Abstract
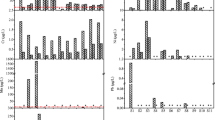
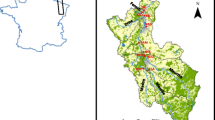
The aim of this study was to assess the particulate metal pollution status and the evolution of particulate metal contamination after the implementation of sewage treatment systems in the Deba River catchment during flood events. Concentrations of suspended particulate matter (SPM), dissolved (DOC) and particulate (POC) organic carbon and metals (Fe, Mn, Zn, Ni, Cu, Cr and Pb) were monitored in the urban watershed over four hydrological years. Geoaccumulation index was used to determine the pollution degree and a number of statistical analyses were performed to elucidate temporal changes. 14 flood events were analyzed from October 2011 to September 2015. The content of metals (Fe, Mn, Zn, Ni, Cr, Cu and Pb) in suspended solids showed a high degree of temporal variability which depended on number of factors being the hydrodynamic process the main one controlling the behaviour of particulate metals. Zn, Ni Cr and Cu appear to be mainly related to anthropogenic sources, whereas Pb appears to be lithogenic in character (like Fe) possibly related to an ageing process. The decrease of metal pollution degree and the homogenisation of organic and metal sources could be a consequence of the wastewater treatment, despite it seems likely that this will be a long-term process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akin BS, Kirmizigül O (2017) Heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of Gökçekaya Dam Lake, Eskişehir, Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 76:402
Alloway BJ (2013) Sources of heavy metals and metalloids in soils. In: Alloway BJ (ed) Heavy metals in soils. Trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability, environmental pollution, vol 22, 3rd edn. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 12–50. Print ISBN: 978-94-007-4469-1. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-4470-7_2
Alonso E, Villar P, Santos A, Aparicio I (2006) Fractionation of heavy metals in sludge from anaerobic wastewater stabilization ponds in Southern Spain. Waste Manag 26:1270–1276
American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association & Water Pollution Control Federation (APHA-AWWA-WPCF) (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Association, Washington, DC
Banas D, Marin B, Skraber S, Chopin EIB, Zanella A (2010) Copper mobilization affected by weather conditions in a stormwater detention system receiving runoff waters from vineyard soils (Champagne, France). Environ Pollut 158:476–482
Barać N, Ŝkrivanj S, Bukumirić Z, Živojinović D, Manojlović D, Barać M, Petrović R, Ćorac A (2016) Distribution and mobility of heavy elements in floodplain agricultural soils along the Ibar River (Southern Serbia and Northern Kosovo). Chemometric investigation of pollutant sources and ecological risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:9000–9011
Bibby RL, Webster-Brown JG (2005) Characterisation of urban catchment suspended particulate matter (Auckland region, New Zealand); a comparison with non-urban SPM. Sci Total Environ 343:177–197
Bibby RL, Webster-Brown JG (2006) Trace metal adsorption onto urban stream suspended particulate matter (Auckland region, New Zealand). Appl Geochem 21:1135–1151
Borja A, Galparsoro I, Solaun O, Muxika I, Tello EM, Uriarte A, Valencia V (2006) The European Water Framework Directive and the DPSIR, a methodological approach to assess the risk of failing to achieve good ecological status. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 66:84–96
Carter J, Walling DE, Owens PN, Leeks GJL (2006) Spatial and temporal variability in the concentration and speciation of metals in suspended sediment transported by the River Aire, Yorkshire, UK. Hydrol Process 20:3007–3027
Chen J, Bouchez J, Gaillardet J, Louvat P (2014) Behaviors of major and trace elements during single flood event in the Seine River, France. Proc Earth Planet Sci 10:343–348
Cheng H, Liang A, Zhi Z (2017) Heavy metals sedimentation risk assessment and sources analysis accompanied by typical rural water level fluctuating zone in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Environ Earth Sci 76:418
Chon HS, Ohandja DG, Voulvoulis N (2012) The role of sediments as a source of metals in river catchments. Chemosphere 88:1250–1256
Coates-Marnane J, Olley J, Burton J, Grinham A (2016) The impact of a high magnitude flood on metal pollution in a shallow subtropical estuarine embayment. Sci Total Environ 569–570:716–731
Coynel A, Schäfer J, Blanc G, Bossy C (2007) Scenario of particulate trace metal and metalloid transport during a major flood event inferred from transient geochemical signals. Appl Geochem 22:821–836
Dojlido J, Best A (1993) Chemistry of water and water pollution. Ellis Horwood Limited, Chichester, ISBN: 0138789193
Du Laing G, Rinklebe J, Vandecasteele B, Meers E, Tack FMG (2009) Trace metal behaviour in estuarine and riverine floodplain soils and sediments: a review. Sci Total Environ 407:3972–3985
Eggleton J, Thomas KV (2004) A review of factors affecting the release and bioavailability of contaminants during sediment disturbance events. Environ Int 30:973–980
EVE (Ente Vasco de la Energía), (1989) Mapa geológico del País Vasco a escala 1:25.000: 63-I, 63-III, 88-I y 88-III, planos
Gonelli C, Renella G (2013) Chromium and Nickel. In: Alloway BJ (ed) Heavy metals in soils. Trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability, environmental pollution, vol 22, 3rd edn. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 313–334. Print ISBN: 978-94-007-4469-1. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-4470-7_2
Hargreaves AJ, Vale P, Whelan J, Constantino C, Dotro G, Campo P, Cartmell E (2017) Distribution of trace metals (Cu, Pb, Ni, Zn) between particulate, colloidal and truly dissolved fractions in wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 175:239–246
Hu N, Liu J, Huang P, Yan S, Shi X, Ma D (2017) Sources, geochemical speciation, and risk assessment of metals in coastal sediments: a case study in the Bohai Sea, China. Environ Earth Sci 76:309
Islam Md S, Ahmed MK, Raknuzzaman M, Habibullah-Al-Mamun M, Islam MK (2015) Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: a preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol Ind 48:282–291
Kumar M (2016) Understanding the remobilization of copper, zinc, cadmium and lead due to ageing through sequential extraction and isotopic exchangeability. Environ Monit Assess 188:381
Li LY, Hall K, Yuan Y, Mattu G, MnCallum D, Chen M (2009) Mobility and bioavailability of trace metals in the water-sediment system of the highly urbanized brunette watershed. Water Air Soil Pollut 197:249–266
Liu J, Li S-L, Chen J-B, Zhong J, Yue F-J, Lang Y, Ding H (2017) Temporal transport of major and trace elements in the upper reaches of the Xijiang River, SW China. Environ Earth Sci 76:299
Ma Y, Qin Y, Zheng B, Zhao Y, Zhang L, Yang C, Shi Y, Wen Q (2016) Three Gorges Reservoir: metal pollution in surface water and suspended particulate matter on different reservoir operation periods. Environ Earth Sci 75:1413
Martínez-Santos M, Antigüedad I, Ruiz-Romera E (2013) Hydrochemical variability during flood events within a small forested catchment in Basque Country (Northern Spain). Hydrol Process 28:5367–5381. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10011
Martínez-Santos M, Probst A, García-García J, Ruiz-Romera E (2015) Influence of anthropogenic inputs and a high-magnitude flood event on metal contamination pattern in surface bottom sediments from the Deba River urban catchment. Sci Total Environ 514:10–25
Mellor A (2001) Lead and zinc in the Wallsend Burn, an urban catchment in Tyneside, UK. Sci Total Environ 269:49–63
Myangan O, Kawahigashi M, Oyuntsetseg B, Fujitake N (2017) Impact of land uses on heavy metal distribution in the Selenga River system in Mongolia. Environ Earth Sci 76:346
Nazeer S, Hashmi MZ, Malik RF (2014) Heavy metals distribution, risk assessment and water quality characterization by water quality index of the River Soan, Pakistan. Ecol Ind 43:262–270
Nicolau R, Lucas Y, Merdy P, Raynaud M (2012) Base flow and stormwater net fluxes of carbon and trace metals to the Mediterranean sea by an urbanized small river. Water Res 46:6625–6637
Ollivier P, Radakovitch O, Hamelin B (2006) Unusual variations of dissolved As, Sb and Ni in the Rhône River during flood events. J Geochem Explor 88:394–398
Ollivier P, Radakovitch O, Hamelin B (2011) Major and trace element partition and fluxes in the Rhône River. Chem Geol 285:15–31
Orkun ID, Galip S, Cagatayhay BE, Turan Y, Bulent S (2011a) Assessment of metal pollution in water and surface sediments of the Seyhan River, Turkey, Using Different Indexes. Clean Soil Air Water 39(2):185–194
Orkun ID, Galip S, Cagatayhay BE, Turan Y, Bulent S (2011b) Heavy metal content and distribution in surface sediments of the Seyhan River, Turkey. J Environ Manag 92:2250–2259
Oursel B, Garnier C, Zebracki M, Durrieu G, Pairaud I, Omanović D, Cossa D, Lucas Y (2014) Flood inputs in a Mediterranean coastal zone impacted by a large urban area: dynamic and fate of trace metals. Mar Chem 167:44–56
Owens PN, Xu Z (2011) Recent advances and future directions in soils and sediments research. J Soils Sediments 11:875–888
Palleiro L, Rodríguez-Blanco ML, Taboada-Castro MM, Taboada-Castro MT (2014) Hydroclimatic control of sediment and metal export from a rural catchment in Northwest Spain. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci Discuss 11:3757–3786
Peraza-Castro M, Sauvage S, Sánchez-Pérez JM, Ruiz-Romera E (2016) Effect of flood events on transport of suspended sediments, organic matter and particulate metals in a forest watershed in the Basque Country (Northern Spain). Sci Total Environ 569–570:784–797
Pereira P, Ferreira AJD, Sarah P et al. (2016) Preface. J Soils Sediments 16: 2493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1566-3
Radakovitch O, Roussiez V, Ollivier P, Ludwig W, Grenz C, Probst JL (2008) Input of particulate heavy metals from rivers and associated sedimentary deposits on the Gulf of Lion continental shelf. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 77:285–295
Roussiez V, Probst A, Probst JL (2013) Significance of floods in metal dynamics and export in a small agricultural catchment. J Hydrol 499:71–81
Ruiz E, Echeandía A, Romero F (1991) Microanalytical determination of metallic constituents of river sediments. J Anal Chem 340:223–229
Sakan S, Dordević D, Manojlović DD, Predrag PS (2009) Assessment of heavy metal pollutants accumulation in the Tisza river sediments. J Environ Manag 90:3382–3390
Sekabira K, Origa HO, Basamba TA, Mutumba G, Kakudidi E (2010) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in the urban stream sediments and its tributaries. Int J Environ Sci Tech 7(3):435–446
USEPA (2007) Sediment quality guideline. Method 3051A: microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, soils and oils. US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington DC. http://www.epa.gov/wastes/hazard/testmethods/%20sw846/online/3_series.htm. Accessed Apr 2013
Violintzts A, Arditsoglou A, Voutsa D (2009) Elemental composition of suspended particulate matter and sediments in the coastal environment of Thermaikos Bay, Greece: delineating the impact of inland waters and wastewaters. J Hazard Mater 166:1250–1260
Wang Y, Liu RH, Zhang YQ, Cue ZQ, Tang AK, Zhang LJ (2016) Transport of heavy metals in the Huanghe River estuary, China. Environ Earth Sci 75:288
Wen Y, Yang Z, Xia X (2013) Dissolved and particulate zinc and nickel in the Yangtze River (China): distribution, sources and fluxes. Appl Geochem 31:199–208
Wong CSC, Li X, Thornton I (2006) Urban environmental geochemistry of trace metals. Environ Pollut 142:1–16
Yang Z, Wang Y, Shen Z, Niu J, Tang Z (2009) Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediments from the mainstream, tributaries, and lakes of the Yangtze River catchment of Wuhan, China. J Hazard Mater 166:1186–1194
Yang Z, Xia X, Wang Y, Ji J, Wang D, Hou Q, Yu T (2014) Dissolved and particulate partitioning of trace elements and their spatial–temporal distribution in the Changjiang River. J Geochem Explor 145:114–123
Zabaleta A, Martínez M, Uriarte JA, Antigüedad I (2007) Factors controlling suspended sediment yield during runoff events in small headwater catchments of the Basque Country. Catena 71:179–190
Zabaleta A, Antigüedad I, Barrio I, Probst JL (2016) Suspended sediment delivery from small catchments to the Bay of Biscay. What are the controlling factors? Earth Surf Process Landforms 41:1894–1910
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Ministry of Science and Innovation (project CGl2011-465 26236), Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (project CTM2014-55270-R), Basque Government through the Consolidated Research Group Project ref. IT-742-13 and Consolidated Research Group Project ref. IT-1029-16 for supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-García, J., Ruiz-Romera, E., Martínez-Santos, M. et al. Temporal variability of metallic properties during flood events in the Deba River urban catchment (Basque Country, Northern Spain) after the introduction of sewage treatment systems. Environ Earth Sci 78, 23 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-8014-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-8014-1