Abstract
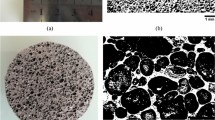
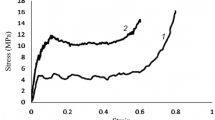
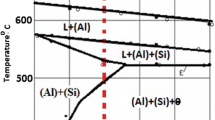
Aluminum foams with different silicon content have been produced by the Alporas method, where calcium and calcium carbonate are used as a thickening and foam agent, respectively. Performing quasi-static compression tests, mechanical behavior such as strain–stress diagram, deformation behavior, and energy absorption properties of the produced foams were investigated in this study. By adding silicon, calcium, and agitation of molten metal Si, SiO2, CaAl2Si2, CaAl2Si2O8 phases were created. These phases increased melt viscosity and improved foamability. The effect of physical properties, foam structure, alloy microstructure, pore size, and distribution on the mechanical behavior of metal foams was investigated in the present study. The foam with 8 wt% Si showed minimum density and maximum foamability, while it possessed a complete peak of stress. Thinner cell walls in Al–Si foams were observed, which could be attributed to the effect of silicon on melt’s surface tension. Results suggested that foams with 0 and 8 wt% Si are suitable for use as an energy absorber.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Fluidity or castability, in casting terminology, is a term commonly used to describe the quality of the molten metal to flow and fill the mold cavity before it is stopped by solidification; this means fluidity in casting is not opposite of viscosity.
References
M.F. Ashby, T. Evans, N.A. Fleck, J. Hutchinson, H. Wadley, L. Gibson, Metal foams: a design guide, Elsevier2000.
J. Banhart, Metallic foams: challenges and opportunities, Eurofoam 2000 (2000) 13-20.
J. Banhart, Prog. Mater Sci. 46(6) (2001) 559
J. Baumeister, J. Banhart, M. Materials & design 18(4–6) (1997) 217
N. Babcsán, J. Banhart, D. Leitlmeier, Metal foams–manufacture and physics of foaming, In Proceedings of the International Conference Advanced Metallic Materials, Citeseer, 2003, p. 5.
L. Cambronero, J. Ruiz-Roman, F. Corpas, J.R. Prieto, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209(4) (2009) 1803
Y. Wang, Aluminum foam stabilization by solid particles, (1996).
M. Alizadeh, M. Mirzaei-Aliabadi, Compressive properties and energy absorption behavior of Al–Al2O3 composite foam synthesized by space-holder technique, Materials & Design 35 (2012) 419-424.
W. Deqing, S. Ziyuan, Materials Science and Engineering: A 361(1-2) (2003) 45
H.J. Luo, L. Zhang, Z.G. Xu, Y.S. Yang, In: Materials Science Forum. Trans Tech Publications Ltd, 2013, p. 356
X. Xia, X. Chen, Z. Zhang, X. Chen, W. Zhao, B. Liao, B. Hur, Materials & Design (1980–2015) 56 (2014) 353
L. Huang, H. Wang, D. Yang, F. Ye, Z. Lu, Effects of scandium additions on mechanical properties of cellular Al-based foams, Intermetallics 28 (2012) 71-76.
S.-H. Park, Y.-S. Um, C.-H. Kum, B.-Y. Hur, Thermophysical properties of Al and Mg alloys for metal foam fabrication, Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 263(1-3) (2005) 280-283.
H.-j. YU, G.-c. YAO, Y.-h. LIU, Tensile property of Al-Si closed-cell aluminum foam, Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China 16(6) (2006) 1335-1340.
V. Kumar, H.M.A. Kumar, Effect of Silicon content on the Mechanical Properties of Aluminum Alloy, International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology 2(4) (2015) 74-86.
J.K. Khabushan, S.B. Bonabi, F.M. Aghbagh, A.K. Khabushan, Materials & Design 55 (2014) 792.
W.-m. Zhao, Z. Zhang, Y.-n. Wang, X.-c. Xia, H. Feng, J. Wang, Compressive characteristics of closed-cell aluminum foams with different percentages of Er element, China Foundry 13(1) (2016) 36-41.
I. Standard, ISO (E)(2011) Ref Number ISO 13314(13314) 1.
T. Ferreira, W. Rasband, ImageJ user guide, ImageJ/Fiji 1 (2012).
M. Warmuzek, Aluminum-silicon casting alloys: an atlas of microfractographs, ASM international2004.
H. Kobatake, J. Brillo, J. Schmitz, P.-Y. Pichon, Journal of materials science 50(9) (2015) 3351.
W. Mao, T. Noji, K. Teshima, N. Shinozaki, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A 47(6) (2016) 3201.
J. Banhart, D. Weaire, On the road again: metal foams find favor, Physics Today 55(7) (2002) 37-42.
O. Osman, International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications 5(2) (2015) 109.
Z.-L. Song, L.-Q. Ma, Z.-J. Wu, D.-P. Journal of materials science 35(1) (2000) 15.
C. Yang, H. Nakae, The effects of viscosity and cooling conditions on the foamability of aluminum alloy, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 141(2) (2003) 202-206.
S.H. Elahi, H. Abdi, H.R. Shahverdi, Investigating viscosity variations of molten aluminum by calcium addition and stirring, Mater. Lett. 91 (2013) 376-378.
N. Babcsán, Miskolc Materials Science (2003).
B.P. Binks, T.S. Horozov, Colloidal particles at liquid interfaces. Cambridge University Press (2006).
S.H. Elahi, R.A. Jeshvaghani, H. Shahverdi, Influence of calcium addition and stirring on the cellular structure and foaming behavior of molten zinc, Appl. Phys. A 119(2) (2015) 533-538.
M.G. Kalhapure, P.M. Dighe, Impact of silicon content on mechanical properties of aluminum alloys, Int. J. Sci. Res 4 (2015) 38-40.
F. Stadler, H. Antrekowitsch, W. Fragner, H. Kaufmann, P.J. Uggowitzer, In: Materials science forum. Trans Tech Publications Ltd, 2011, p. 274.
S. Nallusamy, A Review on the Effects of Casting Quality, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Cast Al-Si-0.3 Mg Alloy, International Journal of Performability Engineering 12(2) (2016).
T. Kobayashi, H. Kim, M. Niinomi, Effect of calcium on mechanical properties of recycled aluminiumcasting alloys, Mater. Sci. Technol. 13(6) (1997) 497-502.
K. Al-Helal, Y. Wang, I. Stone, Z.Y. Fan, Materials Science Forum, Trans Tech Publications Ltd, 2013, p. 117.
E. Koza, M. Leonowicz, S. Wojciechowski, F. Simancik, Compressive strength of aluminium foams, Materials Letters 58(1-2) (2004) 132-135.
M. Malekjafarian, S. Sadrnezhaad, Closed-cell Al alloy composite foams: Production and characterization, Materials & Design 42 (2012) 8-12.
Y. Mu, G. Yao, Anisotropic compressive behavior of closed-cell Al–Si alloy foams, Materials Science and Engineering: A 527(4-5) (2010) 1117-1119.
S. Sahu, A. Barnwal, D. Mondal, P. Jain, Indian Foundry Journal 59(8) (2013).
S. Sahu, M. Goel, D. Mondal, S. Das, High temperature compressive deformation behavior of ZA27–SiC foam, Materials Science and Engineering: A 607 (2014) 162-172.
H. Bayani, S. Mirbagheri, Strain-hardening during compression of closed-cell Al/Si/SiC+(TiB2 & Mg) foam, Mater. Charact. 113 (2016) 168-179.
S. Sahu, A. Zahid, A study on manufacturing processes and compressive properties of zinc-aluminium metal foams, Illinois Journal of Mathematics 2015(48) (2004) 50.
U. Ramamurty, A. Paul, Variability in mechanical properties of a metal foam, Acta Mater. 52(4) (2004) 869-876.
S. Nikanorov, M. Volkov, V. Gurin, Y.A. Burenkov, L. Derkachenko, B. Kardashev, L. Regel, W. Wilcox, Structural and mechanical properties of Al–Si alloys obtained by fast cooling of a levitated melt, Materials Science and Engineering: A 390(1-2) (2005) 63-69.
D. Stauffer, A. Aharony, Introduction to Percolation Theory.. 2nd EdTaylor and Francis, London 181pp (1992).
J. Jerz, N. Mináriková, L. Marsavina, E. Linul, Scaling of compression strength in disordered solids: metallic foams, Frattura ed Integrita Strutturale 10(36) (2016) 55-62.
H. Elzanaty, Effect of different Si content on the mechanical properties in Al-based alloy, International Journal of Research in Engineering & Technology (IMPACT: IJRET) 2(7) (2014) 49-54.
S. Yu, J. Liu, Y. Luo, Y. Liu, Compressive behavior and damping property of ZA22/SiCp composite foams, Materials Science and Engineering: A 457(1-2) (2007) 325-328.
S. Sahu, M.Z. Ansari, A Study on Manufacturing Processes and Compressive Properties of Zinc-Aluminium Metal Foams, American Journal of Materials Science 5(3C) (2015) 38-42.
C.J. Yu, J. Banhart, Mechanical properties of metallic foams, Proceedings of Fraunhofer USA Metal Foam Symposium, Stanton, Delaware, 1997, p. 7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farahani, M., Hossein Elahi, S. & Rezaei Ashtiani, H.R. Effect of Silicon Content on Mechanical Properties and Progressive Collapse Behavior of Closed-cell Aluminum Foams. Trans Indian Inst Met 74, 3145–3154 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02390-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02390-8