Abstract
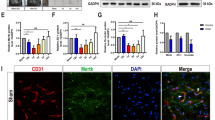
To investigate the effects of dexmedetomidine on chronic constriction injury (CCI)–induced neuropathic pain and to further explore its mechanism. A CCI rat model was established and treatment with dexmedetomidine. The paw withdrawal mechanical threshold (PWMT) and paw withdrawal thermal latency (PWTL) were monitored at different time points, and the effects of hematoxylin-eosin staining on the sciatic nerve morphology of rats were observed. Immunohistochemical and immunofluorescence analyses were used to detect the expression of high mobility group box-1 (HMGB1) protein and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), and protein fluorescence intensity of GFAP in spinal cord tissue, respectively. Moreover, the expression of HMGB1 and Toll-like receptor-4/nuclear factor kappa-B (TLR4/NF-κB) pathway–related proteins were detected by western blot assay. To verify whether dexmedetomidine alleviates CCI-induced neuropathic pain by inhibiting HMGB1-mediated astrocyte activation and the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway, the rats were further treated with an HMGB1 activator or antagonist. Dexmedetomidine was found to improve the pathological changes of the sciatic nerve and alleviate pain in the CCI rats. The expression of HMGB1, GFAP, TLR4, TRAF6, MyD88, and p-P65 were greatly downregulated in the spinal cord tissues of the CCI rats. In addition, a further study showed that an HMGB1 activator can reverse the inhibition of neuropathic pain behaviors of dexmedetomidine. Overexpression of HMGB1 downregulated the PWMT and PWTL and enhanced the astrocyte activity and the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in CCI rats. These results indicated that dexmedetomidine can alleviate neuropathic pain in CCI rats by inhibiting HMGB1-mediated astrocyte activation and the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett GJ, Xie YK (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33:87–107
Brambilla L, Martorana F, Guidotti G, Rossi D (2018) Dysregulation of astrocytic HMGB1 signaling in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front Neurosci 12:622
Chen Y, Chen X, Yu J, Xu X, Wei X, Gu X, Liu C, Zhang D, Xu Z (2016) JAB1 is involved in neuropathic pain by regulating JNK and NF-κB activation after chronic constriction injury. Neurochem Res 41:1119–1129
Chen H, Hu Y, Xie K, Chen Y, Wang H, Bian Y, Wang Y, Dong A, Yu Y (2018) Effect of autophagy on allodynia, hyperalgesia and astrocyte activation in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Int J Mol Med 42:2009–2019
Clark AK, Old EA, Malcangio M (2013) Neuropathic pain and cytokines: current perspectives. J Pain Res 6:803–814
Eng LF, Ghirnikar RS, Lee YL (2000) Glial fibrillary acidic protein: GFAP-thirty-one years (1969–2000). Neurochem Res 25:1439–1451
Freudenberg MA, Tchaptchet S, Keck S, Fejer G, Huber M, Schütze N, Beutler B, Galanos C (2008) Lipopolysaccharide sensing an important factor in the innate immune response to Gram-negative bacterial infections: benefits and hazards of LPS hypersensitivity. Immunobiology 213:193–203
Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C, Joris J (1988) A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 32:77–88
Jiang BC, Cao DL, Zhang X, Zhang ZJ, He LN, Li CH, Zhang WW, Wu XB, Berta T, Ji RR, Gao YJ (2016) CXCL13 drives spinal astrocyte activation and neuropathic pain via CXCR5. J Clin Invest 126:745–761
Kang R, Chen R, Zhang Q, Hou W, Wu S, Cao L, Huang J, Yu Y, Fan XG, Yan Z, Sun X, Wang H, Wang Q, Tsung A, Billiar TR, Zeh HJ 3rd, Lotze MT, Tang D (2014) HMGB1 in health and disease. Mol Asp Med 40:1–116
Kim DS, Figueroa KW, Li KW, Boroujerdi A, Yolo T, Luo ZD (2009) Profiling of dynamically changed gene expression in dorsal root ganglia post peripheral nerve injury and a critical role of injury-induced glial fibrillary acidic protein in maintenance of pain behaviors. Pain 144:345
Kim SW, Lim CM, Kim JB, Shin JH, Lee S, Lee M, Lee JK (2011) Extracellular HMGB1 released by NMDA treatment confers neuronal apoptosis via RAGE-p38 MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Neurotox Res 20:159–169
Klune JR, Dhupar R, Cardinal J, Billiar TR, Tsung A (2008) HMGB1: endogenous danger signaling. Mol Med 14:476–484
Kuang X, Huang Y, Gu HF, Zu XY, Zou WY, Song ZB, Guo QL (2012) Effects of intrathecal epigallocatechin gallate, an inhibitor of Toll-like receptor 4, on chronic neuropathic pain in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 676:51–56
Laaksonen L, Kallioinen M, Långsjö J, Laitio T, Scheinin A, Scheinin J, Kaisti K, Maksimow A, Kallionpää RE, Rajala V, Johansson J, Kantonen O, Nyman M, Sirén S, Valli K, Revonsuo A, Solin O, Vahlberg T, Alkire M, Scheinin H (2018) Comparative effects of dexmedetomidine, propofol, sevoflurane, and S-ketamine on regional cerebral glucose metabolism in humans: a positron emission tomography study. Br J Anaesth 121:281–290
Liang F, Liu M, Fu X, Zhou X, Chen P, Han F (2017) Dexmedetomidine attenuates neuropathic pain in chronic constriction injury by suppressing NR2B, NF-κB, and iNOS activation. Saudi Pharm J 25:649–654
Liu D, Huang Y, Jia C, Li Y, Liang F, Fu Q (2015) Administration of antagomir-223 inhibits apoptosis, promotes angiogenesis and functional recovery in rats with spinal cord injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35:483–491
Martini AC, Berta T, Forner S, Chen G, Bento AF, Ji RR, Rae GA (2016) Lipoxin A4 inhibits microglial activation and reduces neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain after spinal cord hemisection. J Neuroinflammation 13:75
Meng L, Li L, Lu S, Li K, Su Z, Wang Y, Fan X, Li X, Zhao G (2018) The protective effect of dexmedetomidine on LPS-induced acute lung injury through the HMGB1-mediated TLR4/NF-κB and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. Mol Immunol 94:7–17
Otoshi KI, Kikuchi SI, Kato K, Sekiguchi M, Konno S (2011) Anti-HMGB1 neutralization antibody improves pain-related behavior induced by application of autologous nucleus pulposus onto nerve roots in rats. Spine 36:E692–E698
Pabreja K, Dua K, Sharma S, Padi SS, Kulkarni SK (2011) Minocycline attenuates the development of diabetic neuropathic pain: possible anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol 661:15–21
Pang H, Huang T, Song J, Li D, Zhao Y, Ma X (2016) Inhibiting HMGB1 with glycyrrhizic acid protects brain injury after DAI via its anti-inflammatory effect. Mediat Inflamm 2016:4569521
Piotrowska A, Kwiatkowski K, Rojewska E, Makuch W, Mika J (2016) Maraviroc reduces neuropathic pain through polarization of microglia and astroglia—evidence from in vivo and in vitro studies. Neuropharmacology 108:207–219
Popiolekbarczyk K, Mika J (2016) Targeting the microglial signaling pathways: new insights in the modulation of neuropathic pain. Curr Med Chem 23:2908–2928
Saito O, Svensson CI, Buczynski MW, Wegner K, Hua XY, Codeluppi S, Schaloske RH, Deems RA, Dennis EA, Yaksh TL (2010) Spinal glial TLR4-mediated nociception and production of prostaglandin E (2) and TNF. Br J Pharmacol 160:1754–1764
Shao H, Xue Q, Zhang F, Luo Y, Zhu H, Zhang X, Zhang H, Ding W, Yu B (2014) Spinal SIRT1 activation attenuates neuropathic pain in mice. PLoS One 9:e100938
Shibasaki M, Sasaki M, Miura M, Mizukoshi K, Ueno H, Hashimoto S, Tanaka Y, Amaya F (2010) Induction of high mobility group box-1 in dorsal root ganglion contributes to pain hypersensitivity after peripheral nerve injury. Pain 149:514–521
Tanaka H, Katoh A, Oguro K, Shimazaki K, Gomi H, Itohara S, Masuzawa T, Kawai N (2002) Disturbance of hippocampal long-term potentiation after transient ischemia in GFAP deficient mice. J Neurosci Res 67:11–20
Tian J, Song T, Wang W, Wang H, Zhang Z (2019) miR-129-5p alleviates neuropathic pain through regulating HMGB1 expression in CCI rat models. J Mol Neurosci 70:84–93
Vezzani A, Maroso M, Balosso S, Sanchez MA, Bartfai T (2011) IL-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor signaling in infection, inflammation, stress and neurodegeneration couples hyperexcitability and seizures. Brain Behav Immun 25:1281–1289
Weber DJ, Allette YM, Wilkes DS, White FA (2015) The HMGB1-RAGE inflammatory pathway: implications for brain injury-induced pulmonary dysfunction. Antioxid Redox Signal 23:1316–1328
Xia LX, Ke C, Lu JM (2018) NEAT1 contributes to neuropathic pain development through targeting miR-381/HMGB1 axis in CCI rat models. J Cell Physiol 233:7103–7111
Yang YF, Peng K, Liu H, Meng XW, Zhang JJ, Ji FH (2017) Dexmedetomidine preconditioning for myocardial protection in ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rats by downregulation of the high mobility group box 1-toll-like receptor 4-nuclear factor κB signaling pathway. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 44:353–361
Zhan LY, Lei SQ, Zhang BH, Li WL, Wang HX, Zhao B, Cui SS, Ding H, Huang QM (2018) Overexpression of miR-381 relieves neuropathic pain development via targeting HMGB1 and CXCR4. Biomed Pharmacother 107:818–823
Zhao B, Pan Y, Xu H, Song X (2018) Kindlin-1 regulates astrocyte activation and pain sensitivity in rats with neuropathic pain. Reg Anesth Pain Med 43:547–553
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was carried out in strict accordance with the recommendations set out in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (National Institutes of Health Pub. No. 85-23, revised 1996). The protocol was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Significance
Dexmedetomidine may be used to treat neuropathic pain.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, E., Bai, L., Li, S. et al. Dexmedetomidine Alleviates CCI-Induced Neuropathic Pain via Inhibiting HMGB1-Mediated Astrocyte Activation and the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Rats. Neurotox Res 38, 723–732 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00245-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00245-6