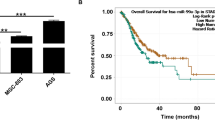
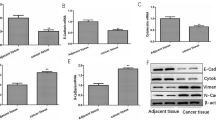
Abstract
Gastric cancer (GC) is a common malignant tumor worldwide, with a high incidence and low survival rate. The transforming growth factor-beta (TGFβ) signaling pathway usually plays a tumor-suppressive role and is normally quietened in GC. The downregulation of transforming growth factor-beta receptor II (TGFBR2) affects TGFβ signaling pathway, which exerts an immense effect on tumor cell proliferation and metastasis. Although the effect of the TGFβ signaling pathway on cancer cells is well studied, little is known about the mechanism by which TGFBR2 expression is downregulated. Here, we showed that TGFBR2 protein, but not TGFBR2 mRNA, was consistently downregulated in GC, suggesting that post-transcriptional mechanism is involved in the regulation of TGFBR2. Bioinformatics analysis and luciferase reporter analysis proved that miR-135b combines precisely with the 3′-UTR of TGFBR2 mRNA. EdU assays and cell migration assays respectively showed that miR-135b overexpression induced the growth and invasion of GC cells. However, the overexpression of TGFBR2 had the opposite effect. TGFBR2 acted as the direct target for miR-135b and was downregulated in gastric cancer cells. Therefore, miR-135b promotes proliferation and migration of GC cells by negatively regulating TGFBR2 expression, displaying an oncomiR effect. Altogether, this conclusive evidence supported that miR-135b mediates the progression of GC by targeting TGFBR2 and miR-135b/TGFBR2 axis can be used in future targeted therapy for GC.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its additional files.
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Chen XL, Hong LL, Wang KL, Liu X, Wang JL, Lei L, Xu ZY, Cheng XD, Ling ZQ (2019) Deregulation of CSMD1 targeted by microRNA-10b drives gastric cancer progression through the NF-kappaB pathway. Int J Biol Sci 15:2075–2086. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.23802
Chen Z, Li Z, Soutto M, Wang W, Piazuelo MB, Zhu S, Guo Y, Maturana MJ, Corvalan AH, Chen X, Xu Z, El-Rifai WM (2019) Integrated analysis of mouse and human gastric neoplasms identifies conserved microRNA networks in gastric carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 156:1127–1139 e1128. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2018.11.052
Darnet S, Moreira FC, Hamoy IG, Burbano R, Khayat A, Cruz A, Magalhaes L, Silva A, Santos S, Demachki S, Assumpcao M, Assumpcao P, Ribeiro-Dos-Santos A (2015) High-throughput sequencing of miRNAs reveals a tissue signature in gastric cancer and suggests novel potential biomarkers. Bioinform Biol Insights 9:1–8. https://doi.org/10.4137/BBI.S23773
Digklia A, Wagner AD (2016) Advanced gastric cancer: current treatment landscape and future perspectives. World J Gastroenterol 22:2403–2414. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2403
Ferro A, Peleteiro B, Malvezzi M, Bosetti C, Bertuccio P, Levi F, Negri E, La Vecchia C, Lunet N (2014) Worldwide trends in gastric cancer mortality (1980-2011), with predictions to 2015, and incidence by subtype. Eur J Cancer 50:1330–1344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2014.01.029
Guo W, Dong Z, Guo Y, Chen Z, Yang Z, Kuang G (2012) Association of polymorphisms in transforming growth factor-β receptors with susceptibility to gastric cardia adenocarcinoma. Mol Biol Rep 39:4301–4309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1217-0
Hammond SM (2015) An overview of microRNAs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 87:3–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2015.05.001
He B, Xu T, Pan B, Pan Y, Wang X, Dong J, Sun H, Xu X, Liu X, Wang S (2018) Polymorphisms of TGFBR1, TLR4 are associated with prognosis of gastric cancer in a Chinese population. Cancer Cell Int 18:191. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-018-0682-0
Heldin CH, Vanlandewijck M, Moustakas A (2012) Regulation of EMT by TGFbeta in cancer. FEBS Lett 586:1959–1970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2012.02.037
Huang Y, Xiao W, Jiang X, Li H (2019) MicroRNA-935 acts as a prognostic marker and promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in colorectal cancer. Cancer Biomark 26:229–237. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-190183
Iorio MV, Croce CM (2012) MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics. A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med 4:143–159. https://doi.org/10.1002/emmm.201100209
Iuliano R, Vismara MF, Dattilo V, Trapasso F, Baudi F, Perrotti N (2013) The role of microRNAs in cancer susceptibility. Biomed Res Int 2013:591931–591939. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/591931
Jin H, Luo S, Wang Y, Liu C, Piao Z, Xu M, Guan W, Li Q, Zou H, Tan QY, Yang ZZ, Wang Y, Wang D, Xu CX (2017) miR-135b stimulates osteosarcoma recurrence and lung metastasis via notch and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 8:111–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2017.06.008
Karimi P, Islami F, Anandasabapathy S, Freedman ND, Kamangar F (2014) Gastric cancer: descriptive epidemiology, risk factors, screening, and prevention. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 23:700–713. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-13-1057
Liu S, Chen S, Zeng J (2018) TGFbeta signaling: a complex role in tumorigenesis (review). Mol Med Rep 17:699–704. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.7970
Lo SS, Hung PS, Chen JH, Tu HF, Fang WL, Chen CY, Chen WT, Gong NR, Wu CW (2012) Overexpression of miR-370 and downregulation of its novel target TGFbeta-RII contribute to the progression of gastric carcinoma. Oncogene 31:226–237. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.226
Lu Y, Hu J, Sun W, Li S, Deng S, Li M (2016) MiR-29c inhibits cell growth, invasion, and migration of pancreatic cancer by targeting ITGB1. Onco Targets Ther 9:99–109. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S92758
Lv ZD, Xin HN, Yang ZC, Wang WJ, Dong JJ, Jin LY, Li FN (2019) miR-135b promotes proliferation and metastasis by targeting APC in triple-negative breast cancer. J Cell Physiol 234:10819–10826. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27906
Magalhaes L, Quintana LG, Lopes DCF, Vidal AF, Pereira AL, D’Araujo Pinto LC, de Jesus Viana Pinheiro J, Khayat AS, Goulart LR, Burbano R, de Assumpcao PP, Ribeiro-Dos-Santos A (2018) APC gene is modulated by hsa-miR-135b-5p in both diffuse and intestinal gastric cancer subtypes. BMC Cancer 18:1055. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4980-7
Mao L, Li Y, Zhao J, Li Q, Yang B, Wang Y, Zhu Z, Sun H, Zhai Z (2017) Transforming growth factor-β1 contributes to oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer via epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Oncol Lett 14:647–654. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.6209
Marques-Lespier JM, Gonzalez-Pons M, Cruz-Correa M (2016) Current perspectives on gastric cancer. Gastroenterol Clin N Am 45:413–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gtc.2016.04.002
Massagué J (1998) TGF-beta signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem 67:753–791. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.753
Massague J (2012) TGFbeta signalling in context. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:616–630. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3434
Michlewski G, Cáceres JF (2019) Post-transcriptional control of miRNA biogenesis. RNA (New York, NY) 25:1-16. doi:https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.068692.118
Mishra S, Yadav T, Rani V (2016) Exploring miRNA based approaches in cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 98:12–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.10.003
Moon H, Ju HL, Chung SI, Cho KJ, Eun JW, Nam SW, Han KH, Calvisi DF, Ro SW (2017) Transforming growth factor-beta promotes liver tumorigenesis in mice via up-regulation of snail. Gastroenterology 153:1378–1391 e1376. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.07.014
Moore-Smith L, Pasche B (2011) TGFBR1 signaling and breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 16:89–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-011-9216-2
Morris SM, Carter KT, Baek JY, Koszarek A, Yeh MM, Knoblaugh SE, Grady WM (2015) TGF-beta signaling alters the pattern of liver tumorigenesis induced by Pten inactivation. Oncogene 34:3273–3282. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.258
Nadauld LD, Garcia S, Natsoulis G, Bell JM, Miotke L, Hopmans ES, Xu H, Pai RK, Palm C, Regan JF, Chen H, Flaherty P, Ootani A, Zhang NR, Ford JM, Kuo CJ, Ji HP (2014) Metastatic tumor evolution and organoid modeling implicate TGFBR2 as a cancer driver in diffuse gastric cancer. Genome Biol 15:428. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0428-9
Pu M, Chen J, Tao Z, Miao L, Qi X, Wang Y, Ren J (2018) Regulatory network of miRNA on its target: coordination between transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. Cell Mol Life Sci 76:441–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2940-7
Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ (2017) MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16:203–222. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.246
Tetreault N, De Guire V (2013) miRNAs: their discovery, biogenesis and mechanism of action. Clin Biochem 46:842–845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2013.02.009
Venerito M, Vasapolli R, Rokkas T, Malfertheiner P (2018) Gastric cancer: epidemiology, prevention, and therapy. Helicobacter 23(Suppl 1):e12518. https://doi.org/10.1111/hel.12518
Wang J, Liu H, Li M (2019) Downregulation of miR-505 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and predicts poor prognosis in breast cancer. Oncol Lett 18:247–254. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10334
Wang YN, Xu F, Zhang P, Wang P, Wei YN, Wu C, Cheng SJ (2019) MicroRNA-575 regulates development of gastric cancer by targeting PTEN. Biomed Pharmacother 113:108716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108716
Wei C, Gao JJ (2019) Downregulated miR-383-5p contributes to the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor prognosis. PeerJ 7:e7882. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7882
Weiss CN, Ito K (2017) A macro view of microRNAs: the discovery of microRNAs and their role in hematopoiesis and hematologic disease. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 334:99–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ircmb.2017.03.007
Xu J, Acharya S, Sahin O, Zhang Q, Saito Y, Yao J, Wang H, Li P, Zhang L, Lowery FJ, Kuo WL, Xiao Y, Ensor J, Sahin AA, Zhang XH, Hung MC, Zhang JD, Yu D (2015) 14-3-3zeta turns TGF-beta’s function from tumor suppressor to metastasis promoter in breast cancer by contextual changes of Smad partners from p53 to Gli2. Cancer Cell 27:177–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2014.11.025
Yin L, Xiao X, Georgikou C, Luo Y, Liu L, Gladkich J, Gross W, Herr I (2019) Sulforaphane induces miR135b-5p and its target gene, RASAL2, thereby inhibiting the progression of pancreatic cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics 14:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2019.03.011
Zhang XY, Zhang PY (2017) Gastric cancer: somatic genetics as a guide to therapy. J Med Genet 54:305–312. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2016-104171
Zhang H, Wu H, Zheng J, Yu P, Xu L, Jiang P, Gao J, Wang H, Zhang Y (2013) Transforming growth factor beta1 signal is crucial for dedifferentiation of cancer cells to cancer stem cells in osteosarcoma. Stem Cells 31:433–446. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.1298
Zhang Z, Gao Y, Xu MQ, Wang CJ, Fu XH, Liu JB, Han DX, Jiang H, Yuan B, Zhang JB (2019) miR-181a regulate porcine preadipocyte differentiation by targeting TGFBR1. Gene 681:45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.09.046
Code availability
Not applicable
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81772629) and the Demonstrative Research Platform of Clinical Evaluation Technology for New Anticancer Drugs (No. 2018ZX09201015). This work was also supported by the Tianjin Science Foundation (No. 18JCYBJC92000) and the Science & Technology Development Fund of the Tianjin Education Commission for Higher Education (2018KJ046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All animal studies were performed by skilled laboratory personnel with the approval of the Ethics Committee of Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital (Tianjin, China), and informed consent was obtained from all patients. All experimental procedures were performed under approved protocols following the principles and procedures outlined in the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from the parents.
Consent for publication
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for the publication of the image in Fig. 1a.
Disclaimer
The funders had no role in the study design, the data collection and analysis, interpretation of the data, the writing of the report, and the decision to submit this article for publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key points
1. miR-135b showed a high expression pattern in GC.
2. The interaction between miR-135b and TGFBR2 contributed to the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells.
3. Our results illustrated that inhibition of miR-135b in GC serves as a new method for clinical treatment.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, M., Wang, P., Yang, J. et al. Identification of miR-135b as a novel regulator of TGFβ pathway in gastric cancer. J Physiol Biochem 76, 549–560 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-020-00759-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-020-00759-9