Abstract
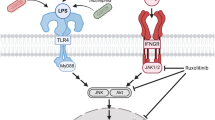
High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) was originally identified as ubiquitously expressed nonhistone DNA-binding protein, but recently, it was found to act as an endogenous danger molecule, which signals danger and traumatic cell death. Previously, the authors showed that HMGB1 is massively released immediately after an ischemic insult and that it subsequently activates microglia and induces inflammation in the postischemic brain. Here, we showed the endogenous danger molecule-like function of HMGB1 in primary cortical cultures. HMGB1 was found to be accumulated in NMDA-treated primary cortical culture media, and media collected from these cultures were able to induce neuronal cell death when added to fresh primary cortical cultures. However, HMGB1-depleted NMDA-conditioned media produced by HMGB1 siRNA transfection or by preincubation with anti-HMGB1 antibody or with HMGB1 A box failed to induce neuronal cell death. Furthermore, siRNA-mediated HMGB1 knockdown substantially suppressed NMDA- or Zn2+-induced cell death. It was interesting to find that extracellular HMGB1-induced neuronal apoptosis, as evidenced by TUNEL staining and caspase 3 assay in combination with double immunofluorescence staining. A series of RAGE and HMGB1 co-immunoprecipitation experiments in the presence of SB203580 and PD98059 (p38 MAPK and ERK inhibitors, respectively) demonstrated that RAGE-p38 MAPK and RAGE-ERK pathway might underlie extracellular HMGB1-mediated neuronal apoptosis. These results together with our previous reports regarding microglial activation by extracellular HMGB1 indicate that HMGB1 functions as a novel danger signal, which aggravates brain damage via autocrine and paracrine manners.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham E, Arcaroli J, Carmody A, Wang H, Tracey KJ (2000) HMG-1 as a mediator of acute lung inflammation. J Immunol 165:2950–2954
Agnello D, Wang H, Yang H, Tracey KJ, Ghezzi P (2002) HMGB-1, a DNA-binding protein with cytokine activity, induces brain TNF and IL-6 production, and mediates anorexia and taste aversion. Cytokine 18:231–236
Arancio O, Zhang HP, Chen X, Lin C, Trinchese F, Puzzo D, Liu S, Hegde A, Yan SF, Stern A, Luddy JS, Lue LF, Walker DG, Roher A, Buttini M, Mucke L, Li W, Schmidt AM, Kindy M, Hyslop PA, Stern DM, Du Yan SS (2004) RAGE potentiates Abetainduced perturbation of neuronal function in transgenic mice. EMBO J 23:4096–4105
Bianchi ME (2007) DAMPs, PAMPs and alarmins: all we need to know about danger. J Leukoc Biol 81:1–5
Bianchi ME, Manfredi AA (2007) High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein at the crossroads between innate and adaptive immunity. Immunol Rev 220:35–46
Bonaldi T, Talamo F, Scaffidi P, Ferrera D, Porto A, Bachi A, Rubartelli A, Agresti A, Bianchi ME (2003) Monocytic cells hyperacetylate chromatin protein HMGB1 to redirect it towards secretion. EMBO J 22:5551–5560
Bustin M (1999) Regulation of DNA-dependent activities by the functional motifs of the high-mobility-group chromosomal proteins. Mol Cell Biol 19:5237–5246
Faraco G, Fossati S, Bianchi ME, Patrone M, Pedrazzi M, Sparatore B, Moroni F, Chiarugi A (2007) High mobility group box 1 protein is released by neural cells upon different stresses and worsens ischemic neurodegeneration in vitro and in vivo. J Neurochem 103:590–603
Graham SH, Chen J (2001) Programmed cell death in cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21:99–109
Hayakawa K, Arai K, Lo EH (2010) Role of ERK map kinase and CRM1 in IL-1betastimulated release of HMGB1 from cortical astrocytes. Glia 58:1007–1015
Hori O, Brett J, Slattery T, Cao R, Zhang J, Chen JX, Nagashima M, Lundh ER, Vijay S, Nitecki D (1995) The receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) is a cellular binding site for amphoterin. Mediation of neurite outgrowth and co-expression of rage and amphoterin in the developing nervous system. J Biol Chem 270:25752–25761
Ivanov S, Dragoi AM, Wang X, Dallacosta C, Louten J, Musco G, Sitia G, Yap GS, Wan Y, Biron CA, Bianchi ME, Wang H, Chu WM (2007) A novel role for HMGB1 in TLR9-mediated inflammatory response to CpG-DNA. Blood 110:1970–1981
Kim JB, Piao CS, Lee KW, Han PL, Ahn JI, Lee YS, Lee JK (2004) Delayed genomic responses to transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. J Neurochem 89:1271–1282
Kim JB, Sig Choi J, Yu YM, Nam K, Piao CS, Kim SW, Lee MH, Han PL, Park JS, Lee JK (2006) HMGB1, a novel cytokine-like mediator linking acute neuronal death and delayed neuroinflammation in the postischemic brain. J Neurosci 26:6413–6421
Kim JB, Lim CM, Yu YM, Lee JK (2008a) Induction and subcellular localization of high-mobility group box-1 (HMGB1) in the postischemic rat brain. J Neurosci Res 86:1125–1131
Kim K, Han JS, Kim HA, Lee M (2008b) Expression, purification and characterization of TAT-high mobility group box-1A peptide as a carrier of nucleic acids. Biotechnol Lett 30:1331–1337
Li J, Qu X, Schmidt AM (1998) Sp1-binding elements in the promoter of RAGE are essential for amphoterin-mediated gene expression in cultured neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 273:30870–30878
Monteiro FA, Sousa MM, Cardoso I, do Amaral JB, Guimarães A, Saraiva MJ (2006) Activation of ERK1/2 MAP kinases in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. J Neurochem 97:151–161
Passalacqua M, Patrone M, Picotti GB, Del Rio M, Sparatore B, Melloni E, Pontremoli S (1998) Stimulated astrocytes release high-mobility group 1 protein, an inducer of LAN-5 neuroblastoma cell differentiation. Neuroscience 82:1021–1028
Pedrazzi M, Raiteri L, Bonanno G, Patrone M, Ledda S, Passalacqua M, Milanese M, Melloni E, Raiteri M, Pontremoli S, Sparatore B (2006) Stimulation of excitatory amino acid release from adult mouse brain glia subcellular particles by high mobility group box 1 protein. J Neurochem 99:827–838
Qiu J, Nishimura M, Wang Y, Sims JR, Qiu S, Savitz SI, Salomone S, Moskowitz MA (2008) Early release of HMGB-1 from neurons after the onset of brain ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:927–938
Scaffidi P, Misteli T, Bianchi ME (2002) Release of chromatin protein HMGB1 by necrotic cells triggers inflammation. Nature 418:191–195
Sha Y, Zmijewski J, Xu Z, Abraham E (2008) HMGB1 develops enhanced proinflammatory activity by binding to cytokines. J Immunol 180:2531–2537
Tian J, Avalos AM, Mao SY, Chen B, Senthil K, Wu H, Parroche P, Drabic S, Golenbock D, Sirois C, Hua J, An LL, Audoly L, La Rosa G, Bierhaus A, Naworth P, Marshak-Rothstein A, Crow MK, Fitzgerald KA, Latz E, Kiener PA, Coyle AJ (2007) Toll-like receptor 9-dependent activation by DNA-containing immune complexes is mediated by HMGB1 an RAGE. Nat Immunol 8:487–496
Wang H, Bloom O, Zhang M, Vishnubhakat JM, Ombrellino M, Che J, Frazier A, Yang H, Ivanova S, Borovikova L, Manogue KR, Faist E, Abraham E, Andersson J, Andersson U, Molina PE, Abumrad NN, Sama A, Tracey KJ (1999a) HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science 285:248–251
Wang H, Vishnubhakat JM, Bloom O, Zhang M, Ombrellino M, Sama A, Tracey KJ (1999b) Proinflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1) stimulate release of high mobility group protein-1 by pituicytes. Surgery 126:389–392
Weise J, Engelhorn T, Dorfler A, Aker S, Bahr M, Hufnagel (2005) Expression time course and spatial distribution of activated caspase-3 after experimental status epilepticus: contribution of delayed neuronal cell death to seizure-induced neuronal injury. Neurobiol Dis 18:582–590
Yan SD, Chen X, Fu J, Chen M, Zhu H, Roher A, Slattery T, Zhao L, Nagashima M, Morser J, Migheli A, Nawroth P, Stern D, Schmidt AM (1996) RAGE and amyloid-β peptide neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 382:685–691
Yang H, Ochani M, Li J, Qiang X, Tanovic M, Harris HE, Susarla SM, Ulloa L, Wang H, DiRaimo R, Czura CJ, Wang H, Roth J, Warren HS, Fink MP, Fenton MJ, Andersson U, Tracey KJ (2004) Reversing established sepsis with antagonists of endogenous high-mobility group box 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:296–301
Youn JH, Oh YJ, Kim ES, Choi JE, Shin JS (2008) High mobility group box 1 protein binding to lipopolysaccharide facilitates transfer of lipopolysaccharide to CD14 and enhances lipopolysaccharide-mediated TNF-alpha production in human monocytes. J Immunol 180:5067–5074
Zhai DX, Kong QF, Xu WS, Bai SS, Peng HS, Zhao K, Li GZ, Wang DD, Sun B, Wang JH, Wang GY, Li HL (2008) RAGE expression is up-regulated in human cerebral ischemia and pMCAO rats. Neurosci Lett 445:117–121
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (R01-2007-000-10852-0) and a grant from KOSEF (2009-0065403), Republic of Korea for J-K Lee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
First two authors contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SW., Lim, CM., Kim, JB. et al. Extracellular HMGB1 Released by NMDA Treatment Confers Neuronal Apoptosis via RAGE-p38 MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway. Neurotox Res 20, 159–169 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-010-9231-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-010-9231-x