Abstract
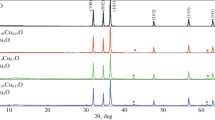
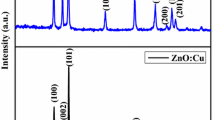
In this work, Zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles in pure, doped and concurrently co-doped with magnesium and copper were synthesized via simple co-precipitation method. The optical properties and morphology of the products were studied. Results from ultraviolet–visible (UV–Vis) spectroscopy showed absorption at 378 nm which proved the formation of pure ZnO and further blue and red shifts occurred in UV absorbance depending on the type of the dopant and its concentration. UV–Vis data also showed a good tailoring of the band gap from 2.87 to 3.56 eV depending upon the dopant. X-ray diffraction studies confirmed the formation of ZnO in all samples with a wurtzite hexagonal structure. The results from field emission scanning electron microscopy confirmed the average size of all particles to be 60 nm with a flake-shaped form. Fourier-transform infrared spectra further verified the presence of different functional groups and formation of ZnO in all samples. This study confirmed that ZnO accompanied by some impurities is a great option for optoelectronic applications such as UV photo-absorbers in the UVA range.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karimi M, et al., Optoelectron Adv Mater 19 (2017) 641.
Shen T, Yang K, Dou B, Wei S-H, Liu Y, and Deng H-X, Appl Phys Lett 120 (2022) 42105.
Ciciliati M A, Silva M F, Fernandes D M, de Melo M A C, Hechenleitner A A W, and Pineda E A G, Mater Lett 159 (2015) 84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.06.023
Priya R, et al., J Mater Sci Mater Electron 32 (2021) 2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04968-2
Jin Z, Fukumura T, Kawasaki M, Ando K, Saito H, Sekiguchi T, Yoo Y Z, Murakami M, Matsumoto Y, Hasegawa T, and Koinuma H, Appl Phys Lett 78 (2001) 3824. https://doi.org/10.1063/11377856
Devi P G, and Velu A S, J Theor Appl Phys 10 (2016) 233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40094-016-0221-0
Ginting M, Taslima S, Sebayang K, Aryanto D, Sudiro T, and Sebayang P, AIP Conf Proc 1862 (2017) 30062. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4991166
Siregar N, Motlan M, and Panggabean J, J Phys Conf Ser 1428 (2020) 12026. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1428/1/012026
Mia MNH, Pervez MF, Khalid Hossain M, Reefaz Rahman M, Jalal Uddin M, Al Mashud MA, Ghosh HK and Hoq M, Res Phys 7 (2017) 2683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2017.07.047
Abhijith A R, Srivastava A K, and Srivastava A, J Phys Conf Ser 1531 (2020) 12005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1531/1/012005
Karmakar S, Panda B, Sahoo B, Routray K L, Varma S, and Behera D, Mater Sci Semicond Process 88 (2018) 198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2018.08.008
Saravade V, Manzoor Z, Corda A, Zhou C, Ferguson IT and Lu L, Quantum Sens Nano Electron Photonics XVII (2020). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2543909.
Boruah B D, Nanoscale Adv 1 (2019) 2059.
Umar A, Lee S, Im Y H, and Hahn Y B, Nanotechnology 16 (2005) 2462. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/16/10/079
Lee Y-J, Sounart T L, Scrymgeour D A, Voigt J A, and Hsu J W P, J Cryst Growth 304 (2007) 80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2007.02.011
Lyu S C, Zhang Y, Lee C J, Ruh H, and Lee H J, Chem. Mater. 15 (2003) 3294. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm020465j
Li Y B, Bando Y, Sato T, and Kurashima K, Appl Phys Lett 81 (2002) 144. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1492008
UsmanAli S M, Nur O, Willander M, and Danielsson B, Sens Actuators B Chem. 145 (2010) 869.
Sirelkhatim A, Mahmud S, Seeni A, Haida N, Kaus M, Ann LC, Khadijah S, Bakhori M, Hasan H and Mohamad D, Nano-Micro Lett. 7(2015) 219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-015-0040-x
Benrezgua E, Zoukel A, Deghfel B, Boukhari A, Amari R, Kheawhom S, and AMohamad A, Mater Today Commun (2022) 103306
Goh E G, Xu X, and McCormick P G, Scr Mater 78–79 (2014) 49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2014.01.033
Kahouli M, Barhoumi A, Bouzid A, Al-Hajry A, and Guermazi S, Superlattices Microstruct 85 (2015) 7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2015.05.007
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dabaghiannejad, B., Arya, S.K. & Kumar, S. Investigation on the Effect of Cu and Mg Concentration on the Optical and Structural Properties of Doped and Co-doped ZnO Nanoparticles. Trans Indian Inst Met 77, 677–684 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-023-03121-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-023-03121-x