Abstract
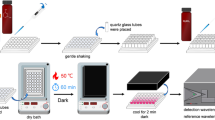
A continuous flow method for the determination of ammonium concentration in seawater from a nanomolar to a micromolar level is described. To prevent spurious peaks derived from salinity difference, a gas-permeable hydrophobic membrane filter was used to separate the manifold into an outgassing section and an indophenol blue reaction section. The indophenol blue reaction section was adopted for colorimetric analysis and is equipped with a 1-m path length liquid capillary cell and a fiber-optic spectrometer, which is able to record the absorbance at multiple wavelengths. The minimum detection limit at wavelength 630 nm is 5.5 ± 1.8 nM, and the calibration curves are linear to at least 2,000 nM. In addition, the minimum detection limit at wavelength 530 nm was 13 ± 5.3 nM, and linear calibration curves were observed until at least 10,000 nM. The slopes of the calibration curves were similar for standards prepared using filtered seawater and ultrapure water. The ammonium concentration of the ultrapure water was similar to those of ion-exchanged water and unfiltered low-nutrient seawater, but was significantly lower than those of filtered seawater and solutions that contained sodium hydroxide. Therefore, ultrapure water is optimal for both blank and standard preparations because of its stable quality and availability. Given its large concentration range and the use of readily available blanks, this method is suitable for the determination of ammonium concentration and helps our understanding of ammonium dynamics in the ocean.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amornthammarong N, Zhang JZ (2008) Shipboard fluorometric flow analyzer for high-resolution underway measurement of ammonium in seawater. Anal Chem 80(4):1019–1026. doi:10.1021/ac701942f
Bronk DA (2002) Dynamics of DON. In: Hansell DA, Carlson CA (eds) Biogeochemistry of marine dissolved organic matter. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 153–247. doi:10.1016/B978-012323841-2/50007-5
Brzezinski MA (1987) Colorimetric determination of nanomolar concentrations of ammonium in seawater using solvent-extraction. Mar Chem 20(3):277–288. doi:10.1016/0304-4203(87)90078-8
Brzezinski MA (1988) Vertical distribution of ammonium in stratified oligotrophic waters. Limnol Oceanogr 33(5):1176–1182. doi:10.4319/lo.1988.33.5.1176
Chen GH, Zhang M, Zhang Z et al (2011) On-line solid phase extraction and spectrophotometric detection with flow technique for the determination of nanomolar level Ammonium in seawater samples. Anal Lett 44(1–3):310–326. doi:10.1080/00032719.2010.500775
Clark DR, Rees AP, Joint I (2007) A method for the determination of nitrification rates in oligotrophic marine seawater by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Mar Chem 103(1–2):84–96. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2006.06.005
Coverly S, Kerouel R, Aminot A (2012) A re-examination of matrix effects in the segmented-flow analysis of nutrients in sea and estuarine water. Anal Chim Acta 712:94–100. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2011.11.008
Dean JA (1998) Lange’s handbook of chemistry. McGraw-Hill Inc, New York
Dortch Q (1990) The interaction between ammonium and nitrate uptake in phytoplankton. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 61(1–2):183–201. doi:10.3354/Meps061183
Eppley RW, Peterson BJ (1979) Particulate organic matter flux and planktonic new production in the deep ocean. Nature 282(5740):677–680. doi:10.1038/282677a0
Francis CA, Roberts KJ, Beman JM et al (2005) Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. Proc Nat Acad Sci 102(41):14683–14688. doi:10.1073/pnas.0506625102
Garside C (1982) A chemiluminescent technique for the determination of nanomolar concentrations of nitrate and nitrite in seawater. Mar Chem 11(2):159–167. doi:10.1016/0304-4203(82)90039-1
Gordon LI, Jennings Jr JC, Ross AA et al (1993) A suggested protocol for continuous flow automated analysis of seawater nutrients (phosphate, nitrate, nitrite and silicic acid) in the WOCE hydrographic program and the joint global ocean fluxes study. WOCE Operations Manual, WHP Office Report WHPO 91-1, WOCE Report No. 68/91. Woods Hole, Massachusetts, USA
Harrison WG, Harris LR, Irwin BD (1996) The kinetics of nitrogen utilization in the oceanic mixed layer: nitrate and ammonium interactions at nanomolar concentrations. Limnol Oceanogr 41(1):16–32. doi:10.4319/lo.1996.41.1.0016
Hashihama F, Kanda J (2010) Automated colorimetric determination of trace silicic acid in seawater by gas-segmented continuous flow analysis with a liquid waveguide capillary cell. La mer 47:119–127
Hashihama F, Furuya K, Kitajima S et al (2009) Macro-scale exhaustion of surface phosphate by dinitrogen fixation in the western North Pacific. Geophys Res Lett vol 36. doi:10.1029/2008gl036866
Hashihama F, Sato M, Takeda S et al (2010) Mesoscale decrease of surface phosphate and associated phytoplankton dynamics in the vicinity of the subtropical South Pacific islands. Deep-Sea Res I 57(3):338–350. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2009.12.005
Hashihama F, Kanda J, Maeda Y et al (2014) Selective depressions of surface silicic acid within cyclonic mesoscale eddies in the oligotrophic western North Pacific. Deep Sea Res I 90:115–124. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2014.05.004
Hydes D, Aoyama M, Aminot A et al (2010) Determination of dissolved nutrients (N, P, Si) in seawater with high precision and inter-comparability using gas-segmented continuous flow analysers. In: The GO-SHIP Repeat Hyrography Manual: a collection of expert reports and guidelines, IOCCP report No. 14, ICPO publication series No. 134, version 1
Ikeda T, Kanno Y, Ozaki K et al (2001) Metabolic rates of epipelagic marine copepods as a function of body mass and temperature. Mar Biol 139(3):587–596. doi:10.1007/s00227-001-0743-z
Jones RD (1991) An improved fluorescence method for the determination of nanomolar concentrations of ammonium in natural waters. Limnol Oceanogr 36(4):814–819. doi:10.4319/lo.1991.36.4.0814
Karl DM, Tien G (1992) MAGIC: a sensitive and precise method for measuring dissolved phosphorus in aquatic environments. Limnol Oceanogr 37(1):105–116. doi:10.4319/lo.1992.37.1.0105
Karl DM, Letelier R, Hebel DV et al (1992) Trichodesmium blooms and new nitrogen in the North Pacific gyre, marine pelagic cyanobacteria: Trichodesmium and other diazotrophs. Springer, Berlin, pp. 219–237
Kerouel R, Aminot A (1997) Fluorometric determination of ammonia in sea and estuarine waters by direct segmented flow analysis. Mar Chem 57(3–4):265–275. doi:10.1016/S0304-4203(97)00040-6
Kirchman DL, Keil RG, Wheeler PA (1990) Carbon limitation of ammonium uptake by heterotrophic Bacteria in the SubArctic Pacific. Limnol Oceanogr 35(6):1258–1266. doi:10.4319/lo.1990.35.6.1258
Kodama T, Furuya K, Hashihama F et al (2011) Occurrence of rain-origin nitrate patches at the nutrient-depleted surface in the East China Sea and the Philippine Sea during summer. J Geophys Res Oceans 116:C08003. doi:10.1029/2010jc006814
Li QP, Hansell DA (2008) Intercomparison and coupling of magnesium-induced co-precipitation and long-path liquid-waveguide capillary cell techniques for trace analysis of phosphate in seawater. Anal Chim Acta 611(1):68–72. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2008.01.074
Li QP, Zhang JZ, Millero FJ et al (2005) Continuous colorimetric determination of trace ammonium in seawater with a long-path liquid waveguide capillary cell. Mar Chem 96(1–2):73–85. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2004.12.001
Lipschultz F (2001) A time-series assessment of the nitrogen cycle at BATS. Deep Sea Res II 48(8–9):1897–1924. doi:10.1016/S0967-0645(00)00168-5
Ma J, Adornato L, Byrne RH et al (2014) Determination of nanomolar levels of nutrients in seawater. Trends Anal Chem 60:1–15. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2014.04.013
Matsumoto K, Furuya K, Kawano T (2004) Association of picophytoplankton distribution with ENSO events in the equatorial Pacific between 145°E and 160°W. Deep Sea Res I 51(12):1851–1871. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2004.07.015
McCarthy MD, Bronk DA (2008) Analytical methods for the study of nitrogen. In: DG Capone, EJ Carpenter, DA Bronk et al (eds) Nitrogen in the marine environment. Academic, London, pp. 1220–1271. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-372522-6.00028-1
Miller JC, Miller JN (1988) Statistics for analytical chemistry. Ellis Horwood series in analytical chemistry. E. Horwood, New York
Nishino S, Itoh M, Kawaguchi Y et al (2011) Impact of an unusually large warm-core eddy on distributions of nutrients and phytoplankton in the southwestern Canada Basin during late summer/early fall 2010. Geophys Res Lett vol 38. doi:10.1029/2011gl047885
O’Connor Šraj L, Almeida M, Swearer SE et al (2014) Analytical challenges and advantages of using flow-based methodologies for ammonia determination in estuarine and marine waters. Chem, Trends Anal. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2014.03.012
Oliveira SM, Marques da Silva Lopes TI, Toth IV et al (2009) Determination of ammonium in marine waters using a gas diffusion multicommuted flow injection system with in-line prevention of metal hydroxides precipitation. J Environ Monit 11(1):228–234. doi:10.1039/b812624k
Parsons TR, Maita Y, Lalli CM (1984) A manual of chemical and biological methods for seawater analysis. Pergamon, Oxford
Patey MD, Rijkenberg MJA, Statham PJ et al (2008) Determination of nitrate and phosphate in seawater at nanomolar concentrations. Trends Anal Chem 27(2):169–182. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2007.12.006
Plant JN, Johnson KS, Needoba JA et al (2009) NH4-Digiscan: an in situ and laboratory ammonium analyzer for estuarine, coastal, and shelf waters. Limnol Oceanogr Methods 7:144–156. doi:10.4319/lom.2009.7.144
Raimbault P, Garcia N (2008) Evidence for efficient regenerated production and dinitrogen fixation in nitrogen-deficient waters of the South Pacific Ocean: impact on new and export production estimates. Biogeosciences 5(2):323–338. doi:10.5194/bg-5-281-2008
Raimbault P, Garcia N, Cerutti F (2008) Distribution of inorganic and organic nutrients in the south Pacific Ocean—evidence for long-term accumulation of organic matter in nitrogen-depleted waters. Biogeosciences 5(2):281–298. doi:10.5194/bg-5-311-2008
Rees AP, Woodward EMS, Joint I (2006) Concentrations and uptake of nitrate and ammonium in the Atlantic Ocean between 60°N and 50°S. Deep Sea Res II 53(14–16):1649–1665. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2006.05.008
Saino T, Otobe H, Wada E et al (1983) Subsurface ammonium maximum in the northern North Pacific and the Bering Sea in summer. Deep Sea Res A 30(11):1157–1171. doi:10.1016/0198-0149(83)90094-8
Schulze G, Liu C, Brodowski M et al (1988) Different approaches to the determination of ammonium ions at low levels by flow injection analysis. Anal Chim Acta 214:121–136. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(00)80435-3
Steinberg DK, Saba GK (2008) Nitrogen consumption and metabolism in marine zooplankton. In: Capone DG, Carpenter EJ, Bronk DA et al (eds) Nitrogen in the marine environment. Academic, London, pp 1135–1196. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-372522-6.00026-8
Van Son M, Schothorst R, Den Boef G (1983) Determination of total ammoniacal introgen in water by flow injection analysis and a gas diffusion membrane. Anal Chim Acta 153:271–275. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(00)85513-0
Ward BB (2011) Measurement and distribution of nitrification rates in the oceans. Meth Enzymol 486:307–323. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-381294-0.00013-4
Wheeler PA, Kirchman DL (1986) Utilization of inorganic and organic nitrogen by bacteria in marine systems. Limnol Oceanogr 31(5):998–1009. doi:10.4319/lo.1986.31.5.0998
Zhu Y, Yuan DX, Huang YM et al (2014) A modified method for on-line determination of trace ammonium in seawater with a long-path liquid waveguide capillary cell and spectrophotometric detection. Mar Chem 162:114–121. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2014.03.011
Acknowledgments
We thank the officers and crewmembers of the R/V Soyo-maru Koda cruise for their cooperation at sea. We are grateful to Mr. H. Kikuchi of BL-TEC for his technical assistance and advice. This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Japan through a research project entitled “Development of technologies for mitigation and adaptation to climate change in Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries” and by a MEXT grant (24121005) to K. F.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kodama, T., Ichikawa, T., Hidaka, K. et al. A highly sensitive and large concentration range colorimetric continuous flow analysis for ammonium concentration. J Oceanogr 71, 65–75 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-014-0260-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-014-0260-6