Abstract
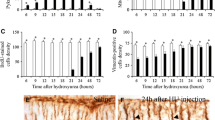
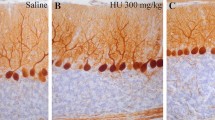
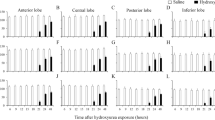
We present a histological study of the cell death of cerebellar neuroepithelial neuroblasts following treatment with the cytotoxic agent hydroxyurea (HU) during the embryonic life. Pregnant rats were treated with a single dose of HU (300 mg/kg) at embryonic days 13, 14, or 15 of gestation, and their fetuses were studied from 5 to 35 h after treatment to elucidate the mechanisms of HU-induced fetotoxicity. Quantification of several parameters such as the density of pyknotic, mitotic, and PCNA-immunoreactive cells indicated that HU compromises the survival of the cerebellar neuroepithelium neuroblasts. On the other hand, our light and electron microscopic investigations during the course of prenatal development indicated that HU leads to two types of cell death: apoptosis and cells presenting cytoplasmic vacuolization, altered organelles, and a recognizable cell nucleus. Both modalities of cell death resulted in a substantial loss of cerebellar neuroepithelium cells. Current results suggest that HU exposure during gestation is toxic to the cerebellar neuroepithelium. Moreover, they allow to examine the mechanisms of HU-induced toxicity during the early development of the central nervous system. Our data also suggest that it is essential to avoid underestimating the adverse effects of HU when administered during early prenatal life.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allin MP (2016) Novel insights from quantitative imaging of the developing cerebellum. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 21(5):333–338
Altman J, Bayer SA (1985) Embryonic development of the rat cerebellum I. Delineation of the cerebellar primordium and early cell movements. J Comp Neurol 231:1–26
Altman J, Bayer SA (1995) Atlas of prenatal rat brain development. CRC Press Inc., Boca Raton
Altman J, Bayer SA (1997) Development of the cerebellar system: in relation to its evolution, structure and functions. CRC Press Inc., Boca Raton
Baima B, Sticherling M (2002) How specific in the TUNEL reaction? An account of a histochemical study on human skin. Am J Dermatopathol 24:130–134
Ballas SK, McCarthy WF, Guo N, DeCastro L, Bellevue R, Barton BA, Waclawiw MA, Multicenter Study of Hydroxyurea in Sickle Cell Anemia (2009) Exposure to hydroxyurea and pregnancy outcomes in patients with sickle cell anemia. J Natl Med Assoc 101(10):1046–1051
Banh S, Hales BF (2013) Hydroxyurea exposure triggers tissue-specific activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and the DNA damage response in organogenesis-stage mouse embryos. Toxicol Sci 133(2):298–308
Borovitskaya AE, Evtushenko VI, Sabol SL (1996) Gamma-radiation-induced cell death in the fetal rat brain possesses molecular characterisitics of apoptosis and is associated with specific messenger RNA elevations. Mol Brain Res 35:19–30
Butts T, Green MJ, Wingate RJ (2014) Development of the cerebellum: simple steps to make a “little brain”. Development 141:4031–4041
Castagna C, Merighi A, Lossi L (2016) Cell death and neurodegeneration in the postnatal development of cerebellar vermis in normal and Reeler mice. Ann Anat 207:76–90
Charriaut-Marlanque C, Ben-Ari Y (1995) A cautionary note on the use of the TUNEL stain to determine apoptosis. Neuroreport 7(1):61–64
Creeley CE, Dikranian KT, Dissen GA, Back SA, Olney JW, Brambrink AM (2014) Isoflurane-induced apoptosis of neurons and oligodendrocytes in the fetal rhesus macaque brain. Anesthesiology 120(3):626–638
Dikranian K, Ishimaru MJ, Tenkova T, Labruyere J, Qin YQ, Ikonomidou C, Olney JW (2001) Apoptosis in the in vivo mammalian forebrain. Neurobiol Dis 8:359–379
Doi K (2011) Mechanisms of neurotoxicity induced in the developing brain of mice and rats by DNA-damaging chemicals. J Toxicol Sci 36(6):695–712
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35:495–516
Green NS, Barral S (2014) Emerging science of hydroxyurea therapy for pediatric sickle cell disease. Pediatr Res 75(1–2):196–204
Grimaldi P, Parras C, Guillemot F, Rossi F, Wassef M (2009) Origins and control of the differentiation of inhibitory interneurons and glia in the cerebellum. Dev Biol 328:422–433
Haines DE, Dietrichs E (2012) The cerebellum, structure and connections. Handb Clin Neurol 103:3–36
Hervás JP, Martí-Clúa J, Muñoz-García A, Santa-Cruz MC (2002) Proliferative activity in the cerebellar ext ernal granular layer evaluated by bromodeoxyuridine labeling. Biotech Histochem 77:27–35
Hossain MM, Nakayama H, Goto N (1995) Apoptosis in the central nervous system of developing mouse fetuses from 5-azacytidine-administered dams. Toxicol Pathol 23(3):367–372
Ikonomidou C, Bosch F, Miksa M, Vockler J, Bittigau P, Pohl D, Dikranian K, Tenkova T, Turski L, Olney JW (1999) Blockade of NMDA receptors and apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing brain. Science 283:70–74
Ikonomidou C, Bittigau P, Ishimaru MJ, Wozniak DF, Koch C, Genz K, Price MT, Stefovska V, Hörster F, Tenkova T, Dikranian K, Olney JW (2000) Ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration and fetal alcohol syndrome. Science 287:1056–1060
Lanzkron S, Strouse JJ, Wilson R, Beach MC, Haywood C, Park H, Witkop C, Bass EB, Segal JB (2008) Systematic review: hydroxyurea for the treatment of adults with sickle cell disease. Ann Intern Med 148:939–955
Lebwohl M, Menter A, Koo J, Feldman SR (2004) Combination therapy to treat moderate to severe psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol 50(3):416–430
Leto K, Bartolini A, Yanagawa Y, Obata K, Magrassi L, Schilling K, Rossi F (2009) Laminar fate and phenotype specification of cerebellar GABAergic interneurons. J Neurosci 29(21):7079–7091
Leto K, Rolando C, Rossi F (2012) The genesis of cerebellar GABAergic neurons: fate potential and specification mechanisms. Front Neuroanat 6:6. doi:10.3389/fnana.2012.00006. eCollection
Leto K, Arancilo M, Becker EBE, Buffo A, Chiang C, Ding B, Dobyns WB, Dusart I, Haldipur P, Hatten ME, Hoshino M, Joyner AL, Kano M, Kilpatrick KJ, Koibuchi N, Marino S, Martínez S, Millen KJ, Millner TO, Miyata T, Parmigiani E, Schilling K, Sekerkova G, Sillitoe RV, Sotelo C, Uesaka N, Wefers A, Wingate RJT, Hawkes R (2016) Consensus paper: cerebellar development. Cerebellum 15:789–828
Lossi L, Gambino G (2008) Apoptosis of the cerebellar neurons. Histol Histopathol 23:367–380
Manto M (2012) Toxic agents causing cerebellar ataxias. Handb Clin Neurol 103:201–213
Martí J, Santa-Cruz MC, Serra R, Hervás JP (2015) Systematic differences in time of cerebellar-neuron origin derived from bromodeoxyuridine immunoperoxidase staining protocols and tritiated thymidine autoradiographic: a comparative study. Int J Dev Neurosci 47:216–228
Martí J, Santa-Cruz MC, Serra R, Hervás JP (2016) Hydroxyurea treatment and development of the rat cerebellum: effects on the neurogenetic profiles and settled patterns of Purkinje cells and deep cerebellar nuclei neurons. Neurotox Res 30(4):563–580
Martí J, Molina V, Santa-Cruz MC, Hervás JP (2017) Developmental injury to the cerebellar cortex following hydroxyurea treatment in early postnatal life: an immunohistochemical and electron microscopic study. Neurotox Res 31(2):187–203
Martínez S, Andreu A, Mecklenburg N, Echevarria D (2013) Cellular and molecular basis of cerebellar development. Front Neuroanat 7:18. doi:10.3389/fnana.2013.00018 eCollection 2013
Marzban H, Del Bigio MR, Alizadeh J, Ghavami S, Zachariah RM, Rastegar M (2015) Cellular commitment in the developing cerebellum. Front Cell Neurosci 8:450. doi:10.3389/fncel.2014.00450. eCollection
Navarra P, Preziosi P (1999) Hydroxyurea: new insights on an old drug. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 29:249–255
Nevitt SJ, Jones AP, Howard J (2017) Hydroxyurea (hydroxycarbamide) for sickle cell disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4:CD002202. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002202.pub2
Pamenter ME, Perkins GA, McGinness AK, Gu XQ, Ellisman MH, Haddad GG (2012) Autophagy and apoptosis are differentially induced in neurons and astrocytes reated with an in vitro mimic of the ischemic penombra. PLoS One 7(12):e51469
Saban N, Bujak M (2009) Hydroxyurea and hydroxamic acid derivatives as antitumor drugs. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 64:213–221
Sampson M, Archibong AE, Powell A, Strange B, Roberson S, Hills ER, Bourne P (2010) Perturbation of the developmental potential of preimplantation mouse embryos by hydroxyurea. Int J Environ Res Public Health 7:2033–2044
Samson M, Claassen DO (2017) Neurodegeneration and the cerebellum. Neurodegener Dis 17(4–5):155–165
Schilling K, Oberdick J, Rossi F, Baader SL (2008) Besides Purkinje cells and granule neurons: an appraisal of the cell biology of the interneurons of the cerebellar cortex. Histochem Cell Biol 130:601–615
Schlisser AE, Hales BF (2013) Deprenyl enhances the teratogenicity of hydroxyurea in organogenesis stage mouse embryos. Toxicol Sci 134:391–399
Shao J, Zhou B, Chu B, Yen Y (2006) Ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors and future drug design. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 6:409–431
Sillitoe RV, Joyner AL (2007) Morphology, molecular codes, and circuitry produce the three-dimensional complexity of the cerebellum. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23:549–577
Strouse JJ, Lanzkron S, Beach MC, Haywood C, Park H, Witkop C, Wilson RF, Bass EB, Segal JB (2008) Hydroxyurea for sickle cell disease: a systematic review for efficacy and toxicity in children. Pediatrics 122(6):1332–1342
Thauvin-Robinet C, Maingueneau C, Robert E, Elefant E, Guy H, Caillot D, Casasnovas RO, Douvier S, Nivelon-Chevallier A (2001) Exposure to hydroxyurea during pregnancy: a case series. Leukemia 15(8):1309–1311
Tong KK, Ching Ma T, Kwan M (2015) BMP/Smad signaling and embryonic cerebellum development: stem cell specification and heterogeneity of anterior rhombic lip. Develop Growth Differ 57:121–134
Ueno M, Nakayama H, Kajikawa S, Katayama K, Suzuki K, Doi K (2002) Expression of ribosomal protein L4 (rpL4) during neurogenesis and 5-azacytidine (5AzC)-induced apoptotic process in the rat. Histol Histopathol 17(3):789–798
Ware RE, Despotovic JM, Mortier NA, Flanagan JM, He J, Smeltzer MP, Kimble AC, Aygun B, Wu S, Howard T, Sparreboom A (2011) Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacogenetics of hydroxyurea treatment for children with sickle cell anemia. Blood 118:4985–4991
Wei L, Han BH, Li Y, Keogh K, Holtzman DMYSP (2006) Cell death mechanism and protective effect of erythropoietin after focal ischemia in the whisker-barrel cortex of neonatal rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317(1):109–116
Woo GH, Katayama K, Jung JY, Uetsuka K, Bak EJ, Nakayama H, Doi K (2003) Hydroxyurea (HU)-induced apoptosis in the mouse fetal tissues. Histol Histopathol 18:387–392
Woo GH, Katayama K, Bak EJ, Ueno H, Tamauchi H, Uetsuka K, Nakayama H, Doi K (2004) Effects of prenatal hydroxyurea-treatment on mouse offspring. Exp Toxicol Pathol 56(1–2):1–7
Woo GH, Bak E-J, Nakayama H, Doi K (2005) Hydroxyurea (HU)-induced apoptosis in the mouse fetal lung. Exp Mol Pathol 79:59–67
Woo GH, Bak EJ, Katayama K, Doi K (2006) Molecular mechanisms of hydroxyurea (HU)-induced apoptosis in the mouse fetal brain. Neurotocol Teratol 28:125–134
Wullimann MF, Mueller T, Distel M, Babaryka A, Grothe B, Köster RW (2011) The long adventurous journey of rhombic lip in jawed vertebrates: a comparative developmental analysis. Front Neuroanat 5:27. doi:10.3389/fnana.2011.00027. eCollection
Yaguchi Y, Yu T, Ahmed MU, Berry M, Mason I, Basson MA (2009) Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) gene expression in the developing cerebellum suggests multiple roles for FGF signaling during cerebellar morphogenesis and development. Dev Dyn 238(8):2058–2072
Zala C, Rouleau D, Montaner JS (2000) Role of hydroxyurea in treatment of disease due to human immunodeficiency virus infection. Clin Infect Dis 30:S143–S150
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to Drs. María del Carmen Santa-Cruz and José Pablo Hervás for providing the animals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experiments in this study were carried out in accordance with the requirements of the Committee for Institutional Animal Care and Use in the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez-Vázquez, L., Martí, J. Effects of Hydroxyurea Exposure on the Rat Cerebellar Neuroepithelium: an Immunohistochemical and Electron Microscopic Study Along the Anteroposterior and Mediolateral Axes. Neurotox Res 32, 671–682 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-017-9785-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-017-9785-y