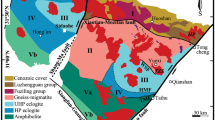
Abstract
For a long time, it has been implicitly believed that oxygen isotopes of hydrothermally altered rocks and/or minerals were only elevated by the heavy water enriched in 18O from the modern geothermal and/or fossil hydrothermal systems around the world. While it is logically likely, there is no any previous attempt to argue for the elevation of oxygen isotopes of hydrothermally altered rocks and/or minerals by a light water depleted in 18O under appropriate natural conditions. Based on a novel procedure recently proposed for dealing with thermodynamic reequilibration of oxygen isotopes between constituent minerals and water, the initial oxygen isotopes of water (i.e., \(\delta {^{18}{\text{O}}}_{\text{W}}^{\text{i}}\) value hereafter) prior to the hydrothermal alteration are theoretically inverted from the early Cretaceous postcollisional granitoid and Triassic gneissic country rock across the Dabie orogen in central-eastern China. The oxygen isotopes of hydrothermally altered rock-forming minerals were concurrently elevated by the magmatic water with moderate to high \({\delta ^{18}{\text{O}}}_{\text{W}}^{\text{i}}\) values ranging from 4.21 ± 0.04 (one standard deviation, 1SD) to 6.57 ± 0.05‰ in the course of postmagmatic processes. By contrast, oxygen isotopes of the susceptible alkali feldspar from a gneissic country rock could be preferentially elevated by the ancient meteoric water with low \(\delta {^{18}{\text{O}}}_{\text{W}}^{\text{i}}\) values down to -8.52 ± 0.56‰ during exhumation processes of the retrograde metamorphism. These fossil hydrothermal systems could kinetically sustain from a short duration of less than 12 thousand years (Kyr) via the surface-reaction oxygen exchange up to 1 million years (Myr) through the diffusive oxygen exchange, respectively, in this study. Cooling rates are further quantified for rock-forming minerals sequentially blocked and/or isolated from the magmatic water. Hereby, oxygen isotopes of constituent minerals can be hydrothermally elevated by diverse sources of water with paradoxical \(\delta {^{18}{\text{O}}}_{\text{W}}^{\text{i}}\) values, especially for the metamorphic rocks with anomalous oxygen isotopes. There is no doubt that more unexpected findings will be scientifically and methodologically decoded and/or unlocked worldwide in the coming decade(s).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allègre CJ (2008) Isotope geology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 512
Ames L, Zhou GZ, Xiong BC (1996) Geochronology and isotopic character of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism with implications for collision of the Sino-Korean and Yangtze cratons, central China. Tectonics 15:472–489
Anthony JW, Bideaux RA, Bladh KW, Nichols MC (2003) Handbook of mineralogy. Mineralogical Society of America, Chantilly (Online version:http://www.handbookofmineralogy.org)
Barnes HL (1997) Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits, 3rd edn. Wiley, Hoboken, p 972
Bryant DL, Ayers JC, Gao S, Miller CF, Zhang HF (2004) Geochemical, age, and isotopic constraints on the location of the Sino-Korean/Yangtze Suture and evolution of the Northern Dabie Complex, east central China. Geol Soc Am Bull 116:698–717
Chacko T, Cole DR, Horita J (2001) Equilibrium oxygen, hydrogen and carbon isotope fractionation factors applicable to geologic systems. Rev Mineral Geochem 43:1–81
Chen L, Yakymchuk C, Zhao K, Zhao ZF, Li DY, Gao P, Chen YX, Sun GH, Liu ZB (2023) The garnet effect on hafnium isotope compositions of granitoids during crustal anataxis. Geology 51:439–443
Cheng H, Zhang C, Vervoort JD, Wu YB, Zheng YF, Zheng S, Zhou ZY (2011) New Lu-Hf geochronology constrains the onset of continental subduction in the Dabie orogen. Lithos 121:41–54
Clayton RN, Kieffer SW (1991) Oxygen isotopic thermometer calibrations. Geochem Soc Spec Publ 3:3–10
Cole DR, Chakraborty S (2001) Rates and mechanisms of isotopic exchange. Rev Mineral Geochem 43:83–223
Cole DR, Ohmoto H (1986) Kinetics of isotopic exchange at elevated temperatures and pressures. Rev Mineral Geochem 16:41–90
Cole DR, Ohmoto H, Lasaga AC (1983) Isotopic exchange in mineral-fluid systems. I. Theoretical evaluation of oxygen isotopic exchange accompanying surface reactions and diffusion. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 47:1681–1693
Cole DR, Ohmoto H, Jacobs GK (1992) Isotopic exchange in mineral-fluid systems: III. Rates and mechanisms of oxygen isotope exchange in the system granite-H2O±NaCl±KC1 at hydrothermal conditions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:445–466
Dai LQ, Zhao ZF, Zheng YF (2015) Tectonic development from oceanic subduction to continental collision: Geochemical evidence from postcollisional mafic rocks in the Hong’an-Dabie orogens. Gondwana Res 27:1236–1254
Deng X, Yang KG, Polat A, Kusky TM, Wu KB (2014) Zircon U-Pb ages, major and trace elements, and Hf isotope characteristics of the Tiantangzhai granites in the North Dabie orogen, Central China: Tectonic implications. Geol Mag 151:916–937
Dickin AP (2018) Radiogenic isotope geology, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 482
Dodson MH (1973) Closure temperature in cooling geochronological and petrological systems. Contrib Mineral Petrol 40:259–274
Dodson MH (1976) Kinetic processes and thermal history of slowly cooling solids. Nature 259:551–553
Dodson MH (1979) Theory of cooling ages. In: Jager E, Hunziker JC (eds) Lectures in isotope geology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, pp 194–202
Ernst WG, Tsujimori T, Zhang RY, Liou JG (2007) Permo-Triassic collision, subduction-zone metamorphism, and tectonic exhumation along the East Asian continental margin. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 35:73–110
Faure G, Mensing TM (2005) Isotopes: Principles and applications, 3rd edn. Wiley, Hoboken, p 897
Fu B, Kita NT, Wilde SA, Liu XC, Cliff J, Greig A (2013) Origin of the Tongbai-Dabie-Sulu Neoproterozoic low-δ18O igneous province, east-central China. Contrib Mineral Petrol 165:641–662
Giletti BJ, Yund RA (1984) Oxygen diffusion in quartz. J Geophys Res 89:4039–4046
Giletti BJ, Semet MP, Yund RA (1978) Studies in diffusion - III. Oxygen in feldspars: An ion microprobe determination. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 42:45–57
Hacker BR, Ratschbacher L, Webb L, Ireland T, Walker D, Dong SW (1998) U/Pb zircon ages constrain the architecture of the ultrahigh-pressure Qinling-Dabie orogen, China. Earth Planet Sci Lett 161:215–230
Hacker BR, Ratschbacher L, Webb L, McWilliams MO, Ireland T, Calvert A, Dong SW, Wenk HR, Chateigner D (2000) Exhumation of ultrahigh-pressure continental crust in east central China: Late Triassic-Early Jurassic tectonic unroofing. J Geophys Res 105:13339–13364
He YS, Li SG, Hoefs J, Kleinhanns IC (2013) Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of Early Cretaceous granitoids from the Dabie orogen: Constraints on the recycled lower continental crust. Lithos 156–159:204–217
Hoefs J (2021) Stable isotope geochemistry, 9th edn. Springer Nature Switzerland AG, Cham, p 504
Hofmann AW, Giletti BJ, Yoder HSJr, Yund RA, (1974) Geochemical transport and kinetics. Carnegie Inst Wash Publ 634:1–353
Holk GJ, Taylor HPJr, (2007) 18O/16O evidence for contrasting hydrothermal regimes involving magmatic and meteoric-hydrothermal waters at the Valhalla metamorphic core complex, British Columbia. Econ Geol 102:1063–1078
Holk GJ, Taylor HPJr, Gromet LP, (2006) Stable isotope evidence for large-scale infiltration of metamorphic fluids generated during shallow subduction into the Eastern Peninsular Ranges Mylonite Zone (EPRMZ), Southern California. Intl Geol Rev 48:209–222
Jahn B-m, Conichet J, Cong BL, Yui TF (1996) Ultrahigh-εNd(t) eclogites from an ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic terrane of China. Chem Geol 127:61–79
Jahn B-m, Wu FY, Lo CH, Tsai CH (1999) Crustal-mantle interaction induced by deep subduction of the continental crust: Geochemical and Sr-Nd isotopic evidence from post-collisional mafic-ultramafic intrusions of the northern Dabie complex, central China. Chem Geol 157:119–146
Kieffer SW (1982) Thermodynamics and lattice vibrations of minerals: 5, Applications to phase equilibria, isotopic fractionation, and high-pressure thermodynamic properties. Rev Geophys 20:827–849
King EM, Barrie CT, Valley JW (1997) Hydrothermal alteration of oxygen isotope ratios in quartz phenocrysts, Kidd Creek mine, Ontario: Magmatic values are preserved in zircon. Geology 25:1079–1082
Lasaga AC (1998) Kinetic theory in the Earth sciences. Princeton University Press, NJ, p 811
Lasaga AC, Kirkpatrick RJ (1981) Kinetics of geochemical processes. Rev Mineral Geochem 8:1–398
Li SG, Xiao YL, Liu DL, Chen YZ, Ge NJ, Zhang ZQ, Sun S-s, Cong BL, Zhang RY, Hart SR, Wang SS (1993) Collision of the North China and Yangtze Blocks and formation of coesite-bearing eclogites: Timing and processes. Chem Geol 109:89–111
Li SG, Jagoutz E, Chen YZ, Li QL (2000) Sm-Nd and Rb-Sr isotopic chronology and cooling history of ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks and their country rocks at Shuanghe in the Dabie Mountains, Central China. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64:1077–1093
Liu DY, Jian P, Kröner A, Xu ST (2006) Dating of prograde metamorphic events deciphered from episodic zircon growth in rocks of the Dabie-Sulu UHP complex, China. Earth Planet Sci Lett 250:650–666
Ma CQ, Li ZC, Ehlers C, Yang KG, Wang RJ (1998) A post-collisional magmatic plumbing system: Mesozoic granitoid plutons from the Dabieshan high-pressure and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic zone, east-central China. Lithos 45:431–456
Matthews A, Goldsmith JR, Clayton RN (1983) On the mechanisms and kinetics of oxygen isotope exchange in quartz and feldspars at elevated temperatures and pressures. Geol Soc Am Bull 94:396–412
Miller CF, McDowell SM, Mapes RW (2003) Hot and cold granites? Implications of zircon saturation temperatures and preservation of inheritance. Geology 31:529–532
Nabelek PI, Labotka TC, O’Neil JR, Papike JJ (1984) Contrasting fluid/rock interaction between the Notch Peak granitic intrusion and argillites and limestones in western Utah: Evidence from stable isotopes and phase assemblages. Contrib Mineral Petrol 86:25–34
Reiners PW, Carlson RW, Renne PR, Cooper KM, Granger DE, McLean NM, Schoene B (2018) Geochronology and thermochronology. Wiley, Hoboken, p 464
Rowley DB, Xue F, Tucker RD, Peng ZX, Baker J, Davis A (1997) Ages of ultrahigh pressure metamorphism and protolith orthogneisses from the Central Dabie Shan: U/Pb zircon geochronology. Earth Planet Sci Lett 155:191–203
Rumble D, Giorgis D, Oreland T, Zhang ZM, Xu HF, Yui TF, Yang JS, Xu ZQ, Liou JG (2002) Low δ18O zircons, U-Pb dating, and the age of the Qinglongshan oxygen and hydrogen isotope anomaly near Donghai in Jiangsu province, China. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66:2299–2306
Schauble EA, Young ED (2021) Mass dependence of equilibrium oxygen isotope fractionation in carbonate, nitrate, oxide, perchlorate, phosphate, silicate, and sulfate minerals. Rev Mineral Geochem 86:137–178
Sheppard SMF (1986) Characterization and isotopic variations in natural waters. Rev Mineral Geochem 16:165–183
Spicuzza MJ, Valley JW, McConnell VS (1998) Oxygen isotope analysis of whole rock via laser fluorination: an air lock approach. Geol Soc Am Abst Prog 30:A80
Taylor HPJr, (1977) Water/rock interactions and the origin of H2O in granitic batholiths. J Geol Soc Lond 133:509–558
Taylor HPJr, O’Neil JR, Kaplan IR, (1991) Stable isotope geochemistry: A tribute to Samuel Epstein. Geochem Soc Spec Publ 3:1–516
Taylor BE, O’Neil JR (1977) Stable isotope studies of metasomatic Ca-Fe-Al-Si skarns and associated metamorphic and igneous rocks, Osgood mountains, Nevada. Contrib Mineral Petrol 63:1–49
Valley JW, Cole DR (2001) Stable Isotopes Geochemistry Rev Mineral Geochem 43:1–662
Valley JW, Graham CM (1996) Ion microprobe analysis of oxygen isotope ratios in quartz from Skye granite: Healed micro-cracks, fluid flow, and hydrothermal exchange. Contrib Mineral Petrol 124:225–234
Valley JW, Taylor HPJr, O’Neil JR, (1986) Stable isotopes in high temperature geological processes. Rev Mineral Geochem 16:1–570
Valley JW, Kitchen NE, Kohn MJ, Niendorf CR, Spicuzza MJ (1995) UWG-2, A garnet standard for oxygen isotope ratio: Strategies for high precision and accuracy with laser heating. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:5223–5231
Valley JW, Kinny PD, Schulze DJ, Spicuzza MJ (1998) Zircon megacrysts from kimberlite: Oxygen isotope variability among mantle melts. Contrib Mineral Petrol 133:1–11
Wang XM, Liou JG, Mao HK (1989) Coesite-bearing eclogite from the Dabie Mountains in central China. Geology 17:1085–1088
Wang Q, Wyman DA, Xu JF, Jian P, Zhao ZH, Li CF, Xu WX, Ma JL, He B (2007) Early Cretaceous adakitic granites in the Northern Dabie Complex, central China: Implications for partial melting and delamination of thickened lower crust. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 71:2609–2636
Watson EB, Cherniak DJ (1997) Oxygen diffusion in zircon. Earth Planet Sci Lett 148:527–544
Wei CS, Zhao ZF (2017) Dual sources of water overprinting on the low zircon δ18O metamorphic country rocks: Disequilibrium constrained through inverse modelling of partial reequilibration. Sci Rep 7:40334
Wei CS, Zhao ZF (2021) Theoretical inversion of the fossil hydrothermal systems with oxygen isotopes of constituent minerals partially re-equilibrated with externally infiltrated fluids. Earth Environ Sci Trans Roy Soc Edinb 112:101–110
Wei CS, Zhao ZF (2022) Paradoxically lowered oxygen isotopes of hydrothermally altered minerals by an evolved magmatic water. Sci Rep 12:16213
Wei CS, Zhao ZF (2023) Palaeo-climate and -topography of the continental orogen: Theoretical inversion with initial oxygen isotopes of ancient meteoric water. Earth Environ Sci Trans Roy Soc Edinb 113:361–372
Wei CS, Zhao ZF, Spicuzza MJ (2008) Zircon oxygen isotopic constraint on the sources of late Mesozoic A-type granites in eastern China. Chem Geol 250:1–15
Wickham SM, Taylor HPJr, (1987) Stable isotope constraints on the origin and depth of penetration of hydrothermal fluids associated with Hercynian regional metamorphism and crustal anatexis in the Pyrenees. Contrib Mineral Petrol 95:255–268
Wickham SM, Peters MT, Fricke HC, O’Neil JR (1993) Identification of magmatic and meteoric fluid sources and upward- and downward-moving infiltration fronts in a metamorphic core complex. Geology 21:81–84
Xu ST, Okay AI, Ji SY, Sengör AMC, Su W, Liu YC, Jiang LL (1992) Diamond from the Dabie Shan metamorphic rocks and its implication for tectonic setting. Science 256:80–82
Xu XJ, Zhao ZF, Zheng YF, Wei CS (2005) Element and isotope geochemistry of Mesozoic intermediate-felsic rocks at Tianzhushan in the Dabie orogen. Acta Petrol Sin 21:607–622
Xu HJ, Ma CQ, Zhang JF, Ye K (2012) Early Cretaceous low-Mg adakitic granites from the Dabie orogen, eastern China: Petrogenesis and implications for destruction of the over-thickened lower continental crust. Gondwana Res 23:190–207
Xue F, Rowley DB, Tucker RD, Peng ZX (1997) U-Pb zircon ages of granitoid rocks in the north Dabie complex, eastern Dabie Shan, China. J Geol 105:744–753
Ye K, Cong BL, Ye DN (2000) The possible subduction of continental material to depths greater than 200 km. Nature 407:734–736
Zhang HF, Gao S, Zhong ZQ, Zhang BR, Zhang L, Hu SH (2002) Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of Cretaceous granitoids: Constraints on tectonic framework and crustal structure of the Dabieshan ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt, China. Chem Geol 186:281–299
Zhao ZF, Zheng YF, Wei CS, Wu YB (2004) Zircon isotope evidence for recycling of subducted continental crust in post-collisional granitoids from the Dabie terrane in China. Geophys Res Lett 31:L22602
Zhao ZF, Zheng YF, Wei CS, Wu YB, Chen FK, Jahn B-m (2005) Zircon U-Pb age, element and C-O isotope geochemistry of post-collisional mafic-ultramafic rocks from the Dabie orogen in east-central China. Lithos 83:1–28
Zhao ZF, Zheng YF, Wei CS, Wu YB (2007) Post-collisional granitoids from the Dabie orogen in China: Zircon U-Pb age, element and O isotope evidence for recycling of subducted continental crust. Lithos 93:248–272
Zhao ZF, Zheng YF, Wei CS, Chen FK, Liu XM, Wu FY (2008) Zircon U-Pb ages, Hf and O isotopes constrain the crustal architecture of the ultrahigh-pressure Dabie orogen in China. Chem Geol 253:222–242
Zhao ZF, Zheng YF, Wei CS, Wu FY (2011) Origin of postcollisional magmatic rocks in the Dabie orogen: Implications for crust-mantle interaction and crustal architecture. Lithos 126:99–114
Zheng YF (1993) Calculation of oxygen isotope fractionation in anhydrous silicate minerals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 57:1079–1091
Zheng YF (2012) Metamorphic chemical geodynamics in continental subduction zones. Chem Geol 328:5–48
Zheng YF, Fu B (1998) Estimation of oxygen diffusivity from anion porosity in minerals. Geochem J 32:71–89
Zheng YF, Fu B, Gong B, Li L (2003) Stable isotope geochemistry of ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks from the Dabie-Sulu Orogen in China: Implications for geodynamics and fluid regime. Earth-Sci Rev 62:105–161
Zheng YF, Wu YB, Chen FK, Gong B, Li L, Zhao ZF (2004) Zircon U-Pb and oxygen isotope evidence for a large-scale 18O-depletion event in igneous rocks during the Neoproterozoic. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:4145–4165
Acknowledgements
Yong-Fei Zheng is thanked for initiating this study. John W. Valley and Michael J. Spicuzza are appreciated for hosting and assisting analytical aspects of this work during the sabbatical visit of C.S.W. at the University of Wisconsin, Madison. This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (40173008 and 40033010), the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZCX2-107 and XDB41000000) and the China Scholarship Council of Ministry of Education (20G05006). Associate Editor Qiuli Li and two anonymous reviewers are sincerely grateful for their professional editorial handling and constructive comments. Editor-in-Chief Lutz Nasdala is kindly acknowledged for his great effort of editorial suggestions, which are very helpful for technically clarifying the final version of our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial handling: Q. Li
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, CS., Zhao, ZF. Were oxygen isotopes of hydrothermally altered minerals just elevated by the 18O-enriched water? Theoretical inversion with thermodynamics and kinetics. Miner Petrol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-024-00857-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-024-00857-2