Abstract
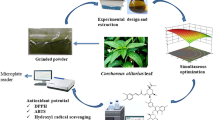
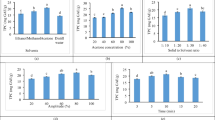
In this study, phenolic compounds were extracted from Argel leaves using an ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) method. The extraction parameters (sonication temperature, time, and ethanol concentration) were optimized using a response surface methodology (Box-Behnken design), in order to maximize the total phenolic content (TPC) and 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) scavenging activity of Argel leaf extracts (ALEs). The phenolic compounds of the ALEs obtained under optimized conditions were also identified. The optimum UAE conditions for achieving maximum TPC (72.27 g gallic acid equivalents kg−1 DW) and DPPH scavenging activity (86.15%) were a 60 °C temperature, a 37.07 min duration, and a 39.14% ethanol concentration. Under these conditions, the experimental values of TPC and DPPH scavenging activity were 73.02 g GAE kg−1 and 85.56%, respectively, which agreed with the predicted values. In addition, the major phenolic acids found in ALEs under the optimized extraction conditions were sinapic, p-coumaric, and ferulic acid. Overall, the findings of this study demonstrated the suitability of UAE and the success of RSM in optimizing the extraction conditions of bioactive compounds from ALEs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali A, Lim XY, Chong CH, Mah SH, Chua BL (2018) Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of natural antioxidants from Piper betle using response surface methodology. LWT Food Sci Technol 89:681–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.11.033
Al-Jaber NA, Awaad AS, Moses JE (2011) Review on some antioxidant plants growing in Arab world. J Saudi Chem Soc 15:293–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2011.07.004
Al-Juhaimi F, Adiamo OQ, Ghafoor K, Babiker EE (2016) Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) seed. CyTA-J Food 14:369–374. https://doi.org/10.1080/19476337.2015.1110202
Al-Juhaimi FY, Shahzad SA, Ahmed AS, Adiamo OQ, Mohamed Ahmed IA, Alsawmahi ON, Ghafoor K, Babiker EE (2018a) Effect of Argel (Solenostemma argel) leaf extract on quality attributes of chicken meatballs during cold storage. J Food Sci Technol 55:1797–1805. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3094-1
Al-Juhaimi FY, Mohamed Ahmed IA, Adiamo OQ, Adisa AR, Ghafoor K, Ozcan MM, Babiker EE (2018b) Effect of Argel (Solenostemma argel) leaf powder on the quality attributes of camel patties during cold storage. J Food Process Preserv 42:e13496. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.13496
Amariei D, Stanescu U, Gille E, Onisei T (1991) The biosynthetic capacity of the active principles of in vitro regenerated Solenostemma argel (SEL) Hayne, callus and shoots. Revue Roumaine de Biologie, Serie de Biologie Vegetale 38:71
Awad AI, Eltayeb IB, Capps PA (2006) Self-medication practices in Khartoum state. Sudan Eur J Clin Pharmacol 62:317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-006-0107-1
Ballesteros LF, Ramirez MJ, Orrego CE, Teixeira JA, Mussatto SI (2017) Optimization of autohydrolysis conditions to extract antioxidant phenolic compounds from spent coffee grounds. J Food Eng 199:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2016.11.014
Bhattacharya D, Bhattacharya S, Patra MM, Chakravorty S, Sarkar S, Chakraborty W, Koley H, Gachhui R (2016) Antibacterial activity of polyphenolic fraction of kombucha against enteric bacterial pathogens. Curr Microbiol 73:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-016-1136-3
Boulous L (2000) Flora of Egypt, vol 2. Al Hadara Publishing, Egypt
Carciochi RA, Manrique GD, Dimitrov K (2015) Optimization of antioxidant phenolic compounds extraction from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) seeds. J Food Sci Technol 52:4396–4404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1514-4
Cho Y-J, Hong J-Y, Chun HS, Lee SK, Min H-Y (2006) Ultrasonication-assisted extraction of resveratrol from grapes. J Food Eng 77:725–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2005.06.076
Corrales M, García AF, Butz P, Tauscher B (2009) Extraction of anthocyanins from grape skins assisted by high hydrostatic pressure. J Food Eng 90:415–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2008.07.003
El-shiekh RA, Al-Mahdy DA, Mouneir SM, Hifnawy MS, Abdel-Sattar EA (2019) Anti-obesity effect of Argel (Solenostemma argel) on obese rats fed a high fat diet. J Ethnopharmacol 238:111893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2019.111893
Ghafoor K (2015) Optimized extraction of phenolic compounds from barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) seed and their radical scavenging properties. J Food Proc Pres 39:793–799. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.12289
Ghafoor K, Choi YH, Jeon JY, Jo IH (2009) Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds, antioxidants, and anthocyanins from grape (Vitis vinifera) seeds. J Agric Food Chem 57:4988–4994. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9001439
Ghafoor K, Hui T, Choi YH (2011) Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of total anthocyanins from grape peel using response surface methodology. J Food Biochem 35:735–746. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4514.2010.00413.x
Hassan HA, Hamed AI, El-Emary NA, Springuel IV, Mitome H, Miyaoka H (2001) Pregnene derivatives from Solenostemma argel leaves. Phytochemistry 57:507–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(01)00121-2
Jayaprakasha G, Selvi T, Sakariah K (2003) Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of grape (Vitis vinifera) seed extracts. Food Res Int 36:117–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0963-9969(02)00116-3
Kamel M (2003) Acylated phenolic glycosides from Solenostemma argel. Phytochemistry 62:1247–1250. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(03)00022-0
Lapornik B, Prošek M, Wondra AG (2005) Comparison of extracts prepared from plant by-products using different solvents and extraction time. J Food Eng 71:214–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2004.10.036
Meyer AS, Yi O-S, Pearson DA, Waterhouse AL, Frankel EN (1997) Inhibition of human low-density lipoprotein oxidation in relation to composition of phenolic antioxidants in grapes (Vitis vinifera). J Agric Food Chem 45:1638–1643. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf960721a
Muddathir AM, Yamauchi K, Batubara I, Mohieldin EAM, Mitsunaga T (2017) Anti-tyrosinase, total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of selected Sudanese medicinal plants. South Afr J Bot 109:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2016.12.013
Ounaissia K, Pertuit D, Mitaine-Offer A-C, Miyamoto T, Tanaka C, Delemasure S, Dutartre P, Smati D, Lacaille-Dubois M-A (2016) New pregnane and phenolic glycosides from Solenostemma argel. Fitoterapia 114:98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2016.08.002
Rostagno MA, Palma M, Barroso CG (2003) Ultrasound-assisted extraction of soy isoflavones. J Chromatogr A 1012:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(03)01184-1
Santos GA, Vila MM, Chaud MV, Silva WL, de Castro AG, de Oliveira Jr JM, Tubino M, Balcao VM (2016) Antimicrobial and antioxidant screening of curcumin and pyrocatechol in the prevention of biodiesel degradation: oxidative stability. Biofuels 7:581–592. https://doi.org/10.1080/17597269.2016.1168023
Spigno G, Tramelli L, De Faveri DM (2007) Effects of extraction time, temperature and solvent on concentration and antioxidant activity of grape marc phenolics. J Food Eng 81:200–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2006.10.021
Teng H, Ghafoor K, Choi YH (2009) Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of active components from Chinese quince using response surface methodology. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 52:694–701. https://doi.org/10.3839/jksabc.2009.115
Toma M, Vinatoru M, Paniwnyk L, Mason TJ (2001) Investigation of the effects of ultrasound on vegetal tissues during solvent extraction. Ultrasonics Sonochem 8:137–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1350-4177(00)00033-X
Vilkhu K, Mawson R, Simons L, Bates D (2008) Applications and opportunities for ultrasound assisted extraction in the food industry—a review. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 9:161–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2007.04.014
Vinatoru M, Toma M, Radu O, Filip P, Lazurca D, Mason T (1997) The use of ultrasound for the extraction of bioactive principles from plant materials. Ultrasonics Sonochem 4:135–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1350-4177(97)83207-5
Wang L, Weller CL (2006) Recent advances in extraction of nutraceuticals from plants. Trends Food Sci Technol 17:300–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2005.12.004
Wang J, Sun B, Cao Y, Tian Y, Li X (2008) Optimisation of ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from wheat bran. Food Chem 106:804–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.06.062
Yilmaz Y, Toledo RT (2004) Health aspects of functional grape seed constituents. Trends Food Sci Technol 15:422–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2004.04.006
Yilmaz Y, Toledo RT (2006) Oxygen radical absorbance capacities of grape/wine industry byproducts and effect of solvent type on extraction of grape seed polyphenols. J Food Comp Anal 19:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2004.10.009
Živković J, Šavikin K, Janković T, Ćujić N, Menković N (2018) Optimization of ultrasound assisted extraction of polyphenolic compounds from pomegranate peel using response surface methodology. Sep Puri Technol 194:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.11.032
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding this work through research group number RG‐1439‐080. We thank Professor Alan Carne (Department of Biochemistry, University of Otago, New Zealand), Professor Abu ElGasim A Yagoub (Department of Food Science and Nutrition, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia), and RSSU (Deanship of Scientific Research, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia) for the assistance in proof reading and English editing of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamed Ahmed, I.A., Al-Juhaimi, F., Adisa, A.R. et al. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity from Argel (Solenostemma argel Hayne) leaves using response surface methodology (RSM). J Food Sci Technol 57, 3071–3080 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04340-6
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04340-6