Abstract
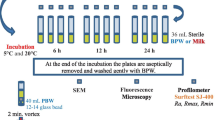
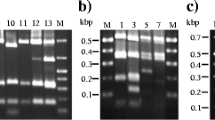
Pseudomonas fluorescens can often be isolated from refrigerated raw milk. Two strains of P. fluorescens PL5.4 and PL7.1, isolated from raw buffalo milk, were evaluated for their proteolytic capacity, exopolysaccharide production and biofilm production. Proteolytic activity was observed in both strains. The P. fluorescens PL5.4 strain presented fluorescence in the presence of calcofluor, indicating exopolysaccharide production. Both strains were able to produce biofilm at 7 °C for 72 h. For the biofilm production test on stainless steel, adherent cell counts of up to 7.1, 7.3 and 8.8 log CFU/cm2 at 7, 23 and 30 °C were obtained. Through scanning electron microscopy, it was possible to observe the biofilm produced by the P. fluorescens PL5.4 strain. Proper cleaning and disinfection practices in order are important to reduce bacterial contamination and extend the useful life of raw material and its derivatives.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alhede M, Qvortrup K, Liebrechts R, Høiby N, Michael Givskov M, Bjarnsholt T (2012) Combination of microscopic techniques reveals a comprehensive visual impression of biofilm structure and composition. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 65:335–342
Al-Shabib NA, Husain FM, Ahmed F, Khan RA, Khan MS, Ansari FA, Alam MZ, Ahmed MA, Khan MS, Mohammad Hassan Baig MH, Khan JM, Shahzad SA, Arshad M, Abdullah Alyousef A, Ahmad I (2018) Low temperature synthesis of superparamagnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles and their ROS mediated inhibition of biofilm formed by food-associated bacteria. Front Microbiol 9:2567–2576
Arslan S, Eyi A, Özdemir F (2011) Spoilage potentials and antimicrobial resistance of Pseudomonas spp. isolated from cheeses. J Dairy Sci 94:5851–5856
Baum MM, Kainović A, O’Keeffe T, Pandita R, McDonald K, Wu S, Webster P (2009) Characterization of structures in biofilms formed by a Pseudomonas fluorescens isolated from soil. BMC Microbiol 9:103. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-9-103
Bernardes O (2014) Desafios na produção de leite de búfalas. Anais I Simpósio Brasileiro de Ruminantes Leiteiros (UDILEITE)—Univ. Federal de Uberlândia/FAMEV 33-72
Boari CA, Alves MP, Tebaldi VMR, Savian TV, Piccoli RH (2009) Biofilm formation by Aeromonas hydrophila and Staphylococcus aureus on stainless steel using milk and different conditions of cultivation. Food Sci Technol 29:886–895
Castro MR, Fernandes MS, Kakubi DY, Kuaye AY (2017) Biofilm formation on stainless steel as a function of time and temperature and control through sanitizers. Int Dairy J 68:9–16
Cleto S, Matos S, Kluskens L, Vieira MJ (2012) Characterization of contaminants from a sanitized milk processing plant. PLoS ONE 7:1–8
De Jonghe V, Coorevits A, Van Hoorde K, Messens W, Van Landschoot A, De Vos P, Heyndrickx M (2011) Influence of storage conditions on the growth of Pseudomonas species in refrigerated raw milk. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:460–470
Goldbeck JC, Victoria FN, Motta AS, Savegnago L, Jacob RG, Perin G, Lenardão EJ, Padilha da Silva W (2014) Bioactivity and morphological changes of bacterial cells after exposure to 3-(pchlorophenyl) thio citronellal. LWT Food Sci Technol 59:813–819
Hrubanova K, Vladislav Krzyzanek V, Nebesarova J, Ruzicka F, Pilat Z, Ota Samek O (2018) Monitoring Candida parapsilosis and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms by a combination of scanning electron microscopy and raman spectroscopy. Sensors 18:4089–4107
Kives J, Orgaz GB, Rivera-Sen A, Varquez J, Jose San (2005) Interactions in biofilms of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris and Pseudomonas fluorescens cultured in cold UHT milk. J Dairy Sci 88:4165–4171
Koo H, Falsetta ML, Klein MI (2013) The exopolysaccharide matrix. J Den Res 92:1065–1073
Lin H, Shavezipur M, Yousef A, Maleky F (2016) Prediction of growth of Pseudomonas fluorescens in milk during storage under fluctuating temperature. J Dairy Sci 99:1822–1830
Marchand S, De Block J, De Jonghe V, Coorevits A, Heyndrickx M, Herman L (2012) Biofilm formation in milk production and processing environments; influence on milk quality and safety. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 11:133–147
Martins ML, Pinto UM, Riedel K, Vanetti MCD, Mantovani HC, Araújo EF (2014) Lack of AHL-based quorum sensing in Pseudomonas fluorescens isolated from milk. Braz J Microbiol 45:1039–1046
Martins ML, Pinto UM, Riedel K, Vanetti MCD (2015) Milk-deteriorating exoenzymes from Pseudomonas fluorescens 041 isolated from refrigerated raw milk. Braz J Microbiol 46:207–217
Moura TM, Campos FS, Caierão J, Franco AC, Roehe P, d’Azevedo PA, Frazzon J, Frazzon APG (2015) Influence of a subinhibitory concentration of vancomycin on the in vitro expression of virulence-related genes in the vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 48:617–621
Nörnberg MBL, Mentges ML, Silveira ST, Tondo EC, Brandelli A (2011) A psychrotrophic Burkholderia cepacia strain isolated from refrigerated raw milk showing proteolytic activity and adhesion to stainless steel. J Dairy Res 78:257–262
Oliveira GB, Favarin L, Luchese RH, McIntosh D (2015) Psychrotrophic bacteria in milk: how much do we really know? Braz J Microbiol 46:313–321
Picoli T, Mendes Peter CM, Zani JL, Waller SB, Lopes MG, Boesche KN, Vargas GDA, Hübner SO, Fischer G (2017) Melittin and its potential in the destruction and inhibition of the biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from bovine milk. Microbial Pathogen 112:57–62
Piercey MJ, Hingston PA, Hansen LT (2016) Genes involved in Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation at a simulated food processing plant temperature of 15 C. Int J Food Microbiol 223:63–74
Pinto CLO, Souza LV, Meloni VAS, Bastista CS, Silva R, Martins EMF, Cruz AG, Martins ML (2017) Microbiological quality of Brazilian UHT milk: identification and spoilage potential of spore-forming bacteria. Int J Dairy Technol 71:20–26
Puga CH, Orgaz B, SanJose C (2016) Listeria monocytogenes impact on mature or old Pseudomonas fluorescens biofilms during growth at 4 and 20 °C. Front Microbiol 7 https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00134
Rossi C, Chaves-López C, Serio A, Goffredo E, Goga BTC, Paparella A (2016) Influence of incubation conditions on biofilm formation by Pseudomonas fluorescens isolated from dairy products and dairy manufacturing plants. Ital J Food Saf 5(5793):154–157
Ruaro A, Andrighetto C, Torriani S, Lombardi A (2013) Biodiversity and characterization of indigenous coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from raw milk and cheese of North Italy. Food Microbiol 34:106–111
Scatamburlo TM, Yamazi AK, Cavicchioli VQ, Pieri FA, Nero LA (2015) Spoilage potential of Pseudomonas species isolated from goat milk. J Dairy Sci 98:759–764
Serrato RV, Sassaki GL, Cruz L, Pedrosa FO, Gorin PAJ, Iacomini M (2006) Culture conditions for the production of an acidic exopolysaccharide by the nitrogen-fixing bacterium Burkholderia tropica. Can J Microbiol 52:489–493
Simões M, Pereira MO, Sillankorva S, Azeredo J, Vieira MJ (2013) The effect of hydrodynamic conditions on the phenotype of Pseudomonas fluorescens biofilms. Biofouling 23(4):249–258
Souza EL, Meira QGS, Barbosa IM, Athayde AJAA, Conceição ML, Junior JPS (2014) Biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus from food contact surfaces in a meat-based broth and sensitivity to sanitizers. Braz J Microbiol 45:67–75
Stepanović S, Vuković D, Dakić I, Savić B, Savić-Vlahovic M (2000) A modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J Microbiol Methods 40:175–179
Zhu J, Yan Y, Wang Y, Qu D (2018) Competitive interaction on dual-species biofilm formation by spoilage bacteria, Shewanella baltica and Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Appl Microbiol 126:1175–1186
Acknowledgements
The Centro de Microscopia e Microánalise (CMM)–UFRGS, Cooperbúfalo and CAPES–Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lauer Cruz, K., de Souza da Motta, A. Characterization of biofilm production by Pseudomonas fluorescens isolated from refrigerated raw buffalo milk. J Food Sci Technol 56, 4595–4604 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03924-1
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03924-1