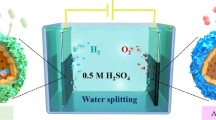
Abstract
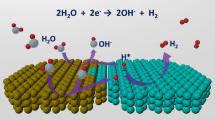
Herein, a novel single-atomic Pt doping and interface-rich CoS/Co(OH)2 (Pt-CoS/Co(OH)2/C) electrocatalyst has been successfully prepared. Benefiting from precise regulation of d-orbital electronic structure modulation on Co site, Pt-CoS/Co(OH)2/C exhibited remarkable HER activity and high stability for hydrogen evolution in splitting both water (73 mV@10 mA·cm−2) and seawater (87 mV@10 mA·cm−2). Notably, atomic Pt doping was introduced into CoS/Co(OH)2, which could produce local unbalanced Coulombic force and significantly increased the number of S vacancies, and then expose abundant Co sites. Meantime, Co(OH)2 in Pt-CoS/Co(OH)2/C could act as the adsorption sites for H2O in hydrogen evolution reaction process. Density functional theory results also proved that atomic Pt doping, S vacancies and Co(OH)2 coupling could result in the formation of enriched electronic Co sites and optimize \({\text d}_{{z}^{2}}\) orbital electronic structure, and then realize the depth upward shift of d-band center and enhance the adsorption of H* on Co sites.
Graphical abstract

摘要
本文成功制备了一种单原子Pt掺杂、界面丰富的CoS/Co(OH)2 (Pt-CoS/Co(OH)2/C)电催化剂。得益于Co位点d轨道电子结构的精确调控,Pt-CoS/Co(OH)2/C在裂解水(73 mV@10 mA·cm−2)和海水(87 mV@10 mA·cm−2)时表现出显著的HER活性和较高的析氢稳定性。值得注意的是,在CoS/Co(OH)2中引入原子Pt掺杂产生了局部不平衡库仑力,显著增加了S空位的数量,从而暴露出丰富的Co位。同时,Pt-CoS/Co(OH)2/C中的Co(OH)2可作为析氢反应(HER)过程中H2O的吸附位点。密度泛函理论(DFT)结果也证明,原子Pt掺杂、S空位和Co(OH)2耦合可导致富集电子的Co活性位的形成,优化轨道电子结构,进而实现d带中心深度上移,增强H*在Co位上的吸附。







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu J, Hu L, Zhao P, Lee LYS, Wong KY. Recent advances in electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution using nanoparticles. Chem Rev. 2020;120(2):851. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00248.
Cui H, Liao HX, Wang ZL, Xie JP, Tan PF, Chu DW, Jun P. Synergistic electronic interaction between ruthenium and nickel-iron hydroxide for enhanced oxygen evolution reaction. Rare Met. 2022;41(8):2606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02003-3.
Shen B, Huang H, Jiang Y, Xue Y, He H. 3D interweaving MXene–graphene network–confined Ni–Fe layered double hydroxide nanosheets for enhanced hydrogen evolution. Electrochim Acta. 2022;407:139913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2022.139913.
Li C, Zhao DH, Long HL, Li M. Recent advances in carbonized non-noble metal-organic frameworks for electrochemical catalyst of oxygen reduction reaction. Rare Met. 2021;40(10):2657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01694-w.
Huang H, Xue Y, Xie Y, Yang Y, Yang L, He H, Jiang Q, Ying G. MoS2 quantum dot-decorated MXene nanosheets as efficient hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts. Inorgan Chem Front. 2022;9:1171. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1qi01528a.
Sun J, Zhou Y, Zhao Z, Meng X, Li Z. Modification strategies to improve electrocatalytic activity in seawater splitting: a review. J Mater Sci. 2022;57(41):19243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07875-5.
Sun JP, Zhao Z, Li J, Li ZZ, Meng XC. Recent advances in electrocatalytic seawater splitting. Rare Met. 2023;42(3):751. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02168-x.
Fu WY, Lin YX, Wang MS, Si S, Wei L, Zhao XS, Wei YS. Sepaktakraw-like catalyst Mn-doped CoP enabling ultrastable electrocatalytic oxygen evolution at 100 mA·cm−2 in alkali media. Rare Met. 2022;41(9):3069. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02006-0.
He H, Chen Y, Yang C, Yang L, Jiang Q, Huang H. Constructing 3D interweaved MXene/graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets/graphene nanoarchitectures for promoted electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J Energy Chem. 2022;67:483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2021.10.019.
Fang XJ, Ren LP, Li F, Jiang ZX, Wang ZG. Modulating electronic structure of CoSe2 by Ni doping for efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Rare Met. 2021;41(3):901. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-021-01819-9.
Mosallanezhad A, Wei C, Ahmadian Koudakan P, Fang Y, Niu S, Bian Z, Liu B, Huang T, Pan H, Wang G. Interfacial synergies between single-atomic Pt and CoS for enhancing hydrogen evolution reaction catalysis. Appl Catal B Environ. 2022;315:121534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121534.
Feng Y, Zhang T, Zhang J, Fan H, He C, Song J. 3D 1T-MoS2/CoS2 heterostructure via interface engineering for ultrafast hydrogen evolution reaction. Small. 2020;16:2002850. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202002850.
Sun J, Huang Z, Huang T, Wang X, Wang X, Yu P, Zong C, Dai F, Sun D. Defect-rich porous CoS1.097/MoS2 hybrid microspheres as electrocatalysts for pH-universal hydrogen evolution. ACS Appl Energy Mater. 2019;2(10):7504. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.9b01486.
Zhou F, Zhou Y, Liu GG, Wang CT, Wang J. Recent advances in nanostructured electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Rare Met. 2021;40(12):3375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-021-01735-y.
Lin Z, Xiao B, Huang M, Yan L, Wang Z, Huang Y, Shen S, Zhang Q, Gu L, Zhong W. Realizing negatively charged metal atoms through controllable d-electron transfer in ternary Ir1−xRhxSb intermetallic alloy for hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv Energy Mater. 2022;12:2200855. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.202200855.
Gong C, Li W, Lei Y, He X, Chen H, Du X, Fang W, Wang D, Zhao L. Interfacial engineering of ZIF-67 derived CoSe/Co(OH)2 catalysts for efficient overall water splitting. Compos Part B Eng. 2022;236:109823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.109823.
Sun YM, Xue ZQ, Liu QL, Jia YL, Li YL, Liu K, Lin YY, Liu M, Li GQ, Su CY. Modulating electronic structure of metal-organic frameworks by introducing atomically dispersed Ru for efficient hydrogen evolution. Nat Commun. 2021;12:1369. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21595-5.
Tan H, Tang B, Lu Y, Ji Q, Lv L, Duan H, Li N, Wang Y, Feng S, Li Z, Wang C, Hu F, Sun Z, Yan W. Engineering a local acid-like environment in alkaline medium for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. Nat Commun. 2022;13:2024. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29710-w.
Sun Y, Mao K, Shen Q, Zhao L, Shi C, Li X, Gao Y, Li C, Xu K, Xie Y. Surface electronic structure modulation of cobalt nitride nanowire arrays via selenium deposition for efficient hydrogen evolution. Adv Func Mater. 2021;32:2109792. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202109792.
Wu T, Sun MZ, Huang BL. Non-noble metal-based bifunctional electrocatalysts for hydrogen production. Rare Met. 2022;41(7):2169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-021-01914-x.
Sheng M, Bin X, Yang Y, Tang Y, Que W. In situ electrosynthesis of MAX-derived electrocatalysts for superior hydrogen evolution reaction. Small. 2022;18(32):2203471. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202203471.
Zhong W, Wang Z, Gao N, Huang L, Lin Z, Liu Y, Meng F, Deng J, Jin S, Zhang Q, Gu L. Coupled vacancy pairs in Ni-doped CoSe for improved electrocatalytic hydrogen production through topochemical deintercalation. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2020;59:22743. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202011378.
Hao L, He H, Qin J, Ma C, Luo L, Yang L, Huang H. MXene nanosheets induce efficient iron selenide active sites to boost the electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. Inorg Chem. 2022;61(51):21087. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c03666.
Zhou KL, Wang Z, Han CB, Ke X, Wang C, Jin Y, Zhang Q, Liu J, Wang H, Yan H. Platinum single-atom catalyst coupled with transition metal/metal oxide heterostructure for accelerating alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction. Nat Commun. 2021;12:3783. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24079-8.
Wu Y, Ma J, Huang Y. Enhancing oxygen reduction reaction of Pt–Co/C nanocatalysts via synergetic effect between Pt and Co prepared by one-pot synthesis. Rare Met. 2023;42(1):146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02119-6.
Zhou SZ, Jang H, Qin Q, Li ZJ, Kim MG, Ji XQ, Liu XE, Cho J. Ru atom-modified Co4N-CoF2 heterojunction catalyst for high-performance alkaline hydrogen evolution. Chem Eng J. 2021;414:128865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128865.
Liu Y, Hua X, Xiao C, Zhou T, Huang P, Guo Z, Pan B, Xie Y. Heterogeneous spin states in ultrathin nanosheets induce subtle lattice distortion to trigger efficient hydrogen evolution. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138:5087. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b00858.
Xie J, Zhang J, Li S, Grote F, Zhang X, Zhang H, Wang R, Lei Y, Pan B, Xie Y. Controllable disorder engineering in oxygen-incorporated MoS2 ultrathin nanosheets for efficient hydrogen evolution. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135:17881. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja4129636.
Dong J, Zhang X, Huang J, Hu J, Chen Z, Lai Y. In-situ formation of unsaturated defect sites on converted CoNi alloy/Co-Ni LDH to activate MoS2 nanosheets for pH-universal hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem Eng J. 2021;412:128556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128556.
Yoon T, Kim KS. One-step synthesis of CoS-doped β-Co(OH)2@amorphous MoS2+x hybrid catalyst grown on nickel foam for high-performance electrochemical overall water splitting. Adv Funct Mater. 2016;26:7386. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201602236.
Ye S, Xiong W, Liao P, Zheng L, Ren X, He C, Zhang Q, Liu J. Removing the barrier to water dissociation on single-atom Pt sites decorated with a CoP mesoporous nanosheet array to achieve improved hydrogen evolution. J Mater Chem A. 2020;8:11246. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ta02936j.
Shen S, Wang Z, Lin Z, Song K, Zhang Q, Meng F, Gu L, Zhong W. Crystalline-amorphous interfaces coupling of CoSe2/CoP with optimized d-band center and boosted electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv Mater. 2022;34:2110631. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202110631.
Gou WY, Li JY, Gao W, Xia ZM, Zhang S, Ma YY. Downshifted d-band center of Ru/MWCNTs by turbostratic carbon nitride for efficient and robust hydrogen evolution in alkali. ChemCatChem. 2019;11:1970. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201900006.
Yang T, Xie H, Ma N, Liu E, Shi C, He C, Zhao N. Unraveling the mechanism of hydrogen evolution reaction on cobalt compound electrocatalysts. Appl Surf Sci. 2021;550:149355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149355.
Dai Q, Wang L, Wang K, Sang X, Li Z, Yang B, Chen J, Lei L, Dai L, Hou Y. Accelerated water dissociation kinetics by electron-enriched cobalt sites for efficient alkaline hydrogen evolution. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;32:2109556. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202109556.
Shao J, Wan Z, Liu H, Zheng H, Gao T, Shen M, Qu Q, Zheng H. Metal organic frameworks-derived Co3O4 hollow dodecahedrons with controllable interiors as outstanding anodes for Li storage. J Mater Chem A. 2014;2:12194. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta01966k.
Ji X, Lin Y, Zeng J, Ren Z, Lin Z, Mu Y, Qiu Y, Yu J. Graphene/MoS2/FeCoNi(OH)x and Graphene/MoS2/FeCoNiPx multilayer-stacked vertical nanosheets on carbon fibers for highly efficient overall water splitting. Nat Commun. 2021;12:1380. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21742-y.
Qiu Y, Liu S, Wei C, Fan J, Yao H, Dai L, Wang G, Li H, Su B, Guo X. Synergistic effect between platinum single atoms and oxygen vacancy in MoO2 boosting pH-Universal hydrogen evolution reaction at large current density. Chem Eng J. 2022;427:131309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131309.
Wang L, Chen MX, Yan Q, Xu S, Chu S, Chen P, Lin Y, Liang H. A sulfur-tethering synthesis strategy toward high-loading atomically dispersed noble metal catalysts. Sci Adv. 2019;5(10):6332. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aax6322.
Yin P, Luo X, Ma Y, Chu SQ, Chen S, Zheng X, Lu J, Wu XJ, Liang HW. Sulfur stabilizing metal nanoclusters on carbon at high temperatures. Nat Commun. 2021;12:3135. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23426-z.
Zhang S, Zhang Z, Si Y, Li B, Deng F, Yang L, Liu X, Dai W, Luo S. Gradient hydrogen migration modulated with self-adapting S vacancy in copper-doped ZnIn2S4 nanosheet for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. ACS Nano. 2021;15(9):15238. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23426-z.
Li H, Tsai C, Koh AL, Cai L, Contryman AW, Fragapane AH, Zhao J, Han HS, Manoharan HC, Abild-Pedersen F, Norskov JK, Zheng X. Corrigendum: activating and optimizing MoS2 basal planes for hydrogen evolution through the formation of strained sulphur vacancies. Nat Mater. 2016;15:364. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4564.
Shi Y, Zhang D, Huang H, Miao H, Wu X, Zhao H, Zhan T, Chen X, Lai J, Wang L. Mixture phases engineering of PtFe nanofoams for efficient hydrogen evolution. Small. 2022;18:2106947. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202106947.
Hu X, Song J, Luo J, Zhang H, Sun Z, Li C, Zheng S, Liu Q. Single-atomic Pt sites anchored on defective TiO2 nanosheets as a superior photocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. J Energy Chem. 2021;62:1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2021.03.003.
Li L, Shi YX, Hou M, Zhang ZC. Research progress of copper-based materials for rlectrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction. Chin J Rare Met. 2022;46(6):681. https://doi.org/10.13373/j.cnki.cjrm.XY21120017.
Xu XH, Zhang YJ, Miao XY. Synthesis and electrocatalytic performance of 3D coral-like NiCo-P. Chin J Rare Met. 2022;46(11):1449. https://doi.org/10.13373/j.cnki.cjrm.XY22080001.
Wang YH, Li RQ, Li HB, Huang HL, Guo ZJ, Chen HY, Zheng Y, Qu KG. Controlled synthesis of ultrasmall RuP2 particles on N, P-codoped carbon as superior pH-wide electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. Rare Met. 2021;40(5):1040. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01665-1.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2021QB056) and Taishan Scholars Foundation of Shandong province (No. tsqn201909058). The authors would like to thank Shiyanjia Lab (https://www.shiyanjia.com) for the XRD, SEM, XPS, etc., analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, JP., Zheng, Y., Zhang, ZS. et al. Modulation of d-orbital to realize enriched electronic cobalt sites in cobalt sulfide for enhanced hydrogen evolution in electrocatalytic water/seawater splitting. Rare Met. 43, 511–521 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02427-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02427-5