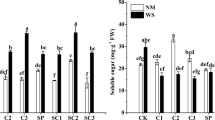
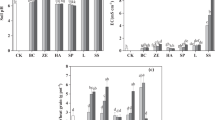
Abstract
Sepiolite shows great potential to reduce pollution risk of cadmium (Cd)-contaminated rice of acidic paddy soils, but its effect was the synergy of water–organic fertilizer coupling in practical application. In this study, we studied the effect of goat manure (GM) in primordial and sepiolite (SP) amended soil under aerobic, intermittent, and flooded irrigation condition. The results showed that the application of goat manure in SP-amended soil increased soil pH by 15.6%–23.6%. The application of goat manure increased the content of DOM by 244.3%, 135.2% in unamended and sepiolite amended soil, respectively. As a consequence, the application of GM increased available Cd extracted by DTPA in SP-amended soil under aerobic and flooded condition, but decreased available Cd under intermittent irrigation condition. The application of sepiolite alone in Cd polluted soil decreased the accumulation of Cd in unpolished rice at the first year, but Cd content witnessed slight increase at the second year. Under intermittent condition, the application of goat manure in SP-amended soil decreased Cd content by 229.2%, 59.3% of unpolished rice in the first and second year, respectively. As a result, the application of goat manure and intermittent irrigation pattern could present a water–organic fertilizer coupling effect in SP-amended soil and further increased the long-term passivation effect of sepiolite.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal A, Sahu KK (2006) Kinetic and isotherm studies of cadmium adsorption on manganese nodule residue. J Hazard Mater 137:915–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.03.039
Bermudez GMA, Jasan R, Pla R et al (2012) Heavy metals and trace elements in atmospheric fall-out: their relationship with topsoil and wheat element composition. J Hazard Mater 213–214:447–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.02.023
Bi XY, Feng XB, Yang YG et al (2006) Environmental contamination of heavy metals from zinc smelting areas in Hezhang County, western Guizhou. China Environ Int 32:883–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2006.05.010
Bian PY, Zhang JJ, Zhang CL, Huang H, Rong Q, Wu HX, Li X, Xu MM, Liu Y, Ren SW (2018) Effects of silk-worm excrement biochar combined with different iron-based materials on the speciation of cadmium and lead in soil. Appl Sci 8(10):1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101999
Bolan N, Mahimairaja S, Kunhikrishnan A, Naidu R (2013) Sorption-bioavailability nexus of arsenic and cadmium in variable-charge soils. J Hazard Mater 261:725–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.09.074
Cang L, Xing J, Liu C, Wang Y, Zhou D (2020) Effects of different water management strategies on the stability of cadmium and copper immobilization by biochar in rice-wheat rotation system. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 202:110887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110887
Chen ZY, Lu ZW, Zhang YP, Li BB, Chen CH, Shen K (2021) Effects of biochars combined with ferrous sulfate and pig manure on the bioavailability of Cd and potential phytotoxicity for wheat in an alkaline contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 753:141832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141832
Ekaterina VR, Jurate K, Lars G, Allan H (2005) Changes in soil organic matter composition and quantity with distance to a nickel smelter—a case study on the Kola Peninsula. NW Russia 127(3–4):216–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.12.010
Ekoa Bessa AZ, Ngueutchoua G, Kwewouo Janpou A, El-Amier YA, Njike Njome Mbella Nguetnga O-A, Kankeu Kayou UR, Armstrong-Altrin JS (2020) Heavy metal contamination and its ecological risks in the beach sediments along the Atlantic Ocean (Limbe coastal fringes Cameroon). Earth Syst Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-020-00167-5
Fellet G, Marmiroli M, Marchiol L (2014) Elements uptake by metal accumulator species grown on mine tailings amended with three types of biochar. Sci Total Environ 468–469:598–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.072
Fulda B, Voegelin A, Ehlert K, Kretzschmar R (2013) Redox transformation, solid phase speciation and solution dynamics of copper during soil reduction and reoxidation as affected by sulfate availability. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 123:385–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2013.07.017
Gao J, Lv J, Wu H, Dai Y, Nasir M (2018) Impacts of wheat straw addition on dissolved organic matter characteristics in cadmiumcontaminated soils: insights from fluorescence spectroscopy and environmental implications. Chemosphere 193:1027–1035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.112
Hansen V, Hauggaard-Nielsen H, Petersen CT, Mikkelsen TN, Müller-Stöver D (2016) Effects of gasification biochar on plant-available water capacity and plant growth in two contrasting soil types. Soil Tillage Res 161:1–9
He M, Wang T, Liu T, Ma X (2020) Attapulgite and processed oyster shell powder effectively reduce cadmium accumulation in grains of rice growing in a contaminated acidic paddy field. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 209:111840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111840
Jiang H, Li TQ, Han X, Yang XE, He ZL (2012) Effects of pH and low molecular weight organic acids on competitive adsorption and desorption of cadmium and lead in paddy soils. Environ Monit Assess 184(10):6325–6335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2422-y
Jin ZH, Zhang M, Li R, Zhang X, Wang GL, Liu XS, Qu JJ, Jin Y (2020) Spent mushroom substrate combined with alkaline amendment passivates cadmium and improves soil property. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(2):16317–16325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08099-3
Khaokaew S, Chaney RL, Landrot G, Ginder-Vogel M, Sparks DL (2011) Speciation and release kinetics of cadmium in an alkaline paddy soil under various flooding periods and draining conditions. Environ Sci Technol 45:4249–4255. https://doi.org/10.1021/es103971y
Kögel-Knabner I, Amelung W, Cao Z, Fiedler S, Frenzel P, Jahn R, Kalbitz K, Kölbl A, Schloter M (2010) Biogeochemistry of paddy soils. Geoderma 157(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.03.009
Lahori HA, Zhang ZQ, Guo ZY, Mahar A, Li RH, Kumar AM, Ali ST, Kumbhar F, Wang P, Shen F, Zhao JC, Huang H (2017) Potential use of lime combined with additives on (im)mobilization and phytoavailability of heavy metals from Pb/Zn smelter contaminated soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 145:313–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.07.049
Li RY, Zhou ZG, Xie XJ, Li YX, Zhang YH, Xu XH (2016) Effects of dissolved organic matter on uptake and translocation of lead in Brassica chinensis and potential health risk of Pb. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13(7):687. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13070687
Li G, Khan S, Ibrahim M, Sun TR, Tang JF, Cotner JB, Xu YY (2018) Biochars induced modification of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in soil and its impact on mobility and bioaccumulation of arsenic and cadmium. J Hazard Mater 348:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.01.031
Liang XF, Xu Y, Xu YM, Wang L, Sun YB, Huang QQ, Huang R (2016) Two-year stability of immobilization effect of sepiolite on Cd contaminants in paddy soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:12922–12931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6466-y
Liang XF, Qin X, Huang QQ, Huang R, YinWangSunXu XLYBYM (2017) Mercapto functionalized sepiolite: a novel and efficient immobilization agent for cadmium polluted soil. RSC Adv 7(63):39955–39961. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra07893e
Lin JJ, He FX, Owens G, Chen ZL (2021) How do phytogenic iron oxide nanoparticles drive redox reactions to reduce cadmium availability in a flooded paddy soil. J Hazard Mater 403:123736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123736
Liu Y, Xu Y, Qin X et al (2019a) Effects of water and organic manure coupling on the immobilization of cadmium by sepiolite. J Soils Sediments 19:798–808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2081-5
Liu Y, Xu Y, Huang Q et al (2019b) Effects of chicken manure application on cadmium and arsenic accumulation in rice grains under different water conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:30847–30856. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06271-y
Liu ZB, Huang Y, Ji XH, Xie YH, Peng JW, Eissa MA, Fahmy AE, Abou-Elwafa SF (2020) Effects and mechanism of continuous liming on cadmium immobilization and uptake by rice grown on acid paddy soils. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20:2316–2328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00297-9
Luo C, Wei R, Guo D, Zhang S, Yan S (2013) Adsorption behavior of MnO2 functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes for the removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 225:406–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.03.128
Lv YF, Ren YF, Liu D, Zhang YC, He JY (2014) Effects of different water managements on yield and cadmium accumulation in rice. Adv Mater Res 1073–1076:248–252. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.1073-1076.248
Maisch M, Lueder U, Kappler A, Schmidt C (2019) Iron Lung—how rice roots induce iron redox changes in the rhizosphere and create niches for microaerophilic Fe(II)-oxidizing bacteria. Environ Sci Technol 6(10):600–605. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.9b00403
Mohamed I, Ahamadou B, Li M, Gong CX, Cai P, Wei L, Huang QY (2010) Fractionation of copper and cadmium and their binding with soil organic matter in a contaminated soil amended with organic materials. J Soils Sediments 10(6):973–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-010-0199-1
Nanda KF, Adriano SN (2014) Management of soil acidity of South American soils for sustainable crop production. Adv Agron 128:221–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-802139-2.00006-8
Ran HZ, Guo ZH, Shi L, Feng WL, Xiao XY, Peng C, Xue QH (2019) Effects of mixed amendments on the phytoavailability of Cd in contaminated paddy soil under a rice-rape rotation system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(14):14128–14136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04477-8
Ren J, Fan W, Wang X, Ma QQ, Li XM, Xu ZZ, Wei CY (2016) Influences of size fractionated humic acids on arsenite and arsenate complexation and toxicity to Daphnia magna. Water Res 108:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.10.052
Richard C, Guyot G, Trubetskaya O, Trubetskoj M, Cavani L (2009) Fluorescence analysis of humic-like substances extracted from composts: influence of composting time and fractionation. Environ Chem Lett 7(1):61–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-008-0136-3
Rinklebe J, Shaheen SM, Yu K (2016) Release of As, Ba, Cd, Cu, Pb, and Sr under pre-definite redox conditions in different rice paddy soils originating from the USA and Asia. Geoderma 270:21–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.10.011
Rizwan M, Ali S, Ibrahim M, Farid M, Adrees M, Bharwana SA, Rehman MZ, Qayyum MF, Abbas F (2015) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of drought and salt stress in plants: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:15416–15431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5305-x
Rizwan M, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Ibrahim M, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Abbas T, Ok YS (2016) Mechanisms of biochar-mediated alleviation of toxicity of trace elements in plants: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(3):2230–2248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5697-7
Salati S, Quadri G, Tambone FA (2010) Fresh organic matter of municipal solid waste enhances phytoextraction of heavy metals from contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 158(5):1899–1906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.10.039
Song T, Das D, Hu QJ, Yang F, Zhang JH (2021) Alternate wetting and drying irrigation and phosphorus rates affect grain yield and quality and heavy metal accumulation in rice. Sci Total Environ 752:141862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141862
Spokas KA, Novak JM, Masiello CA, Johnson MG, Colosky EC, Ippolito JA, Trigo C (2014) Physical disintegration of biochar: an overlooked process. Environ Sci Technol Lett 1:326–332
Sun T, Yingming Xu, Sun Y, Wang L, Liang X, Jia H (2021) Crayfish shell biochar for the mitigation of Pb contaminated water and soil: Characteristics, mechanisms, and applications. Environ Pollut 271:116308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116308
Tang L, Hamid Y, Zehra A, Shohag MJI, He ZL, Yang XE (2020) Endophytic inoculation coupled with soil amendment and foliar inhibitor ensure phytoremediation and argo-production in cadmium contaminated soil under oilseed rape-rice rotation system. Sci Total Environ 748:142481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142481
Tessier A, Campell PGC, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51:844–851. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac50043a017
Wang AY, Wang MY, Liao Q, He XQ (2016a) Characterization of Cd translocation and accumulation in 19 maize cultivars grown on Cd-contaminated soil: implication of maize cultivar selection for minimal risk to human health and for phytoremediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(6):5410–5419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5781-z
Wang Q, Chen L, He LY, Sheng XF (2016b) Increased biomass and reduced heavy metal accumulation of edible tissues of vegetable crops in the presence of plant growth-promoting Neorhizobium huautlense T1–17 and biochar. Agric Ecosyst Environ 228:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2016.05.006
Wang FY, Zhang SQ, Cheng P, Zhang SW, Sun YH (2020) Effects of soil amendments on heavy metal immobilization and accumulation by maize grown in a multiple-metal-contaminated soil and their potential for safe crop production. Toxic 8:102–117. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040102
Wang FJ, Li WL, Li QS, Wang LL, He T, Wang FP, Xu ZM (2021a) Nitrogen fertilizer management affects remobilization of the immobilized cadmium in soil and its accumulation in crop tissues. Environ Sci Pollut Res (In Press). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12868-z
Wang Y, Yingming Xu, Liang X, Wang L, Sun Y, Qingqing Huang Xu, Qin LZ (2021b) Soil application of manganese sulfate could reduce wheat Cd accumulation in Cd contaminated soil by the modulation of the key tissues and ionomic of wheat. Sci Total Environ 770:145328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145328
Wiggenhauser M, Aucour AM, Bureau S, Campillo S, Telouk P, Romani M, Ma JF, Landrot G, Sarret G (2020) Cadmium transfer in contaminated soil-rice systems: insights from solid-state speciation analysis and stable isotope fractionation. Environ Pollut 269:115934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115934
Xiao SS, Li LQ, Pan GX, Jiao SJ, Gong WQ (2006) Effect of submerging and wetting-redrying on Cd speciation and uptake by sorghum hybrid sudangrass in two paddy soils under spiked Cd. Environ Sci 27(2):351–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2040(06)60041-8
Xiao QQ, Wong MH, Huang L, Ye Z (2015) Effects of cultivars and water management on cadmium accumulation in water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica Forsk.). Plant Soil 391:33–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2409-5
Xie YL, Xiao KM, Sun Y, Gao YF, Yang H, Xu H (2018) Effects of amendments on heavy metal immobilization and uptake by Rhizoma chuanxiong on copper and cadmium contaminated soil. R Soc Open Sci 5(8):181138. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.181138
Yang T, Yingming Xu, Huang Q, Sun Y, Liang X, Lin Wang Xu, Qin LZ (2021) Adsorption characteristics and the removal mechanism of two novel Fe-Zn composite modified biochar for Cd(II) in water. Biores Technol 333:125078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125078
Ye XX, Li HY, Zhang LG, Chai RS, Tu RF (2018) Amendment damages the function of continuous flooding in decreasing Cd and Pb uptake by rice in acid paddy soil. Ecotox Environ Safety 147:708–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.09.034
Yin XL, Xu YM, Huang R, Xie ZL, Cai YM, Liang XF (2017) Remediation mechanisms for Cd-contaminated soil using natural sepiolite at the field scale. Environ Sci Process Impacts 19:1563–1570. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7em00262a
Zhou W, Ren L, Zhu L (2017) Reducement of cadmium adsorption on clay minerals by the presence of dissolved organic matter from animal manure. Environ Pollut 223:247–254
Zhou T, Wu LH, Christie P, Luo YM, Fornara DA (2018a) The efficiency of Cd phytoextraction by S. plumbizincicola increased with the addition of rice straw to polluted soils: the role of particulate organic matter. Plant Soil 429:321–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3698-2
Zhou T, Wu LH, Luo YM, Christie P (2018b) Effects of organic matter fraction and compositional changes on distribution of cadmium and zinc in long-term polluted paddy soils. Environ Pollut 232:514–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.09.081
Zhou H, Zhou X, Zeng M, Liao BH, Liu L, Yang WT, Wu YM, Qiu QY, Wang YJ (2014) Effects of combined amendments on heavy metal accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) planted on contaminated paddy soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 101:226–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.01.001
Zhu B, Gutknecht JLM, Herman DJ, Keck DC, Firestone MK, Cheng WX (2014) Rhizosphere priming effects on soil carbon and nitrogen mineralization. Soil Biol Biochem 76:183–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.04.033
Acknowledgements
The current research was supported by the Science and Technology Support Plan Project of Tianjin (20YFZCSN00650).
Funding
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Support Plan Project of Tianjin (20YFZCSN00650).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. YL and YX contributed to the conception of the study. YL, QH and QX performed the experiment. LZ contributed significantly to data collection. XL, LW, and YS helped perform the analysis with constructive discussions. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YL and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Xu, Y., Huang, Q. et al. Effects of water–organic fertilizer coupling on immobilization remediation technology using sepiolite. Environ Earth Sci 81, 388 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10472-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10472-z