Abstract
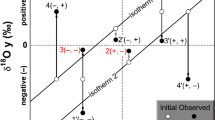
The environmental isotopes such as deuterium and oxygen-18 and the deuterium excess values have been used to assess groundwater recharge sources and their dynamics in Khan Younis City in the Gaza Strip in Palestine. Three isotopic lines for the relationship between δ2H and δ18O were used in the assessment. These lines are the global meteoric water line, the local meteoric water line and the groundwater evaporation line. The δ2H, δ18O and D-excess values indicate that deuterium and oxygen-18 isotopes originated in the groundwater from groundwater mixing with rainfall and other water sources; the groundwater in the area recharged from rainfall from a distant source that came from the Mediterranean Sea and from other sources such as wastewater, irrigation return flow and saline water.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreha AG (2014) Hydrogeochemical and water quality investigation on irrigation and drinking water supplies in the Mekelle region, northern Ethiopia. Master thesis, University of Twente, Netherlands
Abu Jabal MS, Abustan I, Rozaimy MR, El Najar H (2015) Groundwater beneath the urban area of Khan Younis City, southern Gaza Strip (Palestine): hydrochemistry and water quality. Arab J Geosci 8:2203–2215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1346-6
Abu Jabal MS, Abustan I, Rozaimy MR, El Najar H (2017) Groundwater beneath the urban area of Khan Younis City, southern Gaza Strip (Palestine): assessment for multi-domestic purposes. Arab J Geosci 10:257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3036-7
Adomako D, Osae S, Akiti TT, Faye S, Maloszewski P (2011) Geochemical and isotopic studies of groundwater conditions in the Densu river basin of Ghana. Environ Earth Sci 62:1071–1084. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0595-2
Ako AA (2011) Hydrological study on groundwater in the Banana plain and Mount Cameroon area-Cameroon volcanic line (CVL). Ph.D. thesis, Kumamoto University, Japan
Al-Agha MR (2005) Hydrogeochemistry and carbonate saturation model of groundwater, Khanyounis Governorate—Gaza Strip, Palestine’. Environ Geol 47:898–906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-004-1211-0
Al-Charideh A, Kattaa B (2016) Isotope hydrology of deep groundwater in Syria: renewable and non-renewable groundwater and paleoclimate impact. Hydrogeol J 24:79–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-015-1324-4
Al-Charideh A, Abou-Zakhem B, AL-Charideh A, Abou-Zakhem B (2009) Geochemical and isotopic characterization of groundwater from the Paleogene limestone aquifer of the upper Jezireh, Syria. Environ Earth Sci 59:1065–1078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0098-1
Amiri V, Nakhaei M, Lak R, Kholghi M (2016) Geophysical, isotopic, and hydrogeochemical tools to identify potential impacts on coastal groundwater resources from Urmia hypersaline lake, NW Iran. Envon Sci Pollut Res 23:16738–16760
Ammar SB, Taupin JD, Zouari K, Khouatmia M (2016) Identifying recharge and salinization sources of groundwater in the Oussja Ghar el Melah plain (northeast Tunisia) using geochemical tools and environmental isotopes. Environ Earth Sci 75:606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5431-x
Ayadi R, Zouari K, Saibi H, Trabelsi R, Khanfi H, Itoi R (2016) Determination of the origins and recharge rates of the Sfax aquifer system (southeastern Tunisia) using isotope tracers. Environ Earth Sci 75:636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5445-4
Blasch KW, Bryson JR (2007) Distinguishing sources of ground water recharge by using δ2H and δ18O. Ground Water 45:294–308. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2006.00289.x
CAMP (2000) Coastal aquifer management program, integrated aquifer management plan (Gaza Strip), Final Report. Metcalf & Eddy, Inc., and Camp Dresser & McKee International Inc., Report submitted to the United State Agency for International Development (USAID) mission to Gaza and West Bank, in cooperation with the Palestinian Water Authority (PWA)
Celle-Jeanton H, Travi Y, Blavoux B (2001) Isotopic typology of the precipitation in the western Mediterranean region at three different time scales. Geophys Res Lett 28:1215–1218
Chen L, Ma T, Du Y, Xiao C, Chen X, Liu C, Wang Y (2016) Hydrochemical and isotopic (2H, 18O and 37Cl) constraints on evolution of geothermal water in coastal plain of Southwestern Guangdong Province, China. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 318:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2016.03.003
Chiogna G, Santoni E, Caminb F, Tononb A, Majone B, Trenti A, Bellin A (2014) Stable isotope characterization of the Vermigliana catchment. J Hydrol 509:295–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.11.052
Coplen TB, Wildman JD, Chen J (1991) Improvements in the gaseous hydrogen–water equilibration technique for hydrogen isotope ratio analysis. Anal Chem 63:910–912
Craig H (1961) Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 133:1702–1703
Dansgaard W (1964) Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 16:436–468
Dhaoui Z, Zouari K, Taupin JD, Farouni R (2016) Hydrochemical and isotopic investigations as indicators of recharge processes of the Continental Intercalaire aquifer (eastern piedmont of Dahar, southern Tunisia). Environ Earth Sci 75:1186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5990-x
Edirisinghea EANV, Karunarathneb GRR, Samarakoonb ASMNB, Pitawalac HMTGA, Dharmagunawardhanec HA, Tilakarathna IANDP (2016) Assessing causes of quality deterioration of groundwater in Puttalam, Sri Lanka, using isotope and hydrochemical tools. Isot Environ Health Stud 52:513–528. https://doi.org/10.1080/10256016.2015.1127918
Eshtawi T (2015) Integrated hydrologic modeling as a key for sustainable development planning of urban water resources in the semi arid watersheds of the Gaza Strip. Ph.D. thesis, Universität Bonn, Germany
Ferronsky VI, Polyakov VA (2012) Isotopes of the earth’s hydrosphere. Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-2856-1
Fynn OF, Yidana SM, Chegbeleh LP, Yiran GB (2016) Evaluating groundwater recharge processes using stable isotope signatures-the Nabogo catchment of the White Volta, Ghana. Arab J Geosci 9:279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2299-0
Gat JR (1980) The isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen in precipitation. In: Fritz P, Fontes J (eds) Handbook of environmental isotope geochemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam, Netherland, pp 21–47
Gat JR, Carmi H (1970) Evolution of the isotopic composition of atmospheric waters in the Mediterranean sea area. J Geophys Res 75:3039–3040
Gat JR, Dansgaard W (1972) Stable isotope survey of the freshwater occurrence in Palestine and northern Jordan rift valley. J Hydrol 16:177–212
Gomaah M, Meixner T, Korany EA, Garamoon H, Gomaa MA (2016) Identifying the sources and geochemical evolution of groundwater using stable isotopes and hydrogeochemistry in the Quaternary aquifer in the area between Ismailia and el Kassara canals, Northeastern Egypt. Arab J Geosci 9:437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2444-4
Grassa F, Favara R, Valenza M (2006) Moisture source in the Hyblean mountains region (south-eastern Sicily, Italy): evidence from stable isotopes signature. Appl Geochem 21:2082–2095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2006.07.014
Hadi K, Kumar US, Al-Senafy M, Bhandary H (2016) Environmental isotope systematics of the groundwater system of southern Kuwait. Environ Earth Sci 75:1096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5886-9
Hamed Y, Dahri F (2013) Hydro-geochemical and isotopic composition of groundwater, with emphasis on sources of salinity, in the aquifer system in northwestern Tunisia. J Afr Earth Sci 83:10–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2013.02.004
Horita J (1988) Hydrogen isotope analysis of natural waters using an H2–water equilibration method: a special implication to brines. Chem Geol 72:89–94
Horita J, Ueda A, Mizukami K, Takatori I (1989) Automatic δD and δ18O analyses of multi-water samples using H2–and CO2–water equilibration methods with a common equilibration set-up. Appl Radiat Isot 40:801–805
IAEA (2005) Isotopic composition of precipitation in the Mediterranean basin in relation to air circulation patterns and climate. Final report of coordinated research project 2000–2004. International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), Vienna, Austria
IAEA (2010) Sampling procedures for isotope hydrology. Booklet by the Water Resources Program. International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), Vienna
Isawi H, El-Sayed MH, Eissa M, Shouakar-Stash O, Shawky H, Abdel Mottaleb MS (2016) Integrated geochemistry, isotopes, and geostatistical techniques to investigate groundwater sources and salinization origin in the Sharm El-Shiekh area, south Sinai, Egypt. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2848-5
Jilali A, Fagel N, Amar M, Abbas M, Zarhloule Y (2016) Hydrogeochemical processes constrained by multivariate statistical methods and isotopic evidence of groundwater recharge in the aquifer of Figuig, eastern high atlas of Morocco. Arab J Geosci 9:42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2089-8
Krishnaraj S, Murugesan V, Vijayaraghavan K, Sabarathinam C, Paluchamy A, Ramachandran M (2011) Use of hydrochemistry and stable isotopes as tools for groundwater evolution and contamination investigations. Geosciences 1:16–25. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.geo.20110101.02
Leontiadis L, Vergis S, Christodoulou T (1996) Isotope hydrology study of areas in eastern Macedonia and Thrace, northern Greece. J Hydrol 182:1–17
Li P, Wu J, Qian H, Zhang Y, Yang N, Jing L, Yu P (2016) Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater in and around a wastewater irrigated forest in the southeastern edge of the Tengger desert, northwest China. Expo Health 8:331–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0193-y
Lu Y, Tang C, Chen J, Yao H (2016) Assessment of major ions and heavy metals in groundwater: a case study from Guangzhou and Zhuhai of the Pearl river delta, China. Front Earth Sci 10:340–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-015-0513-8
Mapoma HWT, Xie X, Zhu Y, Liu Y, Sitolo-Banda GC (2016) Trace element geochemical evolution and groundwater origin in North Rukuru–Songwe alluvial aquifer of northern Malawi. Environ Earth Sci 75:877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5682-6
Mazor E (2004) Chemical and isotopic groundwater hydrology, 3rd edn. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York
Mokadem N, Demdoum A, Hamed Y, Bouri S, Hadji R, Boyce A, Laouar R, Saad A (2016) Hydrogeochemical and stable isotope data of groundwater of a multi-aquifer system: northern Gafsa basin-central Tunisia. J Afr Earth Sci 114:174–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2015.11.010
Mook WG (2001) Environmental isotopes in the hydrological cycle, principles and applications, vol 1. International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), Vienna
Pang H, He Y, Zhang Z, Lu A, Gu J (2004) The origin of summer monsoon rainfall at New Delhi by deuterium excess. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 8:115–118
PCBS (2012) Estimated population in the Palestinian territory mid-year in Khan Younis governorate. Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS), Ramallah, Palestine. http://www.pcbs.gov.ps/Portals/_Rainbow/Documents/khana.htm. Accessed 23 April 2017
Peng TR, Huang CC, Zhan WJ, Wang CH (2016) Assessing groundwater sources and their association with reservoir water using stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes: a case study of the Taipei basin, northern Taiwan. Environ Earth Sci 75:753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5544-2
Qian H, Li P, Wu J, Zhou Y (2013) Isotopic characteristics of precipitation, surface and ground waters in the Yinchuan plain, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 70:57–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-2103-3
Rozanski K, Araguas-Araguas L, Gonfiantini R (1993) Isotopic patterns in modern global precipitation. Geophys Monogr 78:1–36
Sakai H, Matsubaya O (1977) Stable isotopic studies of Japanese geothermal system. Geothermics 5:97–124
Sanchez D, Barbera JA, Mudarra M, Andreo B (2015) Hydrogeochemical tools applied to the study of carbonate aquifers: examples from some karst systems of Southern Spain. Environ Earth Sci 74:199–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4307-9
Shah ZA (2013) A qualitative and quantitative study of chemical and isotopic parameters of the groundwater system in parts of Unnao district, Uttar Pradesh, India. Ph.D. thesis, Aligarh Muslim University, India
Shomar BH, Muller G, Yahya A (2005) Geochemical features of topsoils in the Gaza Strip: natural occurrence and anthropogenic inputs. Environ Res 98:372–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2004.10.008
Tiwari SK, Bartarya SK, Rai SK, Gupta AK, Asthana AKL (2016) Isotopic and geochemical studies of groundwater from the Ramganga basin and the middle Ganga Plains: implication for pollution and metal contamination. Environ Earth Sci 75:1170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5971-0
UNEP (2009) Environmental assessment of the Gaza Strip following the escalation of hostilities in December 2008–January 2009. Report by the United Nations Environmental Program (UNEP), Nairobi, Kenya
Vasanthavigar M, Srinivasamoorthy K, Prasanna MV, Ganesh BP (2012) To Understand the characteristics of stable isotopes and trace element in groundwater of Thirumanimuttar Sub-Basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Carp J Earth Environ Sci 7:89–100
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank His Excellency Ambassador Salman Al Harfi, former Ambassador for State of Palestine to the Republic of Tunisia, for his recommendation and support to the Arab Atomic Energy Agency in Tunisia to finance the isotopic analysis and also thank to the Arab Atomic Energy Agency in Tunisia, for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abu Jabal, M.S., Abustan, I., Rozaimy, M.R. et al. The deuterium and oxygen-18 isotopic composition of the groundwater in Khan Younis City, southern Gaza Strip (Palestine). Environ Earth Sci 77, 155 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7335-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7335-4