Abstract
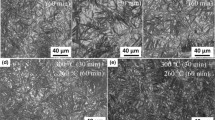
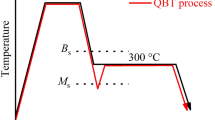
The microstructural evolution and consequent changes in strength and ductility of advanced NANOBAIN steel during prolonged isothermal heat-treatment stages were investigated. The microstructure and mechanical properties of nanostructured bainite were not expected to be influenced by extending the heat-treatment time beyond the optimum value because of the autotempering phenomenon and high tempering resistance. However, experimental results indicated that the microstructure was thermodynamically unstable and that prolonged austempering resulted in carbon depletion from high-carbon retained austenite and carbide precipitations. Therefore, austenite became thermally less stable and partially transformed into martensite during cooling to room temperature. Prolonged austempering did not lead to the typical tempering sequence of bainite, and the sizes of the microstructural constituents were independent of the extended heat-treatment times. This independence, in turn, resulted in almost constant ultimate tensile strength values. However, microstructural variations enhanced the yield strength and the hardness of the material at extended isothermal heat-treatment stages. Finally, although microstructural changes decreased the total elongation and impact toughness, considerable combinations of mechanical properties could still be achieved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia and D.V. Edmonds, Bainite in silicon steels: new composition-property approach Part 1, Met. Sci., 17(1983), p. 411.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia and D.V. Edmonds, Bainite in silicon steels: new composition-property approach Part 2, Met. Sci., 17(1983), p. 420.
S. Khare, K. Lee, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Carbide-free bainite: compromise between rate of transformation and properties, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 41(2010), No. 4, p. 922.
F.G. Caballero, H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, K.J.A. Mawella, D.G. Jones, and P. Brown, Very strong low temperature bainite, Mater. Sci. Technol., 18(2002), p. 279.
F.G. Caballero and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Very strong bainite, Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 8(2004), No. 3-4, p. 251.
C. García Mateo, F.G. Caballero, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Development of hard bainite, ISIJ Int., 43(2003), No. 8, p. 1238.
M.N. Yoozbashi and S. Yazdani, Mechanical properties of nanostructured, low temperature bainitic steel designed using a thermodynamic model, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527(2010), No. 13-14, p. 3200.
M.N. Yoozbashi, S. Yazdani, and T.S. Wang, Design of a new nanostructured, high-Si bainitic steel with lower cost production, Mater. Des., 32(2011), No. 6, p. 3248.
C. Garcia-Mateo and F.G. Caballero, Design of carbide-free low-temperature ultra high strength bainitic steels, Int. J. Mater. Res., 98(2007), No. 2, p. 137.
C. Garcia-Mateo and F.G. Caballero, Ultra-high-strength bainitic steels, ISIJ Int., 45(2005), No. 11, p. 1736.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Nanostructured bainite, Proc. R. Soc. A, 466(2010), p. 3.
F.G. Caballero, M.J. Santofimia, C. Capdevila, C. García-Mateo, and C. García de Andrés, Design of advanced bainitic steels by optimisation of TTT diagrams and T0 curves, ISIJ Int., 46(2006), No. 10, p. 1479.
F.G. Caballero, M.J. Santofimia, C. García-Mateo, J. Chao, and C.G. de Andrés, Theoretical design and advanced microstructure in super high strength steels, Mater. Des., 30(2009), No. 6, p. 2077.
C. Garcia-Mateo, F.G. Caballero, T. Sourmail, J. Cornide, V. Smanio, and R. Elvira, Composition design of nanocrystalline bainitic steels by diffusionless solid reaction, Met. Mater. Int., 3(2014), No. 3, p. 405.
Y. Huang, A.M. Zhao, J.G. He, X.P. Wang, Z.G. Wang, and L. Qi, Microstructure, crystallography and nucleation mechanism of NANOBAIN steel, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 20(2013), No. 12, p. 1155.
C. Garcia-Mateo, F.G. Caballero, T. Sourmail, M. Kuntz, J. Cornide, V. Smanio, and R. Elvira, Tensile behaviour of a nanocrystalline bainitic steel containing 3wt% silicon, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 549(2012), p. 185.
B. Avishan, S. Yazdani, F.G. Caballero, T.S. Wang, and C. Garcia-Mateo, Characterisation of microstructure and mechanical properties in two different nanostructured bainitic steels, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 31(2015), No. 12, p. 1508.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Bainite in Steels, 2nd Ed., Institute of Materials, London, 2001, p. 117.
F.G. Caballero, M.K. Miller, C. Garcia-Mateo, and J. Cornide, New experimental evidence of the diffusionless transformation nature of bainite, J. Alloys Compd., 577(2013), No. s1, p. 626.
H. Bhadeshia and J. Christian, Bainite in steels, Metall. Trans. A, 21(1990), No. 3, p. 767.
F.G. Caballero, M.K. Miller, and C. Garcia-Mateo, The approach to equilibrium during tempering of a bulk nanocrystalline steel: an atom probe investigation, J. Mater. Sci., 43(2008), No. 11, p. 3769.
F.G. Caballero, M.K. Miller, S.S. Babu, and C. García-Mateo, Atomic scale observations of bainite transformation in a high carbon high silicon steel, Acta Mater., 55(2007), No. 1, p. 381.
J. Cornide, G. Miyamoto, F.G. Caballero, T. Furuhara, M.K. Miller, and C. García-Mateo, Distribution of dislocations in nanostructured bainite, Solid State Phenom., 172-174(2011), p. 117.
F.G. Caballero, H.W. Yen, M.K. Miller, J.R. Yang, J. Cornide, and C. Garcia-Mateo, Complementary use of transmission electron microscopy and atom probe tomography for the examination of plastic accommodation in nanocrystalline bainitic steels, Acta Mater., 59(2011), No. 15, p. 6117.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia and A.R. Waugh, Bainite: An atom-probe study of the incomplete reaction phenomenon, Acta Metall., 30(1982), No. 4, p. 775.
F.G. Caballero, C. Garcia-Mateo, M.J. Santofimia, M.K. Miller, and C. García de Andrés, New experimental evidence on the incomplete transformation phenomenon in steel, Acta Mater., 57(2009), No. 1, p. 8.
M. Kabirmohammadi, B. Avishan, and S. Yazdani, transformation kinetics and microstructural features in low-temperature bainite after ausforming process, Mater. Chem. Phys., 184(2016), p. 306.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia and D.V. Edmonds, The bainite transformation in a silicon steel, Metall. Trans. A, 10(1979), No. 7, p. 895.
A. Saha Podder and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Thermal stability of austenite retained in bainitic steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527(2010), No. 7-8, p. 2121.
F.G. Caballero, H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, K.J.A. Mawella, D.G. Jones, and P. Brown, Design of novel high strength bainitic steels: Part 2, Mater. Sci. Technol., 17(2001), No. 5, p. 517.
H.S. Hasan, M.J. Peet, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Severe tempering of bainite generated at low transformation temperatures, Int. J. Mater. Res., 103(2012), No. 11, p. 1319.
C. García-Mateo, F.G. Caballero, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Acceleration of low-temperature bainite, ISIJ Int., 43(2003), No. 11, p. 1821.
B. Avishan, C. Garcia-Mateo, L. Morales-Rivas, S. Yazdani, and F.G. Caballero, Strengthening and mechanical stability mechanisms in nanostructured bainite, J. Mater. Sci., 48(2013), p. 6121.
L.C. Chang and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Austenite films in bainitic microstructures, Mater. Sci. Technol., 11(1995), p. 874.
B.D. Cullity and S.R. Stock, Elements of X-ray Diffraction, 3rd Ed., PrenticeHall, New York, 2001.
D.J. Dyson and B. Holmes, Effect of alloying additions on the lattice parameter of austenite, J. Iron Steel Inst., 208(1970), No. 5, p. 469.
H.W. King and E.A. Payzant, Error corrections for X-ray powder diffractometry, Can. Metall. Q., 40(2001), No. 3, p. 385.
S.B. Singh and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Estimation of bainite plate-thickness in low-alloy steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 245(1998), No. 1, p. 72.
F.G. Caballero, M.K. Miller, and C. Garcia-Mateo, Tracking solute atoms during bainite reaction in a nanocrystalline steel, Mater. Sci. Technol., 26(2010), No. 8, p. 889.
B. Avishan, C. Garcia-Mateo, S. Yazdani, and F.G. Caballero, Retained austenite thermal stability in a nanostructured bainitic steel, Mater. Charact., 81(2013), p. 105.
C. Garcia-Mateo, F.G. Caballero, M.K. Miller, and J.A. Jimenez, On measurement of carbon content in retained austenite in a nanostructured bainitic steel, J. Mater. Sci., 47(2012), No. 2, p. 1004.
C. Garcia-Mateo, M. Peet, F.G. Caballero, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Tempering of hard mixture of bainitic ferrite and austenite, Mater. Sci. Technol., 20(2004), No. 7, p. 814.
C. Garcia-Mateo, F.G. Caballero, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Low temperature bainite, J. Phys. IV, 112(2003), p. 285.
C. Garcia-Mateo, F.G. Caballero, J. Chao, C. Capdevila, and C.G. de Andres, Mechanical stability of retained austenite during plastic deformation of super high strength carbide free bainitic steels, J. Mater. Sci., 44(2009), No. 17, p. 4617.
A. Kammouni, W. Saikaly, M. Dumont, C. Marteau, X. Bano, and A. Charaï, Effect of the bainitic transformation temperature on retained austenite fraction and stability in Ti microalloyed TRIP steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 518(2009), No. 1-2, p. 89.
F.G. Caballero, J. Chao, J. Cornide, C. García-Mateo, M.J. Santofimia, and C. Capdevila, Toughness deterioration in advanced high strength bainitic steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 525 (2009), p. 87.
S. Golchin, B. Avishan, and S. Yazdani, Effect of 10% ausforming on impact toughness of nano bainite austempered at 300°C, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 656 (2016), p. 94.
B. Avishan, S. Yazdani and S.H. Nedjad, Toughness variations in nanostructured bainitic steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 548(2012), p. 106.
Acknowledgments
The author is grateful to Azarbaijan Shahid Madani University for providing the research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avishan, B. Effect of prolonged isothermal heat treatment on the mechanical behavior of advanced NANOBAIN steel. Int J Miner Metall Mater 24, 1010–1020 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-017-1490-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-017-1490-6