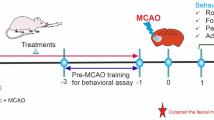
Abstract
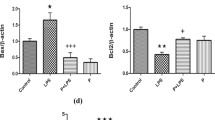
The beneficial effects of probiotics, postbiotics, and paraprobiotics have already been registered in managing ischemic stroke-generated neuroinflammation and gut dysbiosis. Herein, we examined the impact of cell-free supernatant (CFS) obtained from probiotics (Lactobacillus rhamnosus UBLR-58 and Bifidobacterium breve UBBr-01) in a rat transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model of focal cerebral injury. Pre-MCAO supplementation of probiotics (2 × 109 CFU/mL) for 21 days or CFS (1 mL/rat) for 7 days protect the MCAO-induced somatosensory and motor impairments recorded at 24 h and 72 h after reperfusion in foot-fault, rotarod, adhesive removal, and vibrissae-evoked forelimb placing tests. We also noted the reduced infarct area and neuronal degradation in the right hemisphere of probiotics- and CFS-recipient MCAO-operated animals. Moreover, MCAO-induced altered concentrations of glial-fibrillary acidic protein, NeuN, zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), TLR4, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, as well as matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP9) were reversed in the treatment groups. Probiotics and CFS treatment ameliorated the elevated levels of IL-6, IL-1β, and MMP9 in the blood plasma of rats. The disrupted microbial phyla, Firmicutes-to-Bacteroides ratio, villi/crypt ratio, and decreased mucin-producing goblet cells, ZO-1, and occludin in the colon of MCAO-operated rats were recovered following probiotics and CFS treatment. NMR characterization of CFS and rat blood plasma revealed the presence of several important bacterial metabolites. These findings suggest that the CFS obtained from Lactobacillus rhamnosus UBLR-58 and Bifidobacterium breve UBBr-01 has the propensity to improve MCAO-generated neurological dysfunctions in rats by dampening neuroinflammation and modulating the gut-brain axis modulators.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S et al (2018) Heart disease and stroke statistics—2018 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 137(12):e67–492
Hossmann K-A (2006) Pathophysiology and therapy of experimental stroke. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26:1055–1081
Feigin VL, Brainin M, Norrving B, Martins S, Sacco RL, Hacke W et al (2022) World Stroke Organization (WSO): global stroke fact sheet 2022. Int J Stroke 17(1):18–29
Pinzon RT, Wijaya VO (2020) Complications as poor prognostic factors in patients with hemorrhagic stroke: a hospital-based stroke registry. Int J Neurol Neurother 7:96
Ran Y, Su W, Gao F, Ding Z, Yang S, Ye L et al (2021) Curcumin ameliorates white matter injury after ischemic stroke by inhibiting microglia/macrophage pyroptosis through NF-κB suppression and NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:1–25
Caso JR, Pradillo JM, Hurtado O, Lorenzo P, Moro MA, Lizasoain I (2007) Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in brain damage and inflammation after experimental stroke. Circulation 115(12):1599–1608
Bsibsi M, Ravid R, Gveric D, van Noort JM (2002) Broad expression of Toll-like receptors in the human central nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61(11):1013–1021
Rong Z, Huang Y, Cai H, Chen M, Wang H, Liu G et al (2021) Gut microbiota disorders promote inflammation and aggravate spinal cord injury through the TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway. Front Nutr 8:702659
Rahman Z, Bhale NA, Dikundwar AG, Dandekar MP (2023) Multistrain probiotics with fructooligosaccharides improve middle cerebral artery occlusion – driven neurological deficits by revamping microbiota ‑ gut ‑ brain axis. Probiot Antimicrob Prot 26:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-023-10109-y
Díaz-Marugan L, Gallizioli M, Márquez-Kisinousky L, Arboleya S, Mastrangelo A, Ruiz-Jaén F et al (2023) Poststroke lung infection by opportunistic commensal bacteria is not mediated by their expansion in the gut microbiota. Stroke 54(7):1875–1887
Perez-Pardo P, Dodiya HB, Engen PA, Forsyth CB, Huschens AM, Shaikh M et al (2019) Role of TLR4 in the gut-brain axis in Parkinson’s disease: a translational study from men to mice. Gut 68(5):829–843
Cao C, Yang Q, Lv F, Cui J, Fu H, Wang J (2007) Reduced cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in Toll-like receptor 4 deficient mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 353(2):509–514
Ma N, Ma X (2019) Dietary amino acids and the gut-microbiome-immune axis: physiological metabolism and therapeutic prospects. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 18(1):221–242
Armani RG, Ramezani A, Yasir A, Sharama S, Canziani MEF, Raj DS (2017) Gut microbiome in chronic kidney disease. Curr Hypertens Rep 19:1–8
Dandekar MP, Palepu MSK, Satti S, Jaiswal Y, Singh AA, Dash SP et al (2022) Multi-strain probiotic formulation reverses maternal separation and chronic unpredictable mild stress-generated anxiety- and depression-like phenotypes by modulating gut microbiome–brain activity in rats. ACS Chem Neurosci 13(13):1948–1965
Gallizioli M, Arbaizar-Rovirosa M, Brea D, Planas AM (2023) Differences in the post-stroke innate immune response between young and old. Semin Immunopathol. Springer Berlin Heidelberg 45(3):367–376
Battaglini D, Pimentel-Coelho PM, Robba C, Dos Santos CC, Cruz FF, Pelosi P et al (2020) Gut microbiota in acute ischemic stroke: from pathophysiology to therapeutic implications. Front Neurol 11:598
Akhoundzadeh K, Vakili A, Shadnoush M, Sadeghzadeh J (2018) Effects of the oral ingestion of probiotics on brain damage in a transient model of focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Iran J Med Sci 43(1):32–40
Liu J, Sun J, Wang F, Yu X, Ling Z, Li H et al (2015) Neuroprotective effects of clostridium butyricum against vascular dementia in mice via metabolic butyrate. Biomed Res Int 2015:412946
Rahmati H, Momenabadi S, Vafaei AA, Bandegi AR, Mazaheri Z, Vakili A (2019) Probiotic supplementation attenuates hippocampus injury and spatial learning and memory impairments in a cerebral hypoperfusion mouse model. Mol Biol Rep 46:4985–4995
Floch MH (2014) Recommendations for probiotic use in humans—a 2014 update. Pharmaceuticals 7(10):999–1007
Imane HA, Amel D (2018) Characterization and screening of the potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria and Bifidobacterium strains isolated of different biotopes. Med J Nutrition Metab 11(2):145–173
Meini S, Laureano R, Fani L, Tascini C, Galano A, Antonelli A et al (2015) Breakthrough Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG bacteremia associated with probiotic use in an adult patient with severe active ulcerative colitis: case report and review of the literature. Infection 43:777–781
Plaza-Diaz J, Gomez-Llorente C, Abadia-Molina F, Saez-Lara MJ, Campaña-Martin L, Muñoz-Quezada S et al (2014) Effects of Lactobacillus paracasei CNCM I-4034, Bifidobacterium breve CNCM I-4035 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus CNCM I-4036 on hepatic steatosis in Zucker rats. PLoS ONE 9(5):e98401
Camargo AC, Todorov SD, Chihib N-E, Drider D, Nero LA (2018) Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and their bacteriocins as alternative biotechnological tools to control Listeria monocytogenes biofilms in food processing facilities. Mol Biotechnol 60:712–726
Suez J, Zmora N, Segal E, Elinav E (2019) The pros, cons, and many unknowns of probiotics. Nat Med 25(5):716–729
Riquelme AJ, Calvo MA, Guzmán AM, Depix MS, García P, Pérez C et al (2003) Saccharomyces cerevisiae fungemia after Saccharomyces boulardii treatment in immunocompromised patients. J Clin Gastroenterol 36(1):41–43
Aydoğan S, Dilli D, Özyazici A, Aydin N, Şimşek H, Orun UA et al (2021) Lactobacillus rhamnosus sepsis associated with probiotic therapy in a term infant with congenital heart disease. Fetal Pediatr Pathol 41(5):823–827
Besselink MGH, van Santvoort HC, Buskens E, Boermeester MA, van Goor H, Timmerman HM et al (2008) Probiotic prophylaxis in predicted severe acute pancreatitis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 371(9613):651–659
Agus A, Clément K, Sokol H (2021) Gut microbiota-derived metabolites as central regulators in metabolic disorders. Gut 70(6):1174–1182
Wang G, Zeng H (2022) Antibacterial effect of cell-free supernatant from Lactobacillus pentosus L-36 against Staphylococcus aureus from bovine mastitis. Molecules 27(21):7627
Cardoso D L M M, Manzo RM, Tonarelli GG, Simonetta AC (2012) Characterisation of a cell-free supernatant obtained from cultures of Enterococcus faecalis DBFIQ E24 with antagonistic activity against bacteria, yeasts and moulds. Int J Dairy Technol 65(4):568–577
Higashi B, Mariano TB, de Abreu Filho BA, Gonçalves RAC, de Oliveira AJB (2020) Effects of fructans and probiotics on the inhibition of Klebsiella oxytoca and the production of short-chain fatty acids assessed by NMR spectroscopy. Carbohydr Polym 248:116832
Bermudez-Brito M, Munoz-Quezada S, Gomez-Llorente C, Matencio E, Bernal MJ, Romero F et al (2013) Cell-free culture supernatant of Bifidobacterium breve CNCM I-4035 decreases pro-inflammatory cytokines in human dendritic cells challenged with Salmonella typhi through TLR activation. PLoS ONE 8(3):e59370
Keyhani G, Hosseini HM, Salimi A (2022) Effect of extracellular vesicles of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG on the expression of CEA gene and protein released by colorectal cancer cells. Iran J Microbiol 14(1):90
Escamilla J, Lane MA, Maitin V (2012) Cell-free supernatants from probiotic Lactobacillus casei and Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG decrease colon cancer cell invasion in vitro. Nutr Cancer 64(6):871–878
Tong L, Zhang X, Hao H, Liu Q, Zhou Z, Liang X et al (2021) Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG derived extracellular vesicles modulate gut microbiota and attenuate inflammatory in DSS-induced colitis mice. Nutrients 13(10):3319
Li Y, Yang S, Lun J, Gao J, Gao X, Gong Z et al (2020) Inhibitory effects of the Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG effector protein HM0539 on inflammatory response through the TLR4/MyD88/NF-кB axis. Front Immunol 11:551449
Neis EPJG, Dejong CHC, Rensen SS (2015) The role of microbial amino acid metabolism in host metabolism. Nutrients 7(4):2930–2946
Patterson E, Ryan PM, Wiley N, Carafa I, Sherwin E, Moloney G et al (2019) Gamma-aminobutyric acid-producing lactobacilli positively affect metabolism and depressive-like behaviour in a mouse model of metabolic syndrome. Sci Rep 9(1):16323
Wang Y, Liu Y, Sidhu A, Ma Z, McClain C, Feng W (2012) Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG culture supernatant ameliorates acute alcohol-induced intestinal permeability and liver injury. Am J Physiol Liver Physiol 303(1):G32-41
Gu Y, Qin X, Zhou G, Wang C, Mu C, Liu X et al (2022) Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG supernatant promotes intestinal mucin production through regulating 5-HT4R and gut microbiota. Food Funct 13(23):12144–12155
He X, Zeng Q, Puthiyakunnon S, Zeng Z, Yang W, Qiu J et al (2017) Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG supernatant enhance neonatal resistance to systemic Escherichia coli K1 infection by accelerating development of intestinal defense. Sci Rep 7(1):43305
Bermudez-Brito M, Munoz-Quezada S, Gomez-Llorente C, Romero F, Gil A (2014) Lactobacillus rhamnosus and its cell-free culture supernatant differentially modulate inflammatory biomarkers in Escherichia coli-challenged human dendritic cells. Br J Nutr 111(10):1727–1737
Yang B, Chen H, Gao H, Wang J, Stanton C, Ross RP et al (2018) Bifidobacterium breve CCFM683 could ameliorate DSS-induced colitis in mice primarily via conjugated linoleic acid production and gut microbiota modulation. J Funct Foods 49:61–72
Ma Y, Yang S, He Q, Zhang D, Chang J (2021) The role of immune cells in post-stroke angiogenesis and neuronal remodeling: the known and the unknown. Front Immunol 12:5425
Tang W, Zhu H, Feng Y, Guo R, Wan D (2020) The impact of gut microbiota disorders on the blood–brain barrier. Infect Drug Resist 13:3351–3363
Tan Y, Guan Y, Sun Y, Zheng C (2019) Correlation of intestinal mucosal healing and tight junction protein expression in ulcerative colitis patients. Am J Med Sci 357(3):195–204
Rahman Z, Ghuge S, Dandekar MP (2023) Partial blood replacement ameliorates middle cerebral artery occlusion generated neurological aberrations by intervening TLR4 and NLRP3 cascades in rats. Metab Brain Dis 38(7):2339–2354
Savigamin C, Samuthpongtorn C, Mahakit N, Nopsopon T, Heath J, Pongpirul K (2022) Probiotic as a potential gut microbiome modifier for stroke treatment: a systematic scoping review of in vitro and in vivo studies. Nutrients 14(17):3661
Ojha S, Patil N, Jain M, Kole C, Kaushik P (2023) Probiotics for neurodegenerative diseases: a systemic review. Microorganisms 11(4):1083
Martín R, Chain F, Miquel S, Lu J, Gratadoux JJ, Sokol H et al (2014) The commensal bacterium Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is protective in DNBS-induced chronic moderate and severe colitis models. Inflamm Bowel Dis 20(3):417–430
Fuochi V, Coniglio MA, Laghi L, Rescifina A, Caruso M, Stivala A et al (2019) Metabolic characterization of supernatants produced by Lactobacillus spp. with in vitro anti-Legionella activity. Front Microbiol 10:448442
Merrifield CA, Lewis M, Claus SP, Beckonert OP, Dumas M, Duncker S et al (2011) A metabolic system-wide characterisation of the pig: a model for human physiology. Mol BioSyst 7(9):2577–2588
Costello SM, Cheney AM, Waldum A, Tripet B, Cotrina-vidal M, Kaufmann H et al (2023) A Comprehensive NMR Analysis of Serum and Fecal Metabolites in Familial Dysautonomia Patients Reveals Significant Metabolic Perturbations. Metabolites 13(3):433
Balasubramanian R, Bazaz MR, Pasam T, Sharief N, Velip L, Samanthula G et al (2022) Involvement of microbiome gut–brain axis in neuroprotective effect of quercetin in mouse model of repeated mild traumatic brain injury. NeuroMolecular Med 25(2):242–254
Wang L, Zhang B, Yang X, Guo S, Waterhouse GIN, Song G et al (2023) Targeted alleviation of ischemic stroke reperfusion via atorvastatin-ferritin Gd-layered double hydroxide. Bioact Mater 20:126–136
Zhuo Z, Wang H, Zhang S, Bartlett PF, Walker TL, Hou S-T (2023) Selenium supplementation provides potent neuroprotection following cerebral ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 43(7):1060–1076
Liang J, Zhang M, Wang H, Ren Y, Wu Q, Huang R et al (2023) Cholestyramine resin administration alleviated cerebral ischemic injury in obese mice by improving gut dysbiosis and modulating the bile acid profile. Exp Neurol 359:114234
Dandekar MP, Yin X, Peng T, Devaraj S, Morales R, McPherson DD et al (2022) Repetitive xenon treatment improves post-stroke sensorimotor and neuropsychiatric dysfunction. J Affect Disord 301:315–330
Bravo JA, Forsythe P, Chew MV, Escaravage E, Savignac HM, Dinan TG et al (2011) Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(38):16050–16055
Kobayashi Y, Sugahara H, Shimada K, Mitsuyama E, Kuhara T, Yasuoka A et al (2017) Therapeutic potential of Bifidobacterium breve strain A1 for preventing cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep 7(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13368-2
Wang Y, Jaggers RM, Mar P, Galley JD, Shaffer T, Rajab A et al (2021) Lactobacillus reuteri in its bio fi lm state promotes neurodevelopment after experimental necrotizing enterocolitis in rats. Brain, Behav Immun - Heal 14(December 2020):100256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbih.2021.100256
Komotar RJ, Kim GH, Sughrue ME, Otten ML, Rynkowski MA, Kellner CP et al (2007) Neurologic assessment of somatosensory dysfunction following an experimental rodent model of cerebral ischemia. Nat Protoc 2(10):2345–2347
Bharwani A, Mian MF, Surette MG, Bienenstock J, Forsythe P (2017) Oral treatment with Lactobacillus rhamnosus attenuates behavioural deficits and immune changes in chronic social stress. BMC Med 15(1):1–14
Zhu G, Zhao J, Zhang H, Chen W, Wang G (2021) Administration of bifidobacterium breve improves the brain function of aβ1-42-treated mice via the modulation of the gut microbiome. Nutrients 13(5):1602
Chen R, Xu Y, Wu P, Zhou H, Lasanajak Y, Fang Y et al (2019) Transplantation of fecal microbiota rich in short chain fatty acids and butyric acid treat cerebral ischemic stroke by regulating gut microbiota. Pharmacol Res 148:104403
El-Hakim Y, Mani KK, Eldouh A, Pandey S, Grimaldo MT, Dabney A et al (2021) Sex differences in stroke outcome correspond to rapid and severe changes in gut permeability in adult Sprague-Dawley rats. Biol Sex Differ 12:1–16
Simats A, Liesz A (2022) Systemic inflammation after stroke: implications for post‐stroke comorbidities. EMBO Mol Med 14(9):e16269
Roth S, Singh V, Tiedt S, Schindler L, Huber G, Geerlof A et al (2018) Brain-released alarmins and stress response synergize in accelerating atherosclerosis progression after stroke. Sci Transl Med 10(432):eaao1313
Li D, Wu M (2021) Pattern recognition receptors in health and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6(1):291
Lakhan SE, Kirchgessner A, Tepper D, Aidan L (2013) Matrix metalloproteinases and blood-brain barrier disruption in acute ischemic stroke. Front Neurol 4:32
Yang C, Hawkins KE, Doré S, Candelario-jalil XE (2023) Neuroinflammatory mechanisms of blood-brain barrier damage in ischemic stroke. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 316(2):C135–C153
Samer A, Toumi R, Soufli I, Touil-Boukoffa C (2022) Cell-free probiotic supernatant (CFS) treatment alleviates indomethacin-induced enterocolopathy in BALB/c mice by down-modulating inflammatory response and oxidative stress: potential alternative targeted treatment. Inflammopharmacology 30(5):1685–1703
Abdelhamid M, Zhou C, Jung C-G, Michikawa M (2022) Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 mitigates Alzheimer’s disease-related pathologies in wild-type mice. Nutrients 14(12):2543
Famakin BM, Vemuganti R (2020) Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in focal cerebral ischemia: a focus on the neurovascular unit. Mol Neurobiol 57:2690–2701
Sahin GA, Karabulut D, Unal G, Sayan M, Sahin H (2022) Effects of probiotic supplementation on very low dose AFB1-induced neurotoxicity in adult male rats. Life Sci 306:120798
Dziedzic T (2015) Systemic inflammation as a therapeutic target in acute ischemic stroke. Expert Rev Neurother 15(5):523–531
Ge Y, Zadeh M, Yang C, Candelario-Jalil E, Mohamadzadeh M (2022) Ischemic stroke impacts the gut microbiome, ileal epithelial and immune homeostasis. Iscience 25(11):105437
Stahel PF, Shohami E, Younis FM, Kariya K, Otto VI, Lenzlinger PM et al (2000) Experimental closed head injury: analysis of neurological outcome, blood–brain barrier dysfunction, intracranial neutrophil infiltration, and neuronal cell death in mice deficient in genes for pro-inflammatory cytokines. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20(2):369–380
Kumar K, Kumari H, Tripathi AK (2022) Gut microbiota regulation of cerebral stroke. Gut Microbiome Neurol Health Disord. Springer Nature Singapore, p 47–70
Chen Y, Liang J, Ouyang F, Chen X, Lu T, Jiang Z et al (2019) Persistence of gut microbiota dysbiosis and chronic systemic inflammation after cerebral infarction in cynomolgus monkeys. Front Neurol 10:661
Grønberg NV, Johansen FF, Kristiansen U, Hasseldam H (2013) Leukocyte infiltration in experimental stroke. J Neuroinflammation 10(1):1–9
Zhang S, Jin M, Ren J, Sun X, Zhang Z, Luo Y et al (2023) New insight into gut microbiota and their metabolites in ischemic stroke: a promising therapeutic target. Biomed Pharmacother 162:114559
Sinagra E, Pellegatta G, Guarnotta V, Maida M, Rossi F, Conoscenti G et al (2021) Microbiota gut–brain axis in ischemic stroke: a narrative review with a focus about the relationship with inflammatory bowel disease. Life 11(7):715
Houlden A, Goldrick M, Brough D, Vizi ES, Lénárt N, Martinecz B et al (2016) Brain injury induces specific changes in the caecal microbiota of mice via altered autonomic activity and mucoprotein production. Brain Behav Immun 57:10–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2016.04.003
Gorissen L, Raes K, Weckx S, Dannenberger D, Leroy F, De Vuyst L et al (2010) Production of conjugated linoleic acid and conjugated linolenic acid isomers by Bifidobacterium species. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:2257–2266
Winek K, Engel O, Koduah P, Heimesaat MM, Fischer A, Bereswill S et al (2016) Depletion of cultivatable gut microbiota by broad-spectrum antibiotic pretreatment worsens outcome after murine stroke. Stroke 47(5):1354–1363
Yamashiro K, Kurita N, Urabe T, Hattori N (2021) Role of the gut microbiota in stroke pathogenesis and potential therapeutic implications. Ann Nutr Metab 77(Suppl. 2):36–44
Singh V, Sadler R, Heindl S, Llovera G, Roth S, Benakis C et al (2018) The gut microbiome primes a cerebroprotective immune response after stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 38(8):1293–1298
Park MJ, Pilla R, Panta A, Pandey S, Sarawichitr B, Suchodolski J et al (2020) Reproductive senescence and ischemic stroke remodel the gut microbiome and modulate the effects of estrogen treatment in female rats. Transl Stroke Res 11:812–830
Yin J, Liao S, He Y, Wang S, Xia G, Liu F et al (2015) Dysbiosis of gut microbiota with reduced trimethylamine-N-oxide level in patients with large-artery atherosclerotic stroke or transient ischemic attack. J Am Heart Assoc 4(11):e002699
Swer NM, Venkidesh BS, Murali TS, Mumbrekar KD (2023) Gut microbiota-derived metabolites and their importance in neurological disorders. Mol Biol Rep 50(2):1663–1675
He W, Bertram HC (2022) NMR-based metabolomics to decipher the molecular mechanisms in the action of gut-modulating foods. Foods 11(17):2707
Vernocchi P, Del Chierico F, Putignani L (2016) Gut microbiota profiling: metabolomics based approach to unravel compounds affecting human health. Front Microbiol 7:1144
Li Z, Quan G, Jiang X, Yang Y, Ding X, Zhang D et al (2018) Effects of metabolites derived from gut microbiota and hosts on pathogens. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 8:392647
Usami M, Kishimoto K, Ohata A, Miyoshi M, Aoyama M, Fueda Y et al (2008) Butyrate and trichostatin A attenuate nuclear factor κB activation and tumor necrosis factor α secretion and increase prostaglandin E2 secretion in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Nutr Res 28(5):321–328
Acknowledgements
The Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers, and Government of India are acknowledged for their financial support by the authors (ZR, HPP, and MPD). The authors also want to thank Unique Biotech Limited, Hyderabad, India, for providing Lactobacillus rhamnosus UBLR-58 and Bifidobacterium breve UBBr-01 and CFS as gift samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZR carried out the research, compiled the findings, and wrote the article; HPP carried out NMR, and this article was conceptualized, evaluated, and improved by MPD.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, Z., Padhy, H.P. & Dandekar, M.P. Cell-Free Supernatant of Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Bifidobacterium breve Ameliorates Ischemic Stroke-Generated Neurological Deficits in Rats. Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-024-10256-w
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-024-10256-w