Abstract
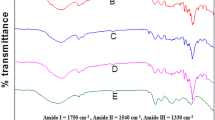
Influence of maleylation on the physicochemical and functional properties of rapeseed protein isolate was studied. Acylation increased whiteness value and dissociation of proteins, but reduced free sulfhydryl and disulfide content (p < 0.05). Intrinsic fluorescence emission and FTIR spectra revealed distinct perturbations in maleylated proteins’ tertiary and secondary conformations. Increase in surface hydrophobicity, foaming capacity, emulsion stability, protein surface load at oil-water interface and decrease in surface tension at air-water interface, occurred till moderate level of modification. While maleylation impaired foam stability, protein solubility and emulsion capacity were markedly ameliorated (p < 0.05), which are concomitant with decreased droplet size distribution (d 32). In-vitro digestibility and cytotoxicity tests suggested no severe ill-effects of modified proteins, especially up to low degrees of maleylation. The study shows good potential for maleylated rapeseed proteins as functional food ingredient.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aachary AA, Thiyam U (2012) A Pursuit of the functional, nutritional and bioactive properties of canola proteins and peptides. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 52:965–979
Achouri A, Zhang W (2001) Effect of succinylation on the physicochemical properties of soy protein hydrolysate. Food Res Int 34:507–514
Aewsiri T, Benjakul S, Visessanguan W, Eun J-B, Wierenga PA, Gruppen H (2009) Antioxidative activity and emulsifying properties of cuttlefish skin gelatin modified by oxidised phenolic compounds. Food Chem 117:160–168
Arancibia C, Bayarri S, Costell E (2015) Effect of hydrocolloid on rheology and microstructure of high-protein soy desserts. J Food Sci Technol 52(10):6435–6444
Aydemir LY, Gökbulut AA, Baran Y, Yemenicioğlu A (2014) Bioactive, functional and edible film-forming properties of isolated hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) meal proteins. Food Hydrocoll 36:130–142
Balange AK, Benjakul S (2009) Effect of oxidised phenolic compounds on the gel property of mackerel (Rastrelliger kanagurta) surimi. Lebensm Wiss Technol 42:1059–1064
Baxter NJ, Lilley TH, Haslam E, Williamson MP (1997) Multiple interactions between polyphenols and a salivary proline-rich protein repeat result in complexation and precipitation. Biochemistry 36:5566–5577
Byaruhanga YB, Emmambux MN, Belton PS, Wellner N, Ng KG, Taylor JRN (2006) Alteration of kafirin and kafirin film structure by heating with microwave energy and tannin complexation. J Agric Food Chem 54:4198–4207
Charlton AJ, Baxter NJ, Khan ML, Moir AJG, Haslam E, Davies AP, Williamson MP (2002) Polyphenol/Peptide binding and precipitation. J Agric Food Chem 50:1593–1601
Chen L, Chen J, Ren J, Zhao M (2011) Modifications of soy protein isolates using combined extrusion pre-treatment and controlled enzymatic hydrolysis for improved emulsifying properties. Food Hydrocoll 25:887–897
Condés MC, Speroni F, Mauri A, Añón MC (2012) Physicochemical and structural properties of amaranth protein isolates treated with high pressure. Innovative Food Sci Emerg Technol 14:11–17
Cui Z, Chen Y, Kong X, Zhang C, Hua Y (2014) Emulsifying properties and oil/water (o/w) interface adsorption behavior of heated soy proteins: effects of heating concentration, homogenizer rotating speed, and salt addition level. J Agric Food Chem 62:1634–1642
Damodaran S (2005) Protein stabilization of emulsions and foams. J Food Sci 70(3):R54–R66
Das Purkayastha M, Dutta G, Barthakur A, Mahanta CL (2015) Tackling correlated responses during process optimization of rapeseed meal protein extraction. Food Chem 170:62–73
Deng Q, Wang L, Wei F, Xie B, Huang FH, Huang W, Shi J, Huang Q, Tian B, Xue S (2011) Functional properties of protein isolates, globulin and albumin extracted from Ginkgo biloba seeds. Food Chem 124:1458–1465
Dickinson E, Golding M (1997) Depletion flocculation of emulsions containing unadsorbed sodium caseinate. Food Hydrocoll 11(1):13–18
El-Adawy TA (2000) Functional properties and nutritional quality of acetylated and succinylated mung bean protein isolate. Food Chem 70:83–91
Franzen KL, Kinsella JE (1976) Functional properties of succinylated and acetylated leaf protein. J Agric Food Chem 24(5):914–918
Gerbanowski A, Malabat C, Rabiller C, Guéguen J (1999) Grafting of aliphatic and aromatic probes on rapeseed 2S and 12S proteins: influence on their structural and physicochemical properties. J Agric Food Chem 47:5218–5226
Groninger HS, Miller R (1979) Some chemical and nutritional properties of acylated fish protein. J Agric Food Chem 27(5):949–955
Gruener L, Ismond MAH (1997) Effects of acetylation and succinylation on the physicochemical properties of the canola 12S globulin. Part I. Food Chem 60(3):357–363
Gueguen J, Bollecker S, Schwenke KD, Raab B (1990) Effect of succinylation on some physicochemical and functional properties of the 12s storage protein from rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). J Agric Food Chem 38(1):61–69
Hassan HMM, Afify AS, Basyiony AE, Ahmed GT (2010) Nutritional and functional properties of defatted wheat protein isolates. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 4(2):348–358
He R, He H-Y, Chao D, Ju X, Aluko R (2014) Effects of high pressure and heat treatments on physicochemical and gelation properties of rapeseed protein isolate. Food Bioprocess Technol 7(5):1344–1353
Hiller B, Lorenzen PC (2008) Surface Hydrophobicity of physicochemically and enzymatically treated milk proteins in relation to techno-functional properties. J Agric Food Chem 56:461–468
Jain A, Prakash M, Radha C (2015) Extraction and evaluation of functional properties of groundnut protein concentrate. J Food Sci Technol 52(10):6655–6662
Karaca AC, Low N, Nickerson M (2011) Emulsifying properties of canola and flaxseed protein isolates produced by isoelectric precipitation and salt extraction. Food Res Int 44:2991–2998
Kim KS, Kinsella JE (1986) Effects of progressive succinylation on some molecular properties of soy glycinin. Cereal Chem 63:342–345
Krause J-P, Wüstneck R, Seifert A, Schwenke KD (1998) Stress-relaxation behaviour of spread films and coalescence stability of o/w emulsions formed by succinylated legumin from faba beans (Vicia faba L.). Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 10:119–126
Lawal OS (2005) Functionality of native and succinylated Lablab bean (Lablab purpureus) protein concentrate. Food Hydrocoll 19:63–72
Lawal OS, Dawodu MO (2007) Maleic anhydride derivatives of a protein isolate: preparation and functional evaluation. Eur Food Res Technol 226:187–198
Li N, Qi G, Sun XS, Stamm MJ, Wang D (2012) Physicochemical properties and adhesion performance of canola protein modified with sodium bisulfite. J Am Oil Chem Soc 89:897–908
Li R, Hettiarachchy N, Rayaprolu S, Davis M, Eswaranandam S, Jha A, Chen P (2015) Improved functional properties of glycosylated soy protein isolate using D-glucose and xanthan gum. J Food Sci Technol 52(9):6067–6072
Mao X-Y, Hua Y-F (2014) Chemical composition, molecular weight distribution, secondary structure and effect of NaCl on functional properties of walnut (Juglans regia L) protein isolates and concentrates. J Food Sci Technol 51(8):1473–1482
Massoura E, Vereijken JM, Kolster P, Derksen JTP (1998) Proteins from crambe abyssinica oilseed. II Biochemical and functional properties. J Am Oil Chem Soc 75(3):329–335
Matemu AO, Kayahara H, Murasawa H, Katayama S, Nakamura S (2011) Improved emulsifying properties of soy proteins by acylation with saturated fatty acids. Food Chem 124:596–602
Moure A, Sineiro J, Domίnguez H, Parajό JC (2006) Functionality of oilseed protein products: a review. Food Res Int 39(9):945–963
Paulson AT, Tung MA (1989) Thermally induced gelation of succinylated canola protein isolate. J Agric Food Chem 37(2):319–326
Peterson GL (1977) A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem 83(2):346–356
Salgado PR, Drago SR, Ortiz SEM, Petruccelli S, Andrich O, González RJ, Mauri AN (2012) Production and characterization of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) protein-enriched products obtained at pilot plant scale. Lebensm Wiss Technol 45:65–72
Sánchez-Vioque R, Bagger CL, Larré C, Guéguen J (2004) Emulsifying properties of acylated rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) peptides. J Colloid Interface Sci 271:220–226
Schwenke KD, Knopfe C, Mikheeva LM, Grinberg VY (1998) Structural changes of legumin from faba beans (Vicia faba L.) by succinylation. J Agric Food Chem 46:2080–2086
Schwenke KD, Mothes R, Dudek S, Görnitz E (2000) Phosphorylation of the 12S globulin from rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) by phosphorous oxychloride: chemical and conformational aspects. J Agric Food Chem 48:708–715
Shevkani K, Singh N, Kaur A, Rana JC (2015) Structural and functional characterization of kidney bean and field pea protein isolates: a comparative study. Food Hydrocoll 43:679–689
Strange ED, Holsinger VH, Kleyn DH (1993) Chemical properties of thiolated and succinylated caseins. J Agric Food Chem 41:30–36
Tang C-H, Wang X-Y, Liu F, Wang C-S (2009) Physicochemical and conformational properties of buckwheat protein isolates: influence of polyphenol removal with cold organic solvents from buckwheat seed flours. J Agric Food Chem 57:10740–10748
Tsoukala A, Papalamprou E, Makri E, Doxastakis G, Braudo EE (2006) Adsorption at the air–water interface and emulsification properties of grain legume protein derivatives from pea and broad bean. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 53:203–208
Vasbinder AJ, Alting AC, Visschers RW, de Kruif CG (2003) Texture of acid milk gels: formation of disulfide cross-links during acidification. Int Dairy J 13:29–38
Wanasundara PKJPD, Shahidi F (1997) Functional properties of acylated flax protein isolates. J Agric Food Chem 45:2431–2441
Xu L, Diosady LL (2002) Removal of phenolic compounds in the production of high-quality canola protein isolates. Food Res Int 35:23–30
Yin S-W, Tang C-H, Wen Q-B, Yang X-Q, Yuan D-B (2010) The relationships between physicochemical properties and conformational features of succinylated and acetylated kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) protein isolates. Food Res Int 43:730–738
Yu H, Huang Q (2013) Investigation of the cytotoxicity of food-grade nanoemulsions in Caco-2 cell monolayers and HepG2 cells. Food Chem 141:29–33
Zhang Q-T, Tu Z-C, Wang H, Huang X-Q, Fan L-L, Bao Z-Y, Xiao H (2015) Functional properties and structure changes of soybean protein isolate after subcritical water treatment. J Food Sci Technol 52(6):3412–3421
Zhao Y, Ma C-Y, Yuen S-N, Phillips DL (2004) Study of succinylated food proteins by raman spectroscopy. J Agric Food Chem 52:1815–1823
Zhong C, Wang R, Zhou Z, Jia S-R, Tan Z-L, Han P-P (2012) Functional properties of protein isolates from Caragana korshinskii Kom. extracted by three different methods. J Agric Food Chem 60:10337–10342
Acknowledgments
The first author is thankful to DST for INSPIRE Fellowship and to Archana Singh for providing amiable help. The generous gift of MEF cells from Dr. Anna Kashina, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104 is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 6125 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das Purkayastha, M., Borah, A.K., Saha, S. et al. Effect of maleylation on physicochemical and functional properties of rapeseed protein isolate. J Food Sci Technol 53, 1784–1797 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2197-9
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2197-9