Abstract
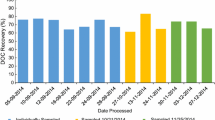
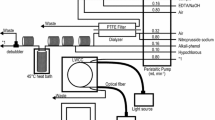
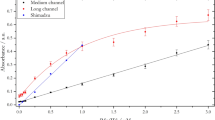
In this study we describe measures taken in our laboratory to improve the long-term precision of nitrate and ammonia analysis in seawater using a microflow segmented-flow analyzer. To improve the nitrate reduction efficiency using a flow-through open tube cadmium reactor (OTCR), we compared alternative buffer formulations and regeneration procedures for an OTCR. We improved long-term stability for nitrate with a modified flow scheme and color reagent formulation and for ammonia by isolating samples from the ambient air and purifying the air used for bubble segmentation. We demonstrate the importance of taking into consideration the residual nutrient content of the artificial seawater used for the preparation of calibration standards. We describe how an operating procedure to eliminate errors from that source as well as from the refractive index of the matrix itself can be modified to include the minimization of dynamic refractive index effects resulting from differences between the matrix of the samples, the calibrants, and the wash solution. We compare the data for long-term measurements of certified reference material under two different conditions, using ultrapure water (UPW) and artificial seawater (ASW) for the sampler wash.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aminot A, Kirkwood DS (1995) The fifth ICES inter-comparison exercise for nutrients in seawater. ICES, Copenhagen, ICES Cooperative Research Report Series 213, 79 p
Aminot A, Kérouel R, Coverly SC (2009) Nutrients in seawater using segmented flow analysis. In: Wurl O (ed) Practical guidelines for the analysis of seawater. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 143–178
Aminot A, Kirkwood DS, Kérouel R (1997) Determination of ammonia in seawater by the indophenol-blue method: evaluation of the ICES NUTS I/C 5 questionnaire. Mar Chem 56:59–75
Aoyama M, Bakker K, van Ooijen J, Ossebaar S, Woodward EMS (2012) Report from an international nutrient workshop focusing on phosphate analysis. Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research, Texel, 65 p
Bindoff, NL, Willebrand J, Artale V, Cazenave A, Gregory J, Gulev S, Hanawa K, Le Quéré C, Levitus S, Nojiri Y, Shum CK, Talley LD, Unnikrishnan A (2007) Observations: oceanic climate change and sea level. In: Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt AB, Tignor M, Miller HL (eds) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 385–433
Coverly SC, Kérouel R, Aminot A (2012). A re-examination of matrix effects in the segmented-flow analysis of nutrients in sea and estuarine waters. Anal Chim Acta 712:94–100
Dugdale RC, Goering JJ (1967) Uptake of new and regenerated forms of nitrogen in primary productivity. Limnol Oceanogr 12:196–206
Garside C (1993) Nitrate reductor efficiency as an error source in seawater analysis. Mar Chem 44:25–30
Gordon LI, Jennings JC, Rosse AA, Krest JM (1993) A suggested protocol for continuous flow automated analysis of seawater nutrients (phosphate, nitrate, nitrite and silicic acid) in the WOCE Hydrographic program and the Joint Global Ocean Fluxes Study. WOCE Hydrographic Program Office, Methods Manual WHPO 91-1, 55 p
Grasshoff K, Kremling K, Ehrhardt M (1999) Methods of seawater analysis. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 600 p
Harrison WG, Harris LR, Irwin BD (1996). The kinetics of nitrogen utilization in the oceanic mixed layer: nitrate and ammonium interactions at nanomolar concentration. Limnol Oceanogr 41:16–32
Holmes RM, Aminot A, Kérouel R, Hooker BA, Peterson BJ (1999) A simple and precise method for measuring ammonium in marine and freshwater ecosystem. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 56:1801–1808
Hydes D, Aoyama M, Aminot A, Bakker K, Becker S, Coverly S, Daniel A, Dickson A, Grosso O, Kérouel R, van Ooijen J, Sato K, Tanhua T, Woodward M, Zhang J (2010) Determination of dissolved nutrients (N, P, Si) in seawater with high precision and inter-comparability using gas-segmented continuous flow analyzers. The GO-SHIP repeat hydrography manual: a collection of expert reports and guidelines, IOCCP report No. 14, ICPO publication series No. 134, 87 p
Jeon HD, Rho T, Lee T (2012) Spatial distribution of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) and their relation to carbon species in the euphotic layer of the northern East Sea. J Kor Soc Oceanogr 17:33–44
Kérouel R, Aminot A (1997) Fluorometric determination of ammonia in sea and estuarine waters by direct segmented flow analysis. Mar Chem 57:265–275
Mantoura RFC, Woodward EMS (1983) Conservative behavior of riverine dissolved organic carbon in the Severn Estuary: chemical and geochemical implications. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 47:1293–1309.
MRI (2008) 2006 Intercomparison exercise for reference material for nutrients in seawater in a seawater matrix. Meteorological Research Institute, Technical Reports of the Meteorological Research Institute No. 58
MRI (2010) 2008 Inter-laboratory comparison study of a reference material for nutrients in seawater. Meteorological Research Institute, Technical Reports of the Meteorological Research Institute No. 60, 134 p
Patton CJ (1982) Novel cadmium reactors for determination of nitrate in water and seawater by segmented, continuous flow colorimetry. Ph.D. Thesis, Michigan State University
Rho TK, Kang D-J, Kim E-S, Kahang S-H, Cho SR, Lee JM, Park EJ, Moon C-R (2015) Development of reference material using natural seawater for nutrient analysis in seawater. J Kor Soc Oceanogr 20:29–35
SEAL Analytical (2010) AACE 6.06 Software operation manual publication no. MB7-60EN-06. SEAL Analytical, Inc
Wheeler PA, Kokkinakis SA (1990) Ammonium recycling limits nitrate use in the oceanic subarctic Pacific. Limnol Oceanogr 35:1267–1278
Wood ED, Armstrong FAJ, Richards FA (1967) Determination of nitrate in sea water by cadmium-copper reduction to nitrite. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 47:23–32
Woodward EMS, Coverly SC, Kérouel R, Aminot A (2010). Some specific analytical considerations for segmented flow nutrient autoanalyzers. In: Aoyama A, Dickson AG, Hydes DJ, Murata A, Oh J-R, Roose P, Woodward EMS (eds) Comparability of nutrients in the world’s ocean. Mother Tank, Tsukuba, pp 69–80
Zhang JZ (1997) Distinction and quantification of carry-over and sample interaction in gas segmented continuous flow analysis. J Autom Chem 19:205–212
Zhang JZ, Fischer CJ and Ortner PB (2000) Comparison of open tubular cadmium reactor and packed cadmium column in automated gas-segmented continuous flow nitrate analysis. Int J Environ An Ch 76(2):99–111
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rho, T.K., Coverly, S., Kim, ES. et al. Practical considerations for the segmented-flow analysis of nitrate and ammonium in seawater and the avoidance of matrix effects. Ocean Sci. J. 50, 709–720 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-015-0064-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-015-0064-7