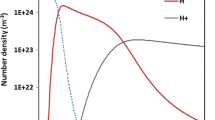
Abstract
Currently, iron is extracted from ores such as hematite by carbothermic reduction. The extraction process includes several unit steps/processes that require large-scale equipment and significant financial investments. Additionally, the extraction process produces a substantial amount of harmful carbon dioxide (CO2). Alternative to carbothermic reduction is the reduction by hydrogen plasma (HP). HP is mainly composed of exciting species that facilitate hematite reduction by providing thermodynamic and kinetic advantages, even at low temperatures. In addition to these advantages, hematite reduction by HP produces water, which is environmentally beneficial. This report reviews the theory and practice of hematite reduction by HP. Also, the present state of the art in solid-state and liquid-state hematite reduction by HP has been examined. The in-flight hematite reduction by HP has been identified as a potentially promising alternative to carbothermic reduction. However, the in-flight reduction is still plagued with problems such as excessively high temperatures in thermal HP and considerable vacuum costs in non-thermal HP. These problems can be overcome by using non-thermal atmospheric HP that deviates significantly from local thermodynamic equilibrium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.C. Sabat and A.B. Murphy, Hydrogen plasma processing of iron ore, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 48(2017), No. 3, p. 1561.
E. Basson, World Steel in Figures, World Steel Association(2020) [2022-01-06]. https://worldsteel.org/steel-by-topic/statistics/world-steel-in-figures/
A. Carpenter, CO2 Abatement in the Iron and Steel Industry Report CCC/193, IEA Clean Coal Centre, London, 2012, p. 1.
K.C. Sabat, P. Rajput, R.K. Paramguru, B. Bhoi, and B.K. Mishra, Reduction of oxide minerals by hydrogen plasma: An overview, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 34(2014), No. 1, p. 1.
H.Y. Sohn and Y. Mohassab, Development of a novel flash ironmaking technology with greatly reduced energy consumption and CO2 emissions, J. Sustainable Metall., 2(2016), No. 3, p. 216.
K.C. Sabat, Physics and chemistry of solid state direct reduction of iron ore by hydrogen plasma, Phys. Chem. Solid State, 22(2021), No. 2, p. 292.
X.B. Chen, S.H. Shen, L.J. Guo, and S.S. Mao, Semiconductor-based photocatalytic hydrogen generation, Chem. Rev., 110(2010), No. 11, p. 6503.
A. Kudo and Y. Miseki, Heterogeneous photocatalyst materials for water splitting, Chem. Soc. Rev., 38(2009), No. 1, p. 253.
H.Y. Sohn and M. Olivas-Martinez, Methods for calculating energy requirements for processes in which a reactant is also a fuel: Need for standardization, JOM, 66(2014), No. 9, p. 1557.
Plasma, Plasma, Everywhere, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Washington, D.C. [2022-01-05]. https://science.nasa.gov/science-news/science-at-nasa/1999/ast07sep99_1.
G.H. Dieke, The molecular spectrum of hydrogen and its isotopes, J. Mol. Spectrosc., 2(1958), No. 1–6, p. 494.
D. Staack, B. Farouk, A. Gutsol, and A. Fridman, DC normal glow discharges in atmospheric pressure atomic and molecular gases, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol., 17(2008), No. 2, p. 025013.
P.J. Bruggeman, N. Sadeghi, D.C. Schram and V. Linss, Gas temperature determination from rotational lines in non-equilibrium plasmas: a review, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol., 23(2014), No. 2, p. 023001.
Y. Shimizu, Y. Kittaka, A. Nezu, H. Matsuura, and H. Akatsuka, Excited state distributions of hydrogen atoms in the microwave discharge hydrogen plasma and the effect of electron energy probabilistic function, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., 43(2015), No. 5, p. 1758.
V.M. Lelevkin, D.K. Otorbaev and D.C. Schram, Physics of Non-Equilibrium Plasmas, North-Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam, 1992.
K.R. Stalder and J.B. Jeffries, Recent results on the deposition of diamond thin films by arcjet plasmas and diagnostic measurements of the plasma-surface region, Diam. Relat. Mater., 2(1993), No. 2–4, p. 443.
R.G. Meulenbroeks, R.H. Engeln, M.A. Beurskens, et al., The argon-hydrogen expanding plasma: Model and experiments, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol., 4(1995), No. 1, p. 74.
F. Hummernbrum, H. Kempkens, A. Ruzicka, et al., Laser-induced fluorescence measurements on the C2Sigma+-X2IIrtransition of the CH radical produced by a microwave excited process plasma, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol., 1(1992), No. 4, p. 221.
J. Luque, W. Juchmann, and J.B. Jeffries, Spatial density distributions of C2, C3, and CH radicals by laser-induced fluorescence in a diamond depositing dc-arcjet, J. Appl. Phys., 82(1997), No. 5, p. 2072.
J. Luque, W. Juchmann, and J.B. Jeffries, Absolute concentration measurements of CH radicals in a diamond-depositing dcarcjet reactor, Appl. Opt., 36(1997), No. 15, p. 3261.
V.I. Gorokhovsky, Characterization of cascade arc assisted CVD diamond coating technology: Part I. Plasma processing parameters, Surf. Coat. Technol., 194(2005), No. 2–3, p. 344.
W.F. Giauque, The entropy of hydrogen and the third law of thermodynamics the free energy and dissociation of hydrogen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 52(1930), No. 12, p. 4816.
M.S. Vardya, Pressure dissociation and molecular hydrogen, Mon Not R Astron Soc, 129(1965), No. 5, p. 345.
J. Meichsner, M. Schmidt, R. Schneider, and H.E. Wagner, Nonthermal Plasma Chemistry and Physics, 1st ed., CRC Press Inc., New York, 2012, p.121.
O. Gabriel, W.E.N. van Harskamp, J.J.A. van den Dungen, D.C. Schram, and R. Engeln, Gas phase kinetics and surface interaction in a hydrogen plasma jet, [in] The 19th International Symposium on Plasma Chemistry (ISPC-19), Bochum, 2009. p. 4.
Y.A. Mankelevich, M.N.R. Ashfold, and J. Ma, Plasma-chemical processes in microwave plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition reactors operating with C/H/Ar gas mixtures, J. Appl. Phys., 104(2008), No. 11, p. 113304.
A. Fridman, Plasma Chemistry, Cambridge University Press, New York, 2008.
H. Kersten, H. Deutsch, and J. Behnke I, On the energy balance of substrate surfaces during plasma cleaning of lubricants, Vacuum, 48(1997), No. 2, p. 123.
M.W. Chase, NIST-JANAF Thermochemical Tables, 4th ed., American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, 1998, p.556.
I.R. Souza Filho, Y. Ma, M. Kulse, et al., Sustainable steel through hydrogen plasma reduction of iron ore: Process, kinetics, microstructure, chemistry, Acta Mater., 213(2021), art. No. 116971.
K.C. Sabat, Production of nickel by cold hydrogen plasma, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 41(2021), No. 5, p. 1329.
K.C. Sabat, Hydrogen plasma — Thermodynamics, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., 1172(2019), No. 1, art. No. 012086.
K.C. Sabat, Iron production by hydrogen plasma, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., 1172(2019), No. 1, art. No. 012043.
K.C. Sabat, R.K. Paramguru, and B.K. Mishra, Formation of copper-nickel alloy from their oxide mixtures through reduction by low-temperature hydrogen plasma, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 38(2018), No. 3, p. 621.
K.C. Sabat, R.K. Paramguru, and B.K. Mishra, Reduction of oxide mixtures of (Fe2O3+CuO) and (Fe2O3+Co3O4) by low-temperature hydrogen plasma, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 37(2017), No. 4, p. 979.
K.C. Sabat, R.K. Paramguru, and B.K. Mishra, Reduction of copper oxide by low-temperature hydrogen plasma, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 36(2016), No. 4, p. 1111.
K.C. Sabat, R.K. Paramguru, S. Pradhan, and B.K. Mishra, Reduction of cobalt oxide (Co3O4) by low temperature hydrogen plasma, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 35(2015), No. 2, p. 387.
P. Rajput, K.C. Sabat, R.K. Paramguru, B. Bhoi, and B.K. Mishra, Direct reduction of iron in low temperature hydrogen plasma, Ironmaking Steelmaking, 41(2014), No. 10, p. 721.
K.C. Sabat, Formation of CuCo alloy from their oxide mixtures through reduction by low-temperature hydrogen plasma, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 39(2019), No. 4, p. 1071.
K.C. Sabat, Production of nickel by cold hydrogen plasma: role of active oxygen, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 42(2022), No. 4, p. 833.
M.E. Choi and H.Y. Sohn, Development of green suspension ironmaking technology based on hydrogen reduction of iron oxide concentrate: Rate measurements, Ironmaking Steelmaking, 37(2010), No. 2, p. 81.
K. Hassouni, A. Gicquel, M. Capitelli, and J. Loureiro, Chemical kinetics and energy transfer in moderate pressure H2 plasmas used in diamond MPACVD processes, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol., 8(1999), No. 3, p. 494.
K. Hassouni, T.A. Grotjohn, and A. Gicquel, Self-consistent microwave field and plasma discharge simulations for a moderate pressure hydrogen discharge reactor, J. Appl. Phys., 86(1999), No. 1, p. 134.
K. Badr, Smelting of Iron Oxides Using Hydrogen Based Plasmas, [Dissertation], University of Leoben, Leoben, 2007, p. 1.
Y.W. Zhang, W.Z. Ding, S.Q. Guo, and K.D. Xu, Reduction of metal oxide in nonequilibrium hydrogen plasma, Chin. J. Nonferrous Met., 14(2004), No. 2, p. 317.
Y.W. Zhang, W.Z. Ding, X.G. Lu, S.Q. Guo, and K.D. Xu, Reduction of TiO2 with hydrogen cold plasma in DC pulsed glow discharge, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 15(2005), No. 3, p. 594.
R.G. Gold, W.R. Sandall, P.G. Cheplick, and D.R.M. Rae, Plasma reduction of iron oxide with hydrogen and natural gas at 100 kW and one megawatt, Ironmaking Steelmaking, 4(1977), p. 10.
D.R. MacRae, Method of Reducing Ores, US Patent, Appl. 4002466, 1977.
F. Kassabji and B. Pateyron, Technical and economical studies for metal production by plasma-steelmaking application, [in] Proceedings of International Symposium on Plasma Chemistry 4, Zurich, 1979, p. 236.
Y. Nakamura, M. Ito, and H. Ishikawa, Reduction and dephosphorization of molten iron oxide with hydrogen-argon plasma, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 1(1981), No. 2, p. 149.
K. Kamiya, N. Kitahara, I. Morinaka, K. Sakuraya, M. Ozawa, and M. Tanaka, Reduction of molten iron oxide and FeO bearing slags by H2-Ar plasma, ISIJ Int., 24(1984), No. 1, p. 7.
E. Bäck, Schmelzreduktion von Eisenoxiden mit Argon-Wasserstoff-Plasma [Dissertation], Montanuniversität Leoben, Leoben, 1998, p. 1.
T. Nagasaka, M. Hino, and S. Ban-Ya, Interfacial kinetics of hydrogen with liquid slag containing iron oxide, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 31(2000), No. 5, p. 945.
A. Weigel, M. Lemperle, W. Lyhs and H. Wilhelmi, Experiments on the reduction of iron ores with an argon hydrogen plasma, [in] Proceedings of International Symposium on Plasma Chemistry 7, Eindhoven, 1985, p. 1.
H. Hiebler and J.F. Plaul, Hydrogen plasma smelting reduction — An option for steelmaking in the future, Metalurgija, 43(2004), p. 155.
M. Naseri Seftejani and J. Schenk, Kinetics of molten iron oxides reduction using hydrogen S cience and technology in steelmaking, La Metall. Ital., 7(2018), p. 5.
M. Naseri Seftejani and J. Schenk, Thermodynamic of liquid iron ore reduction by hydrogen thermal plasma, Metals, 8(2018), No. 12, p. 1051.
M. Naseri Seftejani and J. Schenk, Kinetics of hydrogen plasma smelting reduction of iron oxides, [in] 7th International Congress on Science and Technology of Steelmaking (ICS-2018), Venice, 2018.
M. Naseri Seftejani, J. Schenk, and M.A. Zarl, Reduction of haematite using hydrogen thermal plasma, Materials, 12(2019), No. 10, art. No. E1608.
M. Naseri Seftejani, J. Schenk, D. Spreitzer, and M. Andreas Zarl, Slag formation during reduction of iron oxide using hydrogen plasma smelting reduction, Materials, 13(2020), No. 4, art. No. 935.
M.A. Zarl, M.A. Farkas, and J. Schenk, A study on the stability fields of arc plasma in the HPSR process, Metals, 10(2020), No. 10, p. 1394.
P.R. Behera, B. Bhoi, R.K. Paramguru, P.S. Mukherjee, and B.K. Mishra, Hydrogen plasma smelting reduction of Fe2O3, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 50(2019), No. 1, p. 262.
H.L. Gilles and C.W. Clump, Reduction of iron ore with hydrogen in a direct current plasma jet, Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev., 9(1970), No. 2, p. 194.
T. Kitamura, K. Shibata, and K. Takeda, In-flight reduction of Fe2O3, Cr2O3, TiO2 and Al2O3 by Ar-H2 and Ar-CH4 plasma, ISIJ Int., 33(1993), No. 11, p. 1150.
K. Saito, Y. Morita, K. Okabe and K. Sanbongi, Reduction by Ar-H2 Plasma, Tetsu-To-Hagane., 63(1977), p. 510.
A.R. Dayal and D.R. Sadedin, Application of pulsed traveling hydrogen arcs for metal oxide reduction, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 23(2003), No. 4, p. 627.
R.M. Nikolic and R.S. Segsworth, Extended arc furnace, IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., IA-13(1977), No. 1, p. 45.
J.K. Tylko, High Temperature Treatment of Materials, US Patent, Appl. 3932171, 1976.
J.K. Tylko, Expanded precessive plasmas, [in] Proceedings of IUPAC Symposium on Plasma Chemistry (ISPC-1), Kiel, 1973, p. 2.
H.T. Wang and H.Y. Sohn, Hydrogen reduction kinetics of magnetite concentrate particles relevant to a novel flash ironmaking process, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 44(2013), No. 1, p. 133.
F. Chen, Y. Mohassab, S.Q. Zhang, and H.Y. Sohn, Kinetics of the reduction of hematite concentrate particles by carbon monoxide relevant to a novel flash ironmaking process, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 46(2015), No. 4, p. 1716.
M.E. Choi, Suspension Hydrogen Reduction Of Iron Ore Concentrate [Dissertation], The University of Utah, Utah, 2010.
V. Dembovsky, Plasma Metallurgy: The Principles, 1st ed., Elsevier, New York, 1985, p.111.
S.M.L. Hamblyn, Plasma technology and its application to extractive metallurgy, Min. Sci Eng, 9(1977), No. 3, p. 151.
M. Mihovsky, Thermal plasma application in metallurgy, J. Univ. Chem. Technol. Metall., 45(2010), p. 3.
K. Badr, E. Bäck and W. Krieger, Hydrogen plasma smelting reduction of iron oxide and its process up-scaling, [in] Forum für Metallurgie und Werkstofftechnik, Leoben, 2007, p. 23.
S.H. Kim, X. Zhang, Y. Ma, et al., Influence of microstructure and atomic-scale chemistry on the direct reduction of iron ore with hydrogen at 700°C, Acta Mater., 212(2021), p. 116933.
S. Ban-ya, Y. Iguchi, and T. Nagasaka, Rate of reduction of liquid iron oxide with hydrogen, Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 23(1982), p. 197.
S. Ban-ya, Y. Iguchi, and T. Nagasaka, Rate of reduction of liquid wustite with hydrogen, Tetsu-to-Hagane, 70(1984), No. 14, p. 1689.
S. Hayashi and Y. Iguchi, Hydrogen reduction of liquid iron oxide fines in gas-conveyed systems, ISIJ Int., 34(1994), No. 7, p. 555.
M. Lemerle and A. Weigel, On the smelting reduction of iron ores with hydrogen-argon plasma, Steel Res., 56(1985), No. 9, p. 465.
S. Seetharaman, Treatise on Process Metallurgy, Volume 3: Industrial Processes, Elsevier, Waltham, 2014.
L. Barreto, A. Makihira, and K. Riahi, The hydrogen economy in the 21st century: A sustainable development scenario, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 28(2003), No. 3, p. 267.
J. Turner, Sustainable hydrogen production, Science, 305(2004), p. 972.
G.F. Naterer, I. Dincer, and C. Zamfirescu, Hydrogen Production from Nuclear Energy, Springer, London, 2013.
L. Walters, D. Wade, and D. Lewis, Transition to a nuclear/hydrogen energy system, Nucl. Energy, 42(2003), No. 1, p. 55.
R.S. El-Emam, H. Ozcan, and C. Zamfirescu, Updates on promising thermochemical cycles for clean hydrogen production using nuclear energy, J. Clean. Prod., 262(2020), p. 121424.
C.W. Forsberg, Future hydrogen markets for large-scale hydrogen production systems, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 32(2007), No. 4, p. 431.
D. Lewis, Hydrogen and its relationship with nuclear energy, Prog. Nucl. Energy, 50(2008), No. 2–6, p. 394.
Acknowledgement
I want to express my deep sense of gratitude to Dr. Tony Murphy of the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation for serving as a friend, philosopher, and guide.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The author declared that there is no conflicts of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabat, K.C. Hematite reduction by hydrogen plasma: Where are we now?. Int J Miner Metall Mater 29, 1932–1945 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-022-2467-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-022-2467-7