Abstract
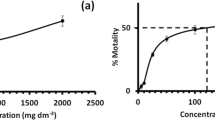
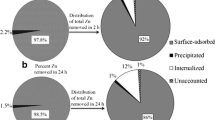
Aquatic environments are often exposed to toxic heavy metals, which gain access to the food chain via microalgae and may cause severe problems at higher trophic levels. However, such a metabolic specificity can be taken advantage of in bioremediation strategies. The potential of a novel wild strain of Scenedesmus obliquus, previously isolated from a heavy metal-contaminated site in northern Portugal, to remove Zn from aqueous solutions was thus studied, using several initial concentrations. The removal extent reached its maximum by 1 day: 836.5 mg Zn/g biomass, at the initial concentration of 75 mg/L, mainly by adsorption onto the cell surface. Comparative studies encompassing a commercially available strain of the same microalgal species led to a maximum removal extent of only 429.6 mg Zn/g biomass, under identical conditions. Heat-inactivated cells permitted a maximum removal of 209.6 mg Zn/g biomass, at an initial concentration of 50 mg Zn/L. The maximum adsorption capacity of Zn, estimated via Langmuir’s isotherm, was 330 mg Zn/g biomass. Finally, Zn removal was highest at pH 6.0–7.0. It was proven, for the first time, that such a wild microalga can uptake and adsorb Zn very efficiently, which unfolds a particularly good potential for bioremediation. Its performance is far better than similar (reference) species, especially near neutrality, and even following heat-treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu Al-Rub FA, El-Naas MH, Benyahia F, Ashour I (2004) Biosorption of nickel on blank alginate beads, free and immobilized algal cells. Proc Biochem 39:1767–1773
Ahuja P, Gupta R, Saxena RK (1999) Zn2+ biosorption by Oscillatoria anguistissima. Proc Biochem 34:77–85
Aksu Z, Dönmez G (2006) Binary biosorption of cadmium(II) and nickel(II) onto dried Chlorella vulgaris: co-ion effect on mono-component isotherm parameters. Proc Biochem 41:860–868
Arica MY, Tüzün İ, Yalçin E, İnce Ö, Bayramoğlu G (2005) Utilisation of native, heat and acid-treated microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii preparations for biosorption of Cr(VI) ions. Proc Biochem 40:2351–2358
Bayramoğlu G, Arica MY (2008) Removal of heavy mercury(II), cadmium(II) and zinc(II) metal ions by live and heat inactivated Lentinus edodes pellets. Chem Eng J 143:133–140
Bayramoğlu G, Tuzun I, Celik G, Yilmaz M, Arica MY (2006) Biosorption of mercury(II), cadmium(II) and lead(II) ions from aqueous system by microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii immobilized in alginate beads. Int J Miner Proc 81:35–43
Borowitzka MA, Borowitzka LJ (1988) Algal media and sources of algal cultures. In: Borowitzka MA, Borowitzka LJ (eds) Micro-Algal Biotechnology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 456–466
Chu KH, Hashim MA (2004) Quantitative analysis of copper biosorption by the microalga Chlorella vulgaris. Environ Eng Sci 21:139–147
Dönmez GÇ, Aksu Z, Öztürk A, Kutsal T (1999) A comparative study on heavy metal biosorption characteristics of some algae. Proc Biochem 34:885–892
Doshi H, Ray A, Kothari IL (2007) Biosorption of cadmium by live and dead Spirulina: IR spectroscopic, kinetics and SEM studies. Curr Microbiol 54:213–218
Gong R, Ding Y, Liu H, Chen Q, Liu Z (2005) Lead biosorption and desorption by intact and pretreated Spirulina maxima biomass. Chemosphere 58:125–130
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008) Biosorption of lead from aqueous solutions by green algae Spirogyra species: kinetics and equilibrium studies. J Hazard Mater 152:407–414
Gupta VK, Rastogi A, Saini VK, Jain N (2006) Biosorption of copper(II) from aqueous solutions by Spirogyra species. J Colloid Interface Sci 296:59–63
Incharoensakdi A, Kitjaharn P (2002) Zinc biosorption from aqueous solution by a halotolerant cyanobacterium Aphanothece halophytica. Curr Microbiol 45:261–264
Kaduková J, Virčíková E (2005) Comparison of differences between copper bioaccumulation and biosorption. Environ Int 31:227–232
King P, Anuradha K, Lahari SB, Kumar YP, Prasad VSRK (2008) Biosorption of zinc from aqueous solution using Azadirachta indica bark: equilibrium and kinetic studies. J Hazard Mater 152:324–329
Lombardi AT, Vieira AVH, Sartori LA (2002) Mucilaginous capsule adsorption and intracellular uptake of copper by Kirchneriella aperta (Chlorococcales). J Phycol 38:332–337
Matsunaga T, Takeyama H, Nakao T, Yamazawa A (1999) Screening of marine microalgae for bioremediation of cadmium-polluted seawater. J Biotechnol 70:33–38
Monteiro CM, Marques APGC, Castro PML, Malcata FX (2009) Characterization of Desmodesmus pleiomorphus isolated from a heavy metal-contaminated site: biosorption of zinc. Biodegradation 20:629–641
Muñoz R, Alvarez MT, Muñoz A, Terrazas E, Guieysse B, Mattiasson B (2006) Sequential removal of heavy metal ions and organic pollutants using an algal-bacterial consortium. Chemosphere 63:903–911
Nishikawa K, Tominaga N (2001) Isolation, growth, ultrastructure, and metal tolerance of the green alga Chlamydomonas acidophila (Chlorophyta). Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65:2650–2656
Oliveira RS, Dodd JC, Castro PML (2001) The mycorrhizal status of Phragmites australis in several polluted soils and sediments of an industrialised region of Northern Portugal. Mycorrhiza 10:241–247
Omar HH (2002) Bioremoval of zinc ions by Scenedesmus obliquus and Scenedesmus quadricauda and its effect on growth and metabolism. Int Biodeter Biodegrad 50:95–100
Özer D, Özer A, Dursun G (2000) Investigation of zinc(II) adsorption on Cladophora crispata in a two-staged reactor. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 75:410–416
Pérez-Rama M, Alonso JA, López CH, Vaamonde ET (2002) Cadmium removal by living cells of the marine microalga Tetraselmis suecica. Bioresour Technol 84:265–270
Philips R, Paperi R, Sili C, Vincenzini M (2003) Assessment of the metal removal capability of two capsulated cyanobacteria, Cyanospira capsulata and Nostoc PCC7936. J Appl Phycol 15:155–160
Pradhan S, Sing S, Rai LC, Parker DL (1998) Evaluation of metal biosorption efficiency of laboratory-grown Microcystis under various environmental conditions. J Microbiol Biotechnol 8:53–60
Radway JC, Wilde EW, Whitaker MJ, Weissman JC (2001) Screening of algal strains for metal removal capabilities. J Appl Phycol 13:451–455
Rangsayatorn N, Upatham ES, Kruatrachue M, Pokethitiyook P, Lanza GR (2002) Phytoremediation potential of Spirulina (Arthorspira) platensis: biosorption and toxicity studies of cadmium. Environ Poll 119:45–53
Schiewer S, Volesky B (2000) Biosorption processes for heavy metal removal. In: Lovley DR (ed) Environmental microbe-metal interactions. ASM Press, Washington DC, pp 329–362
Senthilkumar R, Vijayaraghavan K, Thilakavathi M, Iyer PVR, Velan M (2006) Seaweeds for the remediation of wastewaters contaminated with zinc(II) ions. J Hazard Mater B 136:791–799
Tam NFY, Wong JPK, Wong YS (2001) Repeated use of two Chlorella species, C. vulgaris and WW1, for cyclic nickel biosorption. Environ Poll 114:85–92
Tüzün İ, Bayramoğlu G, Yalçın E, Başaran G, Çelik G, Arica MY (2005) Equilibrium and kinetic studies on biosorption of Hg(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions onto microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Environ Manage 77:85–92
Vannela R, Verma SK (2006) Co2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+ accumulation by cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis. Biotechnol Prog 22:1282–1293
Vasconcelos MT, Tavares HM (1998) Atmospheric metal pollution (Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn) in Oporto city derived from results for low-volume aerosol samplers and for the moss Sphagnum auriculatum bioindicator. Sci Total Environ 212:11–20
Veglio F, Beolchini F (1997) Removal of metals by biosorption: a review. Hydrometallurgy 44:301–316
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Câmara Municipal de Estarreja for allowing full access to the contaminated site. This work was supported by Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia and Fundo Social Europeu (III Quadro Comunitário de Apoio), via a PhD research fellowship granted to author C. M. Monteiro (ref. SFRH/BD/9332/2002), under the supervision of author F.X. Malcata.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monteiro, C.M., Castro, P.M.L. & Xavier Malcata, F. Biosorption of zinc ions from aqueous solution by the microalga Scenedesmus obliquus . Environ Chem Lett 9, 169–176 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-009-0258-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-009-0258-2