Abstract
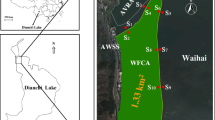
In this study, we examined whether phytoremediation using benthic microalgae (BMA) and a light emitting diode (LED) can remediate eutrophic sediments caused by promoting the growth of BMA. A field application experiment was conducted from September 9 to December 3, 2011, in Masan Bay, Korea. Two chambers were used: an experimental site, which included a red LED (650 nm) lamp and replanted Nitzschia sp. on the surface sediment, and a control site, which did not contain an LED lamp and replanted Nitzschia sp. on the surface sediment. Chlorophyll a (Chl. a) concentration increased at the experimental site, and was 2 times the concentration at the control site. Acid-volatile sulfide (AVS) concentration decreased at the experimental site, with a removal rate of AVS as high as 28%. In addition, the removal rates of dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) and dissolved inorganic phosphorus (DIP) were as high as 19% and 24%, respectively. The removal fluxes for DIN and DIP were 2.02 mg N/m2/day and 0.22 mg P/m2/day, respectively, at the experimental site, and 0.88 mg N/m2/day and 0.10 mg P/m2/day, respectively, at the control site. These changes indicate that oxygen produced by the replanted Nitzschia sp. may have enhanced aerobic bacterial activity, and the nutrients may have been taken up by the Nitzschia sp.. Therefore, phytoremediation using BMA and LED shows potential as a novel and eco-friendly method for the remediation of eutrophic coastal sediments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arkipo GE, Eja ME, Ogbonnaya LO, Opara AA (2004) Cadmium uptake by the green alga Chlorella emersonii. Global J Pure Appl Sci 10:257–262
Cho KJ, Choi MY, Kwak SK, Im SH, Kim DY, Park JG, Kim YE (1998) Eutrophication and seasonal variation of water quality in Masan-Jinhae Bay. J Korean Soc Oceanogr 3:193–202
Coates JD, Bruce AR, Haddock JD (1998) Anoxic bioremediation of hydrocarbons. Nature 396:730
Di Toro DM, Mahony JD, Hansen DJ, Scott KJ, Carlson AR, Ankley GT (1992) Acid volatile sulfide predicts the acute toxicity of cadmium and nickel in sediments. Environ Sci Technol 26:96–101
Froelich PN, Klinkhammer GP, Bender ML, Luedtke NA, Heath GR, Cullen D, Dauphin P, Hammond D, Hartman B, Maynard V (1979) Early oxidation of organic matter in pelagic sediments of the eastern equatorial Atlantic: suboxic diagenesis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 43:1075–1091
Jenkins MC, Kemp M (1984) The coupling of nitrification and denitrification in two estuarine sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 29:609–619
Jørgensen BB, Sorensen J (1985) Seasonal cycles of O2, NO3 - and SO4 2- reduction in estuarine sediments: the significance of an NO3 - reduction maximum in spring. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 24:65–74
Keil RG, Hu FS, Tsamakis EC, Hedges JI (1994) Pollen in marine sediments as an indicator of oxidation of organic matter. Nature 369:639–641
Kristensen E, Blackburn TH (1987) The fate of organic carbon and nitrogen in experimental marine sediment systems: influence of bioturbation and anoxia. J Mar Res 45:231–257
Kwon HK, Oh SJ, Yang HS (2013a) Growth and uptake kinetics of nitrate and phosphate by benthic microalgae for phytoremediation of eutrophic coastal sediments. Bioresour Technol 129:387–395
Kwon HK, Oh SJ, Yang HS, Kim DM, Kang IJ, Oshima Y (2013b) Laboratory study for the phytoremediation of eutrophic coastal sediment using benthic microalgae and light emitting diode (LED). J Fac Agr Kyushu Univ 58:417–425
Luijn FV, van der Molen DT, Luttmer WJ, Boers PCM (1995) Influence of benthic diatoms on the nutrient release from sediments of shallow lakes recovering from eutrophication. Water Sci Tech 32:89–97
Michaud E, Desrosiers G, Mermillod-Blondin F, Sundby B, Stora G (2006) The functional group approach to bioturbation: II. The effect of the Macoma balthica community on fluxes of nutrients and dissolved organic carbon across the sedimentwater interface. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 337:178–189
Miller DC, Geider RJ, MacIntyre HL (1996) Microphytobenthos: the ecological role of the “secret garden” of unvegetated, shallowwater marine habitats. II. Role in sediment stability and shallowwater food webs. Estuaries 19:202–212
Millero FJ (1986) The thermodynamics and kinetics of the hydrogen sulfide system in natural waters. Mar Chem 18:121–127
Monteiro CM, Castro PML, Malcata FX (2011) Biosorption of zinc ions from aqueous solution by the microalgae Scenedesmus obliquus. Environ Chem Lett 9:169–176
Ministry of Land, Transportation and Marine Affairs, Korea (MLTM) (2010) Standard methods for marine environmental analysis. MLTM, Seoul, 495 p
National Fisheries Research and Development Institute, Korea (NFRDI) (2003) Studies on the development of remediation technologies for the polluted sediment in aged aquaculture grounds. NFRDI, Busan, 321 p
Oh HT, Goo JH, Park SE, Choi YS, Jung RH, Choi WJ, Lee WC, Park JS (2005) Analysis of water quality caused by improvement of sewage treatment plant in Masan Bay. J Environ Sci 14:777–783
Oh SJ, Yoon YH, Kim DI, Shimasaki Y, Oshima Y, Honjo T (2006) Effects of light quantity and quality on the growth of the harmful dinoflagellate, Cochlodinium polykrikoides Margalef (Dinophyceae). Algae 21:311–136
Oh, SJ, Kim DI, Sajima T, Shimasaki Y, Matsuyama Y, Oshima Y, Honjo T, Yang HS (2008) Effects of irradiance of various wavelengths from light emitting diodes on the growth of the harmful dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama and the diatom Skeletonema costatum. Fish Sci 74:137–145
Parsons TR, Maita Y, Lalli CM (1984) A manual of biological and chemical methods for seawater analysis. Pergamon, New-York, 173 p
Ruangdej U, Fukami K (2004) Stimulation of photosynthesis and consequent oxygen production in anoxic bottom water by supply of low-intensity light through an optical fiber. Fish Sci 70:421–429
Rysgaard S, Christensen PB, Nielsen LP (1995) Seasonal variation in nitrification and denitrification in estuarine sediment colonized by benthic microalgae and bioturbating infauna. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 126:111–121
Schulz HD, Zabel M (2006) Marine Geochemistry, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin, 574 p
Strickland JDJ, Parsons TR (1972) A practical handbook of seawater analysis, 2nd edn. Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Ottawa, 310 p
Suresh B, Ravishankar GA (2004) Phytoremediation-a novel and promising approach for environmental clean-up. Crit Rev Biotechnol 24:97–124
Suzuki Y, Kelly SD, Kemner KM, Banfield JF (2002) Radionuclide contamination: Nanometre-size products of uranium bioreduction. Nature 419:134
Timmis KN, Pieper DH (1999) Bacteria designed for bioremediation. Trends Biotechnol 17:201–204
Yamaguchi H, Montani S, Tsutsumi H, Hamada KI, Ueda N, Tada K (2007) Dynamics of microphytobenthic biomass in a coastal area of western Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 75:423–432
Yamamoto T, Goto I, Kawaguchi O, Minagawa K, Ariyoshi E, Matsuda O (2008) Phytoremediation of shallow organically enriched marine sediments using benthic microalgae. Mar Pollut Bull 57:108–115
Yim UH, Hong SH, Shim WJ, Oh JR, Chang M (2005) Spatiotemporal distribution and characteristics of PAHs in sediments from Masan Bay, Korea. Mar Pollut Bull 50:319–326
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, H.K., Oh, S.J., Yang, HS. et al. Phytoremediation by benthic microalgae (BMA) and light emitting diode (LED) in eutrophic coastal sediments. Ocean Sci. J. 50, 87–96 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-015-0007-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-015-0007-3