Genotype A50 (Gakuran Daizu/PI 506679) from Japan has 8 out of the 13 beneficial alleles for increased HSW. The diverse genotypes, polymorphic SSR markers and desirable alleles identified for DoF and HSW will be used in future breeding programs to improve reproductive, yield and quality traits.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe J, Xu DH, Suzuki Y, Kanazawa A, Shimamoto Y (2003) Soybean germplasm pools in Asia revealed by nuclear SSRs. Theor Appl Genet 106(3):445–453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-1073-3
Belalia N, Lupini A, Djemel A, Morsli A, Mauceri A, Lotti C, Khelifi-Slaoui M, Khelifi L, Sunseri F (2019) Analysis of genetic diversity and population structure in Saharan maize (Zea mays L.) populations using phenotypic traits and SSR markers. Genet Res Crop Evol 66(1):243–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-018-0709-3
Bisen A, Khare D, Nair P, Tripathi N (2015) SSR analysis of 38 genotypes of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) genetic diversity in India. Phys Mol Biol Plants 21(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-014-0269-8
Bradbury P, Zhang Z, Kroon D, Casstevens TY, Buckler E (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23(19):2633–2635. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm308
Bruce RW, Torkamaneh D, Grainger C, Belzile F, Eskandari M, Rajcan I (2019) Genome-wide genetic diversity is maintained through decades of soybean breeding in Canada. Theor Appl Genet. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03408-y
Carter TE, Nelson RL, Sneller CH, Cui Z (2004) Genetic diversity in soybean. In: Boerma HR, Specht JE (eds) Soybeans: improvement, production, and uses. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 303–416
Chaudhary J, Shivaraj S, Khatri P, Ye H, Zhou L, Klepadlo M, Dhakate P, Kumawat G, Patil G, Sonah H (2019) Approaches, applicability, and challenges for development of climate-smart soybean. Genomic designing of climate-smart oilseed crops. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93536-2_1
Chauhan DK, Bhat JA, Thakur AK, Hussain Z, Satyavathi CT (2017) Understanding genetic relationship and population structure of Indian soybean varieties using microsatellite markers. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B Biol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-017-0847-y
Chen Q, Zhang Z, Liu C, Xin D, Qiu H, Shan D, Shan C, Hu G (2007) QTL analysis of major agronomic traits in soybean. Agric Sci China 6(4):399–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1671-2927(07)60062-5
Chen X, Min D, Yasir TA, Hu Y-G (2012) Genetic diversity, population structure and linkage disequilibrium in elite Chinese winter wheat investigated with SSR markers. PLoS ONE 7(9):e44510. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0044510
Chigeza G, Boahen S, Gedil M, Agoyi E, Mushoriwa H, Denwar N, Gondwe T, Tesfaye A, Kamara A, Chikoye OEAD (2019) Public sector soybean (Glycine max) breeding: advances in cultivar development in the African tropics. Plant Breed. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12682
Chotiyarnwong O, Chatwachirawong P, Chanprame S, Srinives P (2007) Evaluation of genetic diversity in Thai indigenous and recommended soybean varieties by SSR markers. Thai J Agric Sci 40(3–4):119–126
Chung G, Singh RJ (2008) Broadening the genetic base of soybean: a multidisciplinary approach. Crit Rev Plant Sci 27(5):295–341. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352680802333904
Cober ER, Morrison MJ (2010) Regulation of seed yield and agronomic characters by photoperiod sensitivity and growth habit genes in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 120(5):1005. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1228-6
Collard BC, Mackill DJ (2007) Marker-assisted selection: an approach for precision plant breeding in the twenty-first century. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 363(1491):557–572. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2007.2170
Concibido V, Vallee BL, Mclaird P, Pineda N, Meyer J, Hummel L, Yang J, Wu K, Delannay X (2003) Introgression of a quantitative trait locus for yield from Glycine soja into commercial soybean cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 106(4):575–582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-1071-5
Cook DE, Lee TG, Guo X, Melito S, Wang K, Bayless AM, Wang J, Hughes TJ, Willis DK, Clemente TE (2012) Copy number variation of multiple genes at Rhg1 mediates nematode resistance in soybean. Science 338(6111):1206–1209. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1228746
Csanadi G, Vollmann J, Stift G, Lelley T (2001) Seed quality QTLs identified in a molecular map of early maturing soybean. Theor Appl Genet 103(6–7):912–919
Deng W, Wang Y, Liu Z, Cheng H, Xue Y (2014) HemI: a toolkit for illustrating heatmaps. PLoS ONE 9(11):e111988
Denwar NN, Awuku FJ, Diers B, Frimpomaah FA, Chigeza G, Oteng-Frimpong F, Puozaa DK, Barnor MT (2019) Genetic diversity, population structure and key phenotypic traits driving variation within soyabean (Glycine max) collection in Ghana. Plant Breed 00:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12700
Earl DA, Vonholdt BM (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Cons Gen Res 4(2):359–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-011-9548-7
Excoffier L, Lischer H (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol Eco Res 10(3):564–567. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2010.02847.x
Falush D, Matthew S, Pritchard JK (2003) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 164(4):1567–1587. https://doi.org/10.3410/f.1015548.197423
Fehr W, Caviness C, Burmood D, Pennington J (1971) Stage of development descriptions for soybeans, Glycine max (L.) Merrill 1. Crop Sci 11(6):929–931. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1971.0011183X001100060051x
Gai JY, Xiong DJ, Zhao TJ (2015) The pedigrees and germplasm bases of soybean cultivars released in China (1923–2005). China Agricultural Press, Beijing
Gizlice Z, Carter T Jr, Burton J (1994) Genetic base for north American public soybean cultivars released between 1947 and 1988. Crop Sci 34(5):1143–1151. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1994.0011183X003400050001x
Griggs D, Staffordsmith M, Gaffney O, Rockström J, Ohman MC, Shyamsundar P, Steffen W, Glaser G, Kanie N, Noble I (2013) Policy: sustainable development goals for people and planet. Nature 495(7441):305–307. https://doi.org/10.1038/495305a
Guan R, Chang R, Li Y, Wang L, Liu Z, Qiu L (2010) Genetic diversity comparison between Chinese and Japanese soybeans (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) revealed by nuclear SSRs. Gen Res Crop Evol 57(2):229–242
Hao D, Cheng H, Yin Z, Cui S, Zhang D, Wang H, Yu D (2012) Identification of single nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotypes associated with yield and yield components in soybean (Glycine max) landraces across multiple environments. Theor Appl Genet 124(3):447–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1719-0
Hirota T, Sayama T, Yamasaki M, Sasama H, Sugimoto T, Ishimoto M, Yoshida S (2012) Diversity and population structure of black soybean landraces originating from Tanba and neighboring regions. Breed Sci 61(5):593. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.61.593
Hu Z, Zhang D, Zhang G, Kan G, Hong D, Yu D (2014) Association mapping of yield-related traits and SSR markers in wild soybean (Glycine soja Sieb. and Zucc.). Breed Sci 63(5):441. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.63.441
Hua X, Guan R, Chang R, Qiu L (2005) Genetic diversity of Chinese summer soybean germplasm revealed by SSR markers. Chin Sci Bull 50(6):526–535
Hyten DL, Song Q, Zhu Y, Choi I-Y, Nelson RL, Costa JM, Specht JE, Shoemaker RC, Cregan PB (2006) Impacts of genetic bottlenecks on soybean genome diversity. Proc Nat Acad Sci 103(45):16666–16671. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0604379103
Jun T, Kyujung V, Moonyoung K, Sukha L, Davidr W (2008) Association analysis using SSR markers to find QTL for seed protein content in soybean. Euphytica 162(2):179–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9491-6
Kofsky J, Zhang H, Song BH (2018) The untapped genetic reservoir: the past, current, and future applications of the wild soybean (Glycine soja). Front Plant Sci 9:949. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00949
Kumawat G, Singh G, Gireesh C, Shivakumar M, Arya M, Agarwal DK, Husain SM (2015) Molecular characterization and genetic diversity analysis of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) germplasm accessions in India. Phy Mol Biol Plants 21(1):101–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-014-0266-y
Lam H-M, Xu X, Liu X, Chen W, Yang G, Wong F-L, Li M-W, He W, Qin N, Wang B (2010) Resequencing of 31 wild and cultivated soybean genomes identifies patterns of genetic diversity and selection. Nat Genet 42(12):1053. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.715
Lee G-A, Crawford GW, Li L, Yuka S, Xuexiang C (2011) Archaeological soybean (Glycine max) in East Asia: does size matter? PLoS ONE 6(11):e26720. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0026720
Li YH, Wei ZC, Yang L, Chang RZ, Gaut BS, Qiu LJ (2010) Genetic diversity in domesticated soybean (Glycine max) and its wild progenitor (Glycine soja) for simple sequence repeat and single-nucleotide polymorphism loci. New Phytol 188(1):242–253. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03344.x
Li G, Ra WH, Park JW, Kwon SW, Lee JH, Park CB, Park YJ (2011) Developing EST-SSR markers to study molecular diversity in Liriope and Ophiopogon. Bioch Syst Eco 39(4–6):241–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2011.08.012
Li Y-H, Shan-Cen Z, Jian-Xin M, Dong L, Long Y, Jun L, Xiao-Tian Q, Xiao-Sen G, Le Z, Wei-Ming H (2013) Molecular footprints of domestication and improvement in soybean revealed by whole genome re-sequencing. BMC Genom 14(1):579. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-579
Li J, Zhao J, Li Y, Gao Y, Hua S, Nadeem M, Sun G, Zhang W, Hou J, Wang X (2019) Identification of a novel seed size associated locus SW9-1 in soybean. Crop J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2018.12.010
Lihua CYD (1982) The Principle of high-yielding soybean and its culture technique. Acta Agronom Sin 1:006
Liu K, Muse SV (2005) PowerMarker: an integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 21(9):2128–2129. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti282
Liu X, Jin J, Wang G, Herbert S (2008) Soybean yield physiology and development of high-yielding practices in Northeast China. Field Crops Res 105(3):157–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2007.09.003
Liu Z, Li H, Wen Z, Fan X, Li Y, Guan R, Guo Y, Wang S, Wang D, Qiu L (2017) Comparison of genetic diversity between Chinese and American Soybean (Glycine max (L.)) accessions revealed by high-density SNPs. Front Plant Sci 8:2014–2014. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.02014
Mao T, Li J, Wen Z, Wu T, Wu C, Shi S, Jiang B, Hou W, Li W, Song Q (2017) Association mapping of loci controlling genetic and environmental interaction of soybean flowering time under various photo-thermal conditions. BMC Genom 18(1):415. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-3778-3
Miladinovi J, Svetlana BET, Kristina P, Dragana M (2018) Allelic variation and distribution of the major maturity genes in different soybean collections. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01286
Miranda C, Culp C, Škrabišová M, Joshi T, Belzile F, Grant DM, Bilyeu K (2019) Molecular tools for detecting Pdh1 can improve soybean breeding efficiency by reducing yield losses due to pod shatter. Mol Breed 39(2):27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-019-0935-1
Molnar S, Rai S, Charette MERC (2003) Simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers linked to E1, E3, E4 and E7 maturity genes in soybean. Genome 46(6):1024–1036. https://doi.org/10.1139/g03-079
Nei M (1972) Genetic distance between populations. Am Nat 106(949):283–292
Panthee DR, Pantalone VR, West DR, Saxton AM, Sams CE (2005) Quantitative trait loci for seed protein and oil concentration, and seed size in soybean. Crop Sci 45(5):2015–2022. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2004.0720
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2012) GenAlEx 6.5: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—an update. Bioinformatics 28(28):2537–2539. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts460
Powell W, Machray GC, Provan J (1996) Polymorphism revealed by simple sequence repeats. Trends Plant Sci 1(7):215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/1360-1385(96)86898-1
Prevost A, Wilkinson M (1999) A new system of comparing PCR primers applied to ISSR fingerprinting of potato cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 98(1):107–112
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155(2):945–959
Rodrigues JIDS, Arruda KMA, Cruz CD, Piovesan ND, Barros EGD, Moreira MA (2013) Association of microsatellite markers with contents of oil and protein in soybean. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasil 48(3):255–262
Roldán-Ruiz I, Van Euwijk F, Gilliland T, Dubreuil P, Dillmann C, Lallemand J, De Loose M, Baril C (2001) A comparative study of molecular and morphological methods of describing relationships between perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) varieties. Theor Appl Genet 103(8):1138–1150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220100571
Salgotra RK, Gupta BB, Bhat JA, Sharma S (2015) Genetic diversity and population structure of basmati rice (Oryza sativa L.) germplasm collected from north western himalayas using trait linked SSR markers. PLoS ONE 10(7):e0131858. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0131858
Shi A, Chen P, Zhang B, Hou A (2010) Genetic diversity and association analysis of protein and oil content in food-grade soybeans from Asia and the United States. Plant Breed 129(3):250–256. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.2010.01766.x
Sinclair TR, Marrou H, Soltani A, Vadez V, Chandolu KC (2014) Soybean production potential in Africa. Glob Food Secur 3(1):31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gfs.2013.12.001
Singh N, Choudhury DR, Tiwari G, Singh AK, Kumar S, Srinivasan K, Tyagi RK, Sharma AD, Singh NK, Singh R (2016) Genetic diversity trend in Indian rice varieties: an analysis using SSR markers. BMC Genet 17(1):127. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-016-0437-7
Song QJ, Marek LF, Shoemaker RC, Lark KG, Concibido VC, Delannay X, Specht JE, Cregan PB (2004) A new integrated genetic linkage map of the soybean. Theor Appl Genet 109(1):122–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1602-3
Swamy AA, Reddy G (2004) Genetic divergence and heterosis studies in mungbean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek). Legume Res Int J 27(2):115–118
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Bio Evol 30(12):2725–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Tantasawat P, Trongchuen J, Prajongjai T, Jenweerawat S (2011) SSR analysis of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) genetic relationship and variety identification in Thailand. Aust J Crop Sci 5(3):280–287. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2010.0325
Tefera H, Kamara AY, Asafo-Adjei B, Dashiell KE (2010) Breeding progress for grain yield and associated traits in medium and late maturing promiscuous soybeans in Nigeria. Euphytica 175(2):251–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-010-0181-4
Tsubokura Y, Watanabe S, Xia Z, Kanamori H, Yamagata H, Kaga A, Katayose Y, Abe J, Ishimoto M, Harada K (2014) Natural variation in the genes responsible for maturity loci E1, E2, E3 and E4 in soybean. Ann Bot 113(3):429–441. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mct269
Upadhyay P, Neeraja CN, Kole C, Singh VK (2012) Population structure and genetic diversity in popular rice varieties of India as evidenced from SSR analysis. Biochem Genet 50(9–10):770–783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-012-9519-z
Wang L, Guan R, Zhangxiong L, Chang R, Qiu L (2006) Genetic diversity of Chinese cultivated soybean revealed by SSR markers. Crop Sci 46(3):1032–1038. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2005.0051
Watanabe S, Rumiko H, Zhengjun X, Yasutaka T, Shusei S, Yumi N, Naoki Y, Ryoji T, Masao I, Toyoaki A (2009) Map-based cloning of the gene associated with the soybean maturity locus E3. Genetics 182(4):1251–1262. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.108.098772
Watanabe S, Zhengjun X, Rumiko H, Yasutaka T, Shusei S, Naoki Y, Ryoji T, Toyoaki A, Satoshi T, Keisuke K (2011) A map-based cloning strategy employing a residual heterozygous line reveals that the GIGANTEA gene is involved in soybean maturity and flowering. Genetics 188(2):395–407. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.110.125062
Wilson RF (2008) Soybean: market driven research needs. In: Stacey G (ed) Genetics and genomics of soybean. Springer, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-72299-3_1
Wilson RF (2015) Designing soybeans for 21st century markets. Elsevier, New York
Xia Z, Watanabe S, Tetsuya Y, Yasutaka T, Hiroko N, Hong Z, Toyoaki A, Shusei S, Toshimasa Y, Shixiang L (2012) Positional cloning and characterization reveal the molecular basis for soybean maturity locus E1 that regulates photoperiodic flowering. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(32):E2155. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1117982109
Xiong H, Shi A, Mou B, Qin J, Motes D, Lu W, Ma J, Weng Y, Yang W, Wu D (2016) Genetic diversity and population structure of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp). PLoS ONE 11(8):e0160941. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160941
Yamanaka N, Sato H, Yang Z, Xu DH, Catelli LL, Binneck E, Abdelnoor RV (2007) Genetic relationships between Chinese, Japanese, and Brazilian soybean gene pools revealed by simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Genet Mol Biol 30(1):85–88
Yu J, Gael P, Briggs WH, Irie VB, Masanori Y, Doebley JF, Mcmullen MD, Gaut BS, Nielsen DM, Holland JB (2006) A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet 38(2):203–208. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1702
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFD0100201), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 31571691 and 31871646), the MOE Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (PCSIRT_17R55), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (KYT201801), the Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center for Modern Crop Production (JCIC-MCP) Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TZ conceived and designed the experiments. NND provided some germplasm from Africa. BK performed the experiments, analyzed data and drafted the manuscript. TZ and JAB revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karikari, B., Bhat, J.A., Denwar, N.N. et al. Exploring the genetic base of the soybean germplasm from Africa, America and Asia as well as mining of beneficial allele for flowering and seed weight. 3 Biotech 10, 195 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02186-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02186-5