Abstract
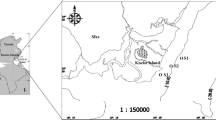
Mesozooplankton community structure and environmental factors were monitored monthly at a fixed station off Tongyeong, southeastern coast of Korea, from 2011 to 2014 to better understand the variability of the mesozooplankton community in relation to changes in the marine environment. Total mesozooplankton density varied from 747 to 8,945 inds. m-3 with peaks in summer. The surface water temperature (r = 0.338, p < 0.05) and chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) concentration (r = 0.505, p < 0.001) were parts of the factors that may have induced the mesozooplankton peaks in summer. Copepods accounted for 71% of total mesozooplankton. Total copepod density, particularly cyclopoid copepods, increased during the study period. Cumulative sum plots and anomalies of the cyclopoid copepod density revealed a change of the cyclopoid density from negative to positive in June 2013. A positive relationship between cyclopoid copepods and the Chl-a concentration (r = 0.327, p < 0.05) appeared to be one of the reasons for the increase in cyclopoids. Dominant mesozooplankton species such as Paracalanus parvus s.l., Oikopleura spp., Evadne tergestina, Cirripedia larvae, Corycaeus affinis, Calanus sinicus, and Oithona similis accounted for 60% of total mesozooplankton density. Based on cluster analysis of the mesozooplankton community by year, the seasonal distinction among groups was different in 2014 compared to other years. P. parvus s.l. and its copepodites contributed most in all groups in all four years. Our results suggest that the high Chl-a concentration since 2013 may have caused the changes in mesozooplankton community structure in the study area.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Alldredge AL (1981) The impact of appendicularian grazing on natural food concentrations in situ. Limnol Oceanogr 26(2): 247–257
Anon (1977) Study on plankton in China Seas. In: Scientific reports of ‘Comprehensive oceanography expedition in China seas’, Ocean Res Off Press, Tianjun, pp 1–159 (in Chinese)
Baranović A, Šolić M, Vučetić T, Krstulović N (1993) Temporal fluctuations of zooplankton and bacteria in the middle Adriatic Sea. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 92:65–75
Beaugrand G, Ibañez F, Reid PC (2000) Spatial, seasonal and longterm fluctuations of plankton in relation to hydroclimatic features in the English Channel, Celtic Sea and Bay Of Biscay. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 200:93–102
Castellani C, Irigoien X, Harris RP, Lampitt RS (2005) Feeding and egg production of Oithona similis in the North Atlantic. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 288:173–182
Chen QC (1964) Study on the reproduction, sex ratio and body size of Calanus sinicus. Oceanol Limnol Sin 6:272–287
Christaki U, Dolan JR, Pelegri S, Rassoulzadegan F (1998) Consumption of picoplankton–size particles by marine ciliates: effects of physiological state of the ciliate and particle quality. Limnol Oceanogr 43(3):458–464
Clarke KR, Warwick RM (2001) An approach to statistical analysis and interpretation. Change in marine communities, 2nd edition. PRIMER-E Ltd., Plymouth, 176 p
Deibel D (1986) Feeding mechanism and house of the appendicularian Oikopleura vanhoeffeni. Mar Biol 93(3):429–436
Gannon JE, Stemberger RS (1978) Zooplankton (especially crustaceans and rotifers) as indicators of water quality. T Am Microsc Soc 97:16–35
Guo X, Miyazawa Y, Yamagata T (2006) The Kuroshio onshore intrusion along the shelf break of the East China Sea: the origin of the Tsushima Warm Current. J Phys Oceanogr 36(12):2205–2231
Hwang OM, Shin KS, Baek SH, Lee WJ, Kim SA, Jang MC (2011) Annual variations in community structure of mesozooplankton by short-term sampling in Jangmok Harbor of Jinhae bay. Ocean Polar Res 33(3):235–253 (in Korean)
Jang MC, Baek SH, Jang PG, Lee WJ, Shin KS (2012) Patterns of zooplankton distribution as related to water masses in the Korea strait during winter and summer. Ocean Polar Res 34(1):37–51 (in Korean)
Jeong DH, Shin HH, Jung SW, Lim DI (2013) Variations and characters of water quality during flood and dry seasons in the eastern coast of South Sea, Korea. Korean J Environ Biol 31(1):19–36 (in Korean)
Jiang X, Tang Y, Lonsdale DJ, Gobler CJ (2009) Deleterious consequences of a red tide dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides for the calanoid copepod Acartia tonsa. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 390:105–116
Jung SW, Kwon OY, Lee JH (2008) Variation and relationship between standing crops and biomass of phytoplankton dominant species in the marine ranching ground of tongyeong coastal waters from 2000 to 2007. Algae 23(1):53–61 (in Korean)
Kang YS, Kwon JN, Shon JK, Jeong CS, Hong SJ, Kong JY (2003) Interrelation between water quality and community structure of phytoplankton around the season of red tide outbreak off the coast of Tongyeong area, 2002. Korean J Fish Aquat Sci 36(5):515–521 (in Korean)
Landsberg JH (2002) The effects of harmful algal blooms on aquatic organisms. Rev Fish Sci 10(2):113–390
Lee JH, Chae JH, Kim WR, Jung SW, Kim JM (2001) Seasonal variation of phytoplankton and zooplankton communities in the coastal waters off Tongyeong in Korea. Ocean Polar Res 23(3):245–253
Lee YS (2006) Factors affecting outbreaks of high–density Cochlodinium polykrikoides red tides in the coastal seawaters around Yeosu and Tongyeong, Korea. Mar Pollut Bull 52(10): 1249–1259
Lim W, Lee YS, Kang YS, Kim SS, Kim SH, Choi HS, Hur YB, Lee TS, Lee JY (2010) Inter–annual variation of Phytoplankton community structure in Aquacultural areas of Tongyeong, SE coastal waters of Korea. J Korean Soc Oceanogr 15(4):158–165 (in Korean)
Marshall SM (1949) On the biology of the small copepods in Loch Striven. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 28(1):45–113
McKinnon AD, Duggan S (2001) Summer egg production rates of paracalanid copepods in subtropical waters adjacent to Australia’s North West Cape. Hydrobiologia 453(1):121–132
Murdoch J (1979) Control charts. Macmillan Press, London, 479 p
Moon SY, Oh HJ, Soh HY (2010) Seasonal variation of zooplankton communities in the southern coastal waters of Korea. Ocean Polar Res 32(4):411–426 (in Korean)
Nakamura Y, Turner JT (1997) Predation and respiration by the small cyclopoid copepod Oithona similisr: How important is feeding on ciliates and heterotrophic flagellates? J Plankton Res 19(9):1275–1288
Park HS, Choi JW, Lee HG (2000) Community structure of macrobenthic fauna under marine fish culture cages near Tong–yong, Southern Coast of Korea. Korean J Fish Aquat Sci 33(1):1–8
Parsons TR, Maita Y, Lalli CM (1984) A manual of biological and chemical methods for seawater analysis. Pergamon Press, Oxford, 173 p
Paffenhöfer GA (1976) On the biology of Appendicularia of the southeastern North Sea. In: Persoone G, Jaspers E (eds) 10th European symposium on marine biology, Vol. 2. Population dynamics. Universa Press, Ostend, pp 437–455
Paffenhöfer GA (1993) On the ecology of marine cyclopoid copepods (Crustacea, Copepoda). J Plankton Res 15(1):37–55
Peterson W, Gomez–Gutierrez J, Morgan CA (2002) Cross–shelf variation in calanoid copepod production during summer 1996 off the Oregon coast, USA. Mar Biol 141(2):353–365
Pu XM, Sun S, Yang B, Ji P, Zhang YS, Zhang F (2004) The combined effects of temperature and food supply on Calanus sinicus in the southern Yellow Sea in summer. J Plankton Res 26(9):1049–1057
Rong W, Hong–yan Z, Ke W, Tao Z (2002) Distribution and population dynamics of Paracalanus parvus, Paracalanus crassirostris, and Acartia bifilosa (copepoda, calanoida) in the Bohai Sea. Chin J Oceanol Limn 20(4):348–357
Sabatini M, Kiørboe T (1994) Egg production, growth and development of the cyclopoid copepod Oithona similis. J Plankton Res 16(10):1329–1351
Song B (2015) Grazing effect of size–fractionated copepods on their prey in the coastal waters of Tong–young. M.D. Thesis, Inha University, 46 p (in Korean)
Shannon CE, Weaver W (1963) The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana, 125 p
Sherr E, Sherr B (1988) Role of microbes in pelagic food webs: A revised concept. Limnol Oceanogr 33(5):1225–1227
Shin K, Jang MC, Jang PK, Ju SJ, Lee TK, Chang M (2003) Influence of food quality on egg production and viability of the marine planktonic copepod Acartia omorii. Prog Oceanogr 57(3):265–277
Stoecker DK, Capuzzo JM (1990) Predation on protozoa: its importance to zooplankton. J Plankton Res 12(5):891–908
Sugimoto T, Tadokoro K (1997) Interannual–interdecadal variations in zooplankton biomass, chlorophyll concentration and physical environment in the subarctic Pacific and Bering Sea. Fish Oceanogr 6(2):74–93
Sun XH, Sun S, Li CL, Zhang GT (2008) Seasonal and spatial variation in abundance and egg production of Paracalanus parvus (Copepoda: Calanoida) in/out Jiaozhou Bay, China. Estuar Coast Shelf S 79(4):637–643
Suzuki K, Nakamura Y, Hiromi J (1999) Feeding by the small calanoid copepod Paracalanus sp. on heterotrophic dinoflagellates and ciliates. Aquat Microb Ecol 17(1):99–103
Teague WJ, Jacobs GA, Perkins HT, Book JW, Chang KI, Suk MS (2002) Low-frequency current observations in the Korea/ Tsushima strait. J Phys Oceanogr 32(6):1621–1641
Ter Braak CJF, Smilauer P (2002) Canoco for Windows version 4.5. Biometris–Plant Research International, Wageningen
Tomosada A, Odate K (1995) Long–term variability in zooplankton biomass and environment. Umi to Sora 71:1–7 (in Japanese)
Turner JT (2006) Harmful algae interactions with marine planktonic grazers. In: Granéli E, Turner JT (eds) Ecology of harmful algae. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 259–270
Turner JT (2010) Zooplankton community grazing impact on a bloom of Alexandrium fundyense in the gulf of maine. Harmful Algae 9(6):578–589
Turner JT (2014) Planktonic marine copepods and harmful algae. Harmful Algae 32:81–93
Turner JT, Tester PA (1997) Toxic marine phytoplankton, zooplankton grazers, and pelagic food webs. Limnol Oceanogr 42(5): 1203–1213
Uye S (2000) Why does Calanus sinicus prosper in the shelf ecosystem of the Northwest Pacific Ocean? ICES J Mar Sci 57(6):1850–1855
Uye S, Ichino S (1995) Seasonal variations in abundance, size composition, biomass and production rate of Oikopleura dioica (Fol) (Tunicata: Appendicularia) in a temperate eutrophic inlet. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 189(1):1–11
Uye S, Sano K (1998) Seasonal variations in biomass, growth rate and production rate of the small cyclopoid copepod Oithona davisae in a temperate eutrophic inlet. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 163:37–44
Uye S, Takamatsu K (1990) Feeding interactions between planktonic copepods and red-tide flagellates from Japanese coastal waters. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 59:1–2
Viitasalo M, Vuorinene I, Ranta E (1990) Changes in crustacean mesozooplankton and some environmental parameters in the Archipelago Sea (Northern Baltic) in 1976–1984. Ophelia 31(3):207–217
Wang R, Zuo T, Wang K (2003) The Yellow Sea cold bottom water—an oversummering site for Calanus sinicus (Copepoda, Crustacea). J Plankton Res 25(2):169–183
Watras CJ, Garcon VC, Olson RJ, Chisholm SW, Anderson DM (1985) The effect of zooplankton grazing on estuarine blooms of the toxic dinoflagellate Gonyaulax tamarensis. J Plankton Res 7(6):891–908
Yang EJ, Kang HK, Yoo S, Hyun JH (2009) Contribution of auto–and heterotrophic protozoa to the diet of copepods in the Ulleung Basin, East Sea/Japan Sea. J Plankton Res 31(6): 647–659
Yang EJ, Ju SJ, Choi JK (2010) Feeding activity of the copepod Acartia hongi on phytoplankton and micro–zooplankton in Gyeonggi Bay, Yellow Sea. Estuar Coast Shelf S 88(2):292–301
Yi WY, Kang HK, Song B, Choi JK (2013) Egg production rate and hatching success in relation to feeding rate of the planktonic copepod Paracalanus parvus s.l. at a fixed station, southeastern coast of Korea. In: PICES 2013 Annual Meeting, Communicating forecasts, uncertainty and consequences of ecosystem change, Nanaimo, Canada, 11–20
Oct Yoon H, Choi S (2006) Study on resources annexation in Tongyeong Marine ranching: II. Change of growth and stomach contents on night–lights and feeding condition of black rockfish Sebastes inermis. Korean J Environ Biol 24(2):138–146 (in Korean)
You KI, Lim DH (1995) Temporal and spatial distribution of Oithona similis (Copepoda: Cyclopoida) in Masan Bay, Korea. Korean J Environ Biol 13(1):53–60 (in Korean)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, G., Kang, HK. & Myoung, JG. Seasonal and interannual variation in mesozooplankton community structure off Tongyeong, southeastern coast of Korea, from 2011 to 2014. Ocean Sci. J. 52, 113–125 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-017-0005-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-017-0005-8