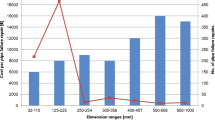
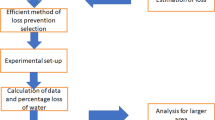
Abstract
Water distribution systems in Korea that are responsible for maintaining a stable supply of tap water and ensuring water quality are experiencing many problems, such as pipe leakage, corrosion, and aging of pipes. There have been many recommendations for improved pipe network assessment, diagnosis, design, operation, maintenance, etc. However, improvements to the water pipe network have been limited. Additionally, leaks in the tap water supply have caused deterioration of waterworks facilities. To solve this problem, water distribution maintenance projects have focused on rehabilitation and replacement of old water pipes using pipe installation age as a factor. Evaluation methods using hydraulic pressure, such as the demand energy ratio, did not previously exist in Korean water distribution systems. In this study, we have proposed a decision-making model that considers the economic efficiency of waterworks improvement projects, using a non-revenue water (NRW) multiple regression equation. Rather than placing priority of water distribution pipe rehabilitation and replacement projects on those systems with the oldest pipe installations, additionally we have proposed using cost benefit (C/B) and life cycle cost (LCC) analysis, which can be evaluated and qualified economically through the demand energy ratio, to set priority. As project priority changes are made according to the proposed decision-making model, it is also important optimize parameters according to specific waterworks facilities operations and management.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balasubramanian R, Choi SC (2010) Urbanization, population pressure and agricultural intensification: evidences from Tamil Nadu in India. J Rural Dev 33(2):87–108
Choi GW, Jang YG, Lee SW (2006) Effect of estimation method of demand water on the analysis of water distribution system. In: Proceedings of the Korea Water Resources Association Conference, pp 1425–1430 (in Korean)
Choi IC, Shin HJ, Nguyen TT, Tenhunen J (2017) Water Policy Reforms in South Korea: a Historical Review and Ongoing Challenges for Sustainable Water Governance and Management. Water 9:1–20
Fattah MA (2017) A novel statistical feature selection approach for test categorization. J Inf Process Syst 13(5):1397–1409
Jang DW, Park HS, Choi GW (2018) Estimation of leakage ratio using principal component analysis and artificial neural network in water distribution systems. Sustainability 10(3):1–13
Jo HG (2017) Study on influence factors of non-revenue water for sustainable management of water distribution networks. Ph.D. Thesis, Incheon National University, Korea (in Korean)
Jo HG, Choi GW, Jang DW (2016) Development of the non-revenue water analysis equation through the statistical analysis of main parameter in waterworks system in Incheon City. Crisisonomy 12(11):63–75 (In Korean)
Jung HJ, Kim NG (2017) Multicast tree construction with user-experienced quality for multimedia mobile networks. J Inf Process Syst 13(3):546–558
Kim SW (2007) Practical use of SPSS WIN 12.0 for Social Science Research, Kyoyookbook (in Korean)
Kim BS (2017) A Distributed coexistence mitigation scheme for IoT-based smart medical systems. J Inf Process Syst 13(6):1602–1612
Koo DJ (2006) Management of water distribution pipe networks using BFS algorithms, Master thesis, Chonnam National University (in Korean)
Park SW, Kim TY, Lim KY, Jun HD (2011) Fuzzy techniques to establish improvement priorities of water pipes. J Korea Water Resour Assoc 44(11):903–913 (In Korean)
Ryu TS, Ha SR, Cheong TS (2011) Development of optimal network model for conjunctive operation of water supply system with multiple sources. J Korea Water Resour Assoc 44(12):1001–1013 (In Korean)
Waterworks Headquarters Incheon Metropolitan City (2015a) Technical diagnostics report for re-establish basic plan of waterworks maintenance in Incheon Water Distribution Network, Incheon, Korea (in Korean)
Waterworks Headquarters Incheon Metropolitan City (2015b) Waterworks Status; Incheon Metropolitan City, Incheon, Korea (in Korean)
Woo HM (2008) Technological development plan for improvement of water distribution systems, Magazine of Korea Water Resources Association, Water for Future 41:16–23
Yoon JH, Choi DY, Woo HM, Kim JH, (2000) Management and diagnosis of water distribution systems. In: Proceedings of the Conference proceedings of Koran Society of Civil Engineers, pp 153–156 (in Korean)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by Incheon National University (International Cooperative) Research Grant in 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, G.W., Jo, H.G., Park, H.S. et al. Application of decision making model for leakage reduction to economic project in water distribution systems. J Ambient Intell Human Comput (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01634-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01634-2