Abstract
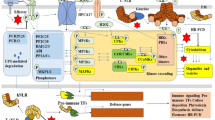
Plants are the ultimate producers of this ecosystem and effect human life directly and/or indirectly. However, being sessile organisms, plants are susceptible to several adverse environmental conditions and pathogen ingress resulting in huge losses to yield and productivity. Therefore, plans are continuously evolving complex regulatory networks to respond to these environmental changes. Due to its impact on pre- and post-harvest losses, biotic stress is of great concern to plant scientists. Interpreting the underlying mechanism of plant response to biotic stresses is therefore of great importance. A brief account about these hostile conditions and plants responses towards them is described in this review.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramovitch, R.B., Anderson, J.C., and Martin, G.B. 2006. Bacterial elicitation and evasion of plant innate immunity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7: 601–611
Abramovitch, R.B., Kim, Y.J., Chen, S., Dickman, M.B., and Martin, G.B. 2003. Pseudomonas type III effector AvrPtoB induces plant disease susceptibility by inhibition of host programmed cell death. EMBO J 22: 60–69
An, C.F., and Mou, Z.L. 2011. Salicylic Acid and its Function in Plant Immunity. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology 53: 412–428
Badel, J.L., Charkowski, A.O., Deng, W.L., and Collmer, A. 2002. A gene in the Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato Hrp pathogenicity island conserved effector locus, hopPtoA1, contributes to efficient formation of bacterial colonies in planta and is duplicated elsewhere in the genome. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15: 1014–1024
Badri, D.V., Loyola-Vargas, V.M., Du, J., Stermitz, F.R., Broeckling, C.D., Iglesias-Andreu, L., and Vivanco, J.M. 2008. Transcriptome analysis of Arabidopsis roots treated with signaling compounds: a focus on signal transduction, metabolic regulation and secretion. New Phytol 179: 209–223
Bari, R., and Jones, J.G. 2009. Role of plant hormones in plant defence responses. Plant Molecular Biology 69: 473–488
Barras, F., Vangijsegem, F., and Chatterjee, A.K. 1994. Extracellular Enzymes and Pathogenesis of Soft-Rot Erwinia. Annual Review of Phytopathology 32: 201–234
Block, A., and Alfano, J.R. 2011. Plant targets for Pseudomonas syringae type III effectors: virulence targets or guarded decoys? Current Opinion in Microbiology 14: 39–46
Brooks, D.M., Bender, C.L., and Kunkel, B.N. 2005. The Pseudomonas syringae phytotoxin coronatine promotes virulence by overcoming salicylic acid-dependent defences in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant Pathol 6: 629–639
Cao, H., Bowling, S.A., Gordon, A.S., and Dong, X.N. 1994. Characterization of an Arabidopsis Mutant That Is Non-responsive to Inducers of Systemic Acquired-Resistance. Plant Cell 6: 1583–1592
Chadha, K.C., and Brown, S.A. 1974. Biosynthesis of phenolic acids in tomato plants infected with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Canadian Journal of Botany 52: 2041–2047
Chen, Z., Zheng, Z., Huang, J., Lai, Z., and Fan, B. 2009. Biosynthesis of salicylic acid in plants. Plant Signal Behav 4: 493–496
Creelman, R.A., and Mullet, J.E. 1997. Biosynthesis and Action of Jasmonates in Plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 48: 355–381
Dangl, J. 2004. Molecular specificity in the plant immune system. Molecular Biology of the Cell 15: 2a–2a
De Torres, M., Mansfield, J.W., Grabov, N., Brown, I.R., Ammouneh, H., Tsiamis, G., Forsyth, A., Robatzek, S., Grant, M., and Boch, J. 2006. Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPtoB suppresses basal defence in Arabidopsis (vol 47, pg 368, 2006). Plant Journal 48: 164-164
Desveaux, D., Singer, A.U., and Dangl, J.L. 2006. Type III effector proteins: doppelgangers of bacterial virulence. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9: 376–382
Durrant, W.E., and Dong, X. 2004. Systemic acquired resistance. Annual Review of Phytopathology 42: 185–209
El-Basyouni, S.Z., Chen, D., Ibrahim, R., Neish, A., and Towers, G. 1964. The biosynthesis of hydroxybenzoic acids in higher plants. Phytochemistry 3: 485–492
Falk, A., Feys, B.J., Frost, L.N., Jones, J.D., Daniels, M.J., and Parker, J.E. 1999. EDS1, an essential component of R genemediated disease resistance in Arabidopsis has homology to eukaryotic lipases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 96: 3292–3297
Farmer, E.E., and Ryan, C.A. 1992. Octadecanoid Precursors of Jasmonic Acid Activate the Synthesis of Wound-Inducible Proteinase Inhibitors. Plant Cell 4: 129–134
Felix, G., and Boller, T. 2003. Molecular sensing of bacteria in plants - The highly conserved RNA-binding motif RNP-1 of bacterial cold shock proteins is recognized as an elicitor signal in tobacco. Journal of Biological Chemistry 278: 6201–6208
Felix, G., Duran, J.D., Volko, S., and Boller, T. 1999. Plants have a sensitive perception system for the most conserved domain of bacterial flagellin. Plant Journal 18: 265–276
Feys, B.J., Wiermer, M., Bhat, R.A., Moisan, L.J., Medina-Escobar, N., Neu, C., Cabral, A., and Parker, J.E. 2005. Arabidopsis SENESCENCE-ASSOCIATED GENE101 stabilizes and signals within an ENHANCED DISEASE SUSCEP-TIBILITY1 complex in plant innate immunity. The Plant Cell 17: 2601–2613
Garcion, C., Lohmann, A., Lamodiere, E., Catinot, J., Buchala, A., Doermann, P., and Metraux, J.P. 2008. Characterization and biological function of the ISOCHORISMATE SYNTH-ASE2 gene of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 147: 1279–1287
Glazebrook, J. 2005. Contrasting mechanisms of defense against biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. Annual Review of Phytopathology 43: 205–227
Gomez-Gomez, L., and Boller, T. 2002. Flagellin perception: a paradigm for innate immunity. Trends Plant Sci 7: 251–256
Gorlach, J., Volrath, S., Knaufbeiter, G., Hengy, G., Beckhove, U., Kogel, K.H., Oostendorp, M., Staub, T., Ward, E., Kessmann, H., and Ryals, J. 1996. Benzothiadiazole, a novel class of inducers of systemic acquired resistance, activates gene expression and disease resistance in wheat. Plant Cell 8: 629–643
Grant, S.R., Fisher, E.J., Chang, J.H., Mole, B.M., and Dangl, J.L. 2006. Subterfuge and manipulation: type III effector proteins of phytopathogenic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 60: 425–449
Gull, A., Lone, A.A., and Wani, N.U.I. (2019). “Biotic and Abiotic Stresses in Plants,” in Abiotic and Biotic Stress in Plants. IntechOpen).
Hammond-Kosack, K.E., and Jones, J.D. 1996. Resistance gene-dependent plant defense responses. The Plant Cell 8: 1773–1791
He, P., Shan, L., Lin, N.C., Martin, G.B., Kemmerling, B., Nurnberger, T., and Sheen, J. 2006. Specific bacterial suppressors of MAMP signaling upstream of MAPKKK in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Cell 125: 563–575
Jones, J.D.G., and Dangl, J.L. 2006. The plant immune system. Nature 444: 323–329
Kazan, K., and Manners, J.M. 2008. Jasmonate signaling: toward an integrated view. Plant Physiol 146: 1459–1468
Kiraly, Z. 1998. Plant infection - Biotic stress. Stress of Life 851: 233–240
Klämbt, H. 1962. Conversion in plants of benzoic acid to salicylic acid and its βd-glucoside
Kunze, G., Zipfel, C., Robatzek, S., Niehaus, K., Boller, T., and Felix, G. 2004. The N terminus of bacterial elongation factor Tu elicits innate immunity in Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell 16: 3496–3507
Laluk, K., and Mengiste, T. 2010. Necrotroph attacks on plants: wanton destruction or covert extortion? The Arabidopsis Book: e0136
Lawton, K.A., Friedrich, L., Hunt, M., Weymann, K., Delaney, T., Kessmann, H., Staub, T., and Ryals, J. 1996. Benzothiadiazole induces disease resistance in Arabidopsis by activation of the systemic acquired resistance signal transduction pathway. Plant Journal 10: 71–82
Li, L., Li, C.Y., and Howe, G.A. 2001. Genetic analysis of wound signaling in tomato. Evidence for a dual role of jasmonic acid in defense and female fertility. Plant Physiology 127: 1414–1417
López, M.A., Bannenberg, G., and Castresana, C. 2008. Controlling hormone signaling is a plant and pathogen challenge for growth and survival. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 11: 420–427
Lu, H. 2009. Dissection of salicylic acid-mediated defense signaling networks. Plant Signal Behav 4: 713–717
Maloy, O.C., and Murray, T.D. (2001). Encyclopedia of plant pathology. Wiley
Mauch, F., Mauch-Mani, B., Gaille, C., Kull, B., Haas, D., and Reimmann, C. 2001. Manipulation of salicylate content in Arabidopsis thaliana by the expression of an engineered bacterial salicylate synthase. Plant J 25: 67–77
Mcconn, M., and Browse, J. 1996. The critical requirement for linolenic acid is pollen development, not photosynthesis, in an arabidopsis mutant. Plant Cell 8: 403–416
Mcconn, M., Creelman, R.A., Bell, E., and Mullet, J.E. 1997. Jasmonate is essential for insect defense in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 94: 5473–5477
Melotto, M., Underwood, W., Koczan, J., Nomura, K., and He, S. 2006. The innate immune function of plant stomata against bacterial invasion
Mou, Z., Fan, W.H., and Dong, X.N. 2003. Inducers of plant systemic acquired resistance regulate NPR1 function through redox changes. Cell 113: 935–944
Mudgett, M.B. 2005. New insights to the function of phyto-pathogenic bacterial type III effectors in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56: 509–531
Mukherjee, S., Keitany, G., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Ball, H.L., Goldsmith, E.J., and Orth, K. 2006. Yersinia YopJ acetylates and inhibits kinase activation by blocking phosphorylation. Science 312: 1211–1214
Navarro, L., Dunoyer, P., Jay, F., Arnold, B., Dharmasiri, N., Estelle, M., Voinnet, O., and Jones, J.D.G. 2006. A plant miRNA contributes to antibacterial resistance by repressing auxin signaling. Science 312: 436–439
Nawrath, C., and Metraux, J.P. 1999. Salicylic acid induction-deficient mutants of Arabidopsis express PR-2 and PR-5 and accumulate high levels of camalexin after pathogen inoculation. Plant Cell 11: 1393–1404
Nejat, N., and Mantri, N. Plant immune system: crosstalk between responses to biotic and abiotic stresses the missing link in understanding plant defence. Signal 2: O2
Nomura, K., Debroy, S., Lee, Y.H., Pumplin, N., Jones, J., and He, S.Y. 2006. A bacterial virulence protein suppresses host innate immunity to cause plant disease. Science 313: 220–223
Pangesti, N., Pineda, A., Pieterse, C.M., Dicke, M., and Van Loon, J.J. 2013. Two-way plant mediated interactions between root-associated microbes and insects: from ecology to mechanisms. Frontiers in plant science 4: 414
Park, J.Y., Jin, J.M., Lee, Y.W., Kang, S., and Lee, Y.H. 2009. Rice Blast Fungus (Magnaporthe oryzae) Infects Arabidopsis via a Mechanism Distinct from That Required for the Infection of Rice. Plant Physiology 149: 474–486
Parker, J.E., Holub, E.B., Frost, L.N., Falk, A., Gunn, N.D., and Daniels, M.J. 1996. Characterization of eds1, a mutation in Arabidopsis suppressing resistance to Peronospora parasitica specified by several different RPP genes. Plant Cell 8: 2033–2046
Petersen, M., Brodersen, P., Naested, H., Andreasson, E., Lindhart, U., Johansen, B., Nielsen, H.B., Lacy, M., Austin, M.J., Parker, J.E., Sharma, S.B., Klessig, D.F., Martienssen, R., Mattsson, O., Jensen, A.B., and Mundy, J. 2000. Arabidopsis MAP kinase 4 negatively regulates systemic acquired resistance. Cell 103: 1111–1120
Rejeb, I.B., Pastor, V., and Mauch-Mani, B. 2014. Plant responses to simultaneous biotic and abiotic stress: molecular mechanisms. Plants 3: 458–475
Rojo, E., León, J., and Sánchez-Serrano, J.J. 1999. Cross-talk between wound signalling pathways determines local versus systemic gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Journal 20: 135–142
Rojo, E., Solano, R., and Sánchez-Serrano, J. 2003. Interactions Between Signaling Compounds Involved in Plant Defense. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation 22: 82–98
Ryan, C.A. 2000. The systemin signaling pathway: differential activation of plant defensive genes. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology 1477: 112–121
Schulze-Lefert, P., and Panstruga, R. 2003. Establishment of biotrophy by parasitic fungi and reprogramming of host cells for disease resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 41: 641–667
Serino, L., Reimmann, C., Baur, H., Beyeler, M., Visca, P., and Haas, D. 1995. Structural Genes for Salicylate Biosynthesis from Chorismate in Pseudomonas-Aeruginosa. Molecular & General Genetics 249: 217–228
Singla, J., Krattinger, S., Wrigley, C., Faubion, J., Corke, H., and Seetharaman, K. 2016. Biotic stress resistance genes in wheat
Sun, W., Dunning, F.M., Pfund, C., Weingarten, R., and Bent, A.F. 2006. Within-species flagellin polymorphism in Xanthomonas campestris pv campestris and its impact on elicitation of Arabidopsis FLAGELLIN SENSING2-dependent defenses. Plant Cell 18: 764–779
Ting, J.P.Y., and Davis, B.K. 2005. Caterpiller: A novel gene family important in immunity, cell death, and diseases. Annual Review of Immunology 23: 387–414
Tsuda, K., Sato, M., Glazebrook, J., Cohen, J.D., and Katagiri, F. 2008. Interplay between MAMP-triggered and SA-mediated defense responses (vol 53, pg 763, 2008). Plant Journal 55: 1061-1061
Turner, J.G., Ellis, C., and Devoto, A. 2002. The jasmonate signal pathway. Plant Cell 14 Suppl: S153–164
Van Kan, J.A. 2006. Licensed to kill: the lifestyle of a necrotrophic plant pathogen. Trends Plant Sci 11: 247–253
Van Wees, S.C., Van Der Ent, S., and Pieterse, C.M. 2008. Plant immune responses triggered by beneficial microbes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11: 443–448
Verberne, M.C., Verpoorte, R., Bol, J.F., Mercado-Blanco, J., and Linthorst, H.J.M. 2000. Overproduction of salicylic acid in plants by bacterial transgenes enhances pathogen resistance. Nature Biotechnology 18: 779–783
Vijayan, P., Shockey, J., Levesque, C.A., Cook, R.J., and Browse, J. 1998. A role for jasmonate in pathogen defense of Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 95: 7209–7214
Wang, D., Pajerowska-Mukhtar, K., Culler, A.H., and Dong, X.N. 2007. Salicylic acid inhibits pathogen growth in plants through repression of the auxin signaling pathway. Current Biology 17: 1784–1790
Wildermuth, M.C., Dewdney, J., Wu, G., and Ausubel, F.M. 2002. Isochorismate synthase is required to synthesize salicylic acid for plant defence (vol 414, pg 562, 2001). Nature 417: 571-571
Yang, Y.X., Ahammed, G.J., Wu, C.J., Fan, S.Y., and Zhou, Y.H. 2015. Crosstalk among Jasmonate, Salicylate and Ethylene Signaling Pathways in Plant Disease and Immune Responses. Current Protein & Peptide Science 16: 450–461
Yu, D.Q., Chen, C.H., and Chen, Z.X. 2001. Evidence for an important role of WRKY DNA binding proteins in the regulation of NPR1 gene express ion. Plant Cell 13: 1527–1539
Yu, M.D., Lamattina, L., Spoel, S.H., and Loake, G.J. 2014. Nitric oxide function in plant biology: a redox cue in deconvolution. New Phytologist 202: 1142–1156
Zabala, M.D., Bennett, M.H., Truman, W.H., and Grant, M.R. 2009. Antagonism between salicylic and abscisic acid reflects early host-pathogen conflict and moulds plant defence responses. Plant Journal 59: 375–386
Zhao, Y., Thilmony, R., Bender, C.L., Schaller, A., He, S.Y., and Howe, G.A. 2003. Virulence systems of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato promote bacterial speck disease in tomato by targeting the jasmonate signaling pathway. Plant J 36: 485–499
Zhou, N., Tootle, T.L., Tsui, F., Klessig, D.F., and Glazebrook, J. 1998. PAD4 functions upstream from salicylic acid to control defense responses in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell 10: 1021–1030
Zipfel, C., and Felix, G. 2005. Plants and animals: a different taste for microbes? Current Opinion in Plant Biology 8: 353–360
Zipfel, C., Kunze, G., Chinchilla, D., Caniard, A., Jones, J.D., Boller, T., and Felix, G. 2006. Perception of the bacterial PAMP EF-Tu by the receptor EFR restricts Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Cell 125: 749–760
Zipfel, C., Robatzek, S., Navarro, L., Oakeley, E.J., Jones, J.D.G., Felix, G., and Boller, T. 2004. Bacterial disease resistance in Arabidopsis through flagellin perception. Nature 428: 764–767
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (SSAC, Grant No., PJ013 42501), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imran, Q.M., Yun, BW. Pathogen-induced Defense Strategies in Plants. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 23, 97–105 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-019-0352-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-019-0352-0