Abstract
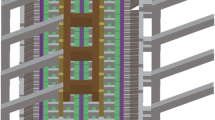
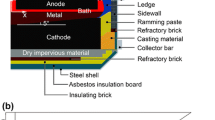
Numerical models of a cathode block assembly in a Hall–Hèroult cell, comprising of liquid aluminium, carbon block, current collector, ramming paste and a copper insert were built and the finite element method simulations were carried out to model the cathode voltage drop (CVD), the current distribution and, the effect of geometrical parameters on the CVD. The objective of the study was to quantify the drop in the CVD for different cathode assembly design. Flat- and inclined-interface carbon block top-surface and a copper insert versus the conventional insert-free designs were simulated with a myriad of other geometrical parameters to optimise the design. The results informed about the optimum insert positioning to about 75 mm from the collector base and the energy saving possibilities due to reduction in the CVD with a cathode design with inclined-interface carbon block and copper insert in the collector bar.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. von Kaenel and J. Antille, Light Met. 2011.
W. T. Choate and J. A. S. Green, “US energy requirements for aluminum production: historical perspective, theoretical limits and new opportunities,” US Department of Energy, Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, BOOK, 2003.
R. Beeler, “An analytical model for cathode voltage drop in aluminum reduction cells,” in LIGHT METALS-WARRENDALE-PROCEEDINGS-, 2003.
M. Blais, M. Désilets, and M. Lacroix, Appl. Therm. Eng., vol. 58, 2013.
S. Das, Y. Morsi, and G. Brooks, JOM, vol. 66, 2014.
A. Gupta, S. Modak, M. Sahoo, and J. Janardhanan, in Light Metals 2015, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2015.
A. Gupta, A. Jha, M. Sahoo, J. Jinil, and J. P. Nayak, in The International Committee for Study of Bauxite, Alumina & Aluminium, 2015.
F. Naixiang, T. Yingfu, P. Jianping, W. Yaowu, Q. Xiquan, and T. Ganfeng, Essent. Readings Light Met. Alum. Reduct. Technol. Vol. 2.
Y. Song, J. P. Peng, Y. W. Wang, Y. Z. Di, B. K. Li, and N. X. Feng, Metalurgija, vol. 55, 2016.
M. Gagnon, P. Goulet, R. Beeler, D. Ziegler, and M. Fafard, Light Met. 2013.
R. von Kaenel, J. Antille, and L. Bugnion, in Light Metals 2015, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2015, pp. 807–812.
P. Morel, “Construction of the lower part of the crucible of igneous electrolysis cells,” US 2846388 A, 05-Aug-1958.
B. Allano, D. Bonnafous, J. Camire, M. Desilets, L. Fiot, P. Fournier, Y. Gauthier, D. Laroche, O. Martin, and P. Thibeault, “Electrolysis cell for the production of aluminum comprising means to reduce the voltage drop,” EP1927679 A1, 06-Aug-2013.
E. Hagen and B. ØYE, “An electrode for aluminium production and a method of making same,” WO2014116117 A1, 31-Jul-2014.
K. R. Von and G. Spinetti, “Cathode current collector for a Hall–Heroult cell,” WO2016079605 A1, 26-May-2016.
L. St-Georges, L. Kiss, and D. Marceau, Minerals, Metals and Materials Society/AIME, 420 Commonwealth Dr., P. O. Box 430 Warrendale PA 15086 USA.[np]. 14-18 Feb. Minerals, Metals and Materials Society/AIME, 420 Commonwealth Dr., P. O. Box 430 Warrendale PA 15086 USA, 2010.
A. Agnihotri, S. U. Pathak, and J. Mukhopadhyay, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., vol. 67, 2014.
A. Agnihotri, S. U. Pathak, and J. Mukhopadhyay, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., vol. 67, 2014.
Ø. Østrem, “Cathode wear in Hall–Héroult cells,” JOUR, Norges teknisk-naturvitenskapelige universitet, Fakultet for naturvitenskap og teknologi, Institutt for materialteknologi, 2013.
M. P. Taylor, W. D. Zhang, V. Wills, and S. Schmid, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., vol. 74, 1996.
V. Gusberti, D. S. Severo, B. J. Welch, and M. Skyllas-Kazacos, Light Met., vol. 2012, 2012.
V. Gusberti, D. S. Severo, B. J. Welch, and M. Skyllas-Kazacos, “Modelling the Aluminium Smelting Cell Mass and Energy Balance–a Tool Based on the 1st Law of Thermodynamics,” in Proceedings of 10th Australian Aluminium Smelting Technology Conference, Launceston, TAS, 2011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R., Das, K., Mishra, A.K. et al. An Approach for Estimation of Cathode Voltage Drop in an Aluminum Reduction Cell with an Inclined Carbon Block and a Copper Insert. Trans Indian Inst Met 70, 1795–1804 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-016-0978-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-016-0978-5