Abstract
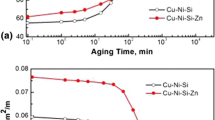
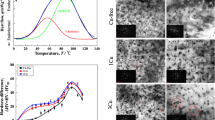
The coarsening behavior of (Ni, Co)2Si particles in Cu–Ni–Co–Si alloy was investigated by experimental observations and coarsening kinetics calculations when aged at 450, 500, 550 and 600 °C for different durations. The results show that the critical particle radius for coherence mismatch is found to be 10.3 nm, and particles larger than 25 nm are generally semi-coherent. The relationship of (Ni, Co)2Si particles size and aging time follows Lifshitz, Slyosov and Wagner (LSW) theory. The particle size distributions fit well to the LSW theoretical distribution. The activation energy for (Ni, Co)2Si coarsening is accurately determined to be (216.21 ± 5.18) kJ·mol−1 when considering the effect of temperature on the solution concentrations in matrix. The coarsening of (Ni, Co)2Si particles in Cu–Ni–Co–Si alloy is controlled by diffusion of Ni, Co and Si in Cu matrix. The growth of particles for long durations suggests that vacancies can be trapped within the structure for long time despite their mobility.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corson MG. Electrical conductor alloy. Electr World. 1927;89(1):137.
Fujiwra H, Kamio A. Effect of alloy composition on precipitation behavior in Cu–Ni–Si alloys. J. Japan Inst Met. 1998;62(4):301.
Young GK, Chung R. Designing an advanced copper-alloy lead frame material. Semicond Int. 1985;8(4):25.
Chenna Krishna S, Jha AK, Pant B, George KM. Achieving higher strength in Cu–Ag–Zr alloy by warm/hot rolling. Rare Met. 2017;36(4):256.
Liu RQ, Xie WB, Huang GJ, Zhang JB, Fan XW, Yang SL. Softening temperature of Cu-3.0Ni-0.75Si alloy with different Co additions. Chin J Rare Met. 2016;40(3):295.
Suzuki S, Shibutani N, Mimura K, Isshiki M, Waseda Y. Improvement in strength and electrical conductivity of Cu–Ni–Si alloys by aging and cold rolling. J. Alloys Compd. 2006;417(1–2):116.
Monzen R, Watanabe C. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu–Ni–Si alloys. Mater Eng A. 2008;483–484(7):117.
Yin XQ, Peng LJ, Kayani S, Cheng L, Wang JW, Xiao W, Wang LG, Huang GJ. Mechanical properties and microstructure of rolled and electrodeposited thin copper foil. Rare Met. 2016;35(12):909.
Izawa K, Ozawa A, Kita K, Watanabe C, Monzen R. Influence of Co on strength and microstructure of Cu–Ni–Co–Si alloy. J Soc Mater Sci Jpn. 2014;63(5):401.
Xiao XP, Yi ZY, Chen TT, Liu RQ, Wang H. Suppressing spinodal decomposition by adding Co into Cu–Ni–Si alloy. J Alloys Compd. 2016;660:178.
Wang QS, Xie GL, Mi XJ, Xiong BQ, Xiao XP. The precipitation and strengthening mechanism of Cu–Ni–Si–Co alloy. Chin Mater Conf. 2012;749:294.
Lifshitz IM, Slyozov VV. The kinetics of precipitation from supersaturated solid solution. J Phy Chem Solids. 1961;19(1–2):35.
Wagner C. Theory of ageing precipitation by umlosen (annual maturation). J Electrochem Rep Bunsenges Phys Chem. 1961;65(7–8):581.
Felip HS, Victor LH, Hector JDR, Maribel KSM, Jorge LGV, Ana MPM. Ostwald ripening of decomposed phases in Cu–Ni–Cr alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2008;457(1–2):106.
Gabriel MN, Alan JA. Precipitation of Al3Sc in binary Al–Sc alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2001;318(1–2):144.
Marquis EA, Seidman DN. Nanoscale structural evolution of Al3Sc precipitates in Al(Sc) alloys. Acta Mater. 2001;49(11):1909.
Chenna Krishna S, Jha AK, Pant B, George KM. Achieving higher strength in Cu–Ag–Zr alloy by warm/hot rolling. Rare Met. 2017;36(4):263.
Jones MJ, Humphreys FJ. Interaction of recrystallization and precipitation: the effect of Al3Sc on the recrystallization behavior of deformed aluminum. Acta Mater. 2003;51(8):2149.
Iwamura S, Miura Y. Loss in coherency and coarsening behavior of Al3Sc precipitates. Acta Mater. 2004;52(3):591.
Marquis EA, Seidman DN, Dunand DC. Effect of Mg addition on the creep and yield behavior of an Al-Sc alloy. Acta Mater. 2003;51(16):4752.
Marquis EA, Seidman DN. Coarsening kinetics of nanoscale Al3Sc precipitates in an Al–Mg–Sc alloy. Acta Mater. 2005;53(15):4259.
Ma R, Wang YX, Chen Z, Miao HC, Zhong HW, Miao SF. Microscopic phase-field of influence of interfacial mismatch stress on coarsening mechanism of aluminum alloy. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2009;19(10):1748.
Prashanth KG, Scudino S, Murty BS, Eckert J. Crystallization kinetics and consolidation of mechanically alloyed Al70Y16Ni10Co4 glassy powders. J Alloys Compd. 2009;477(1):171.
Pang Y, Li Y, Wu X, Liu W, Hou Z. Phase-field simulation of diffusion-controlled coarsening kinetics of γ′ phase in Ni–Al alloy. Int J Mater Res. 2014;106(2):108.
Cale WF, Totemeir TC, Smithells CJ. Metals Reference Book. Oxford: Elsevier; 2004. 117.
Li HY, Song XP, Wang YL, Chen GL. Coarsening and age hardening behaviors of γ’ particles in GH742 during high temperature treatment. J Iron Steel Res Int. 2009;16(5):81.
Nagarjuna S, Sharma KK, Sudhakar I, Sarma DS. Age hardening studies in a Cu-4.5Ti-0.5Co alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2001;313(1–2):251.
Lee E, Han S, Euh K, Lim S, Kim S. Effect of Ti addition on tensile properties of Cu–Ni–Si alloys. Met Mater Int. 2011;17(4):569.
Baumann SF, Williams DB. Experimental observations on the nucleation and growth of δ′ (Al3Li) in dilute Al–Li alloys. Metall Trans A. 1985;16(7):1203.
Wang ZM, Shiflet GJ. Heterogeneous nucleation of σ′ on dislocations in a dilute aluminum-lithium alloy. Metall Mater Trans A. 1996;27(6):1599.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51561008 and 51461017) and Jiangxi Yorth Major Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 20171ACB21044 and 20161BBE50030). We thank professor Rui-Qing Liu and Dr. Hang Wang for enlightening discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, XP., Xu, H., Chen, JS. et al. Coarsening behavior of (Ni, Co)2Si particles in Cu–Ni–Co–Si alloy during aging treatment. Rare Met. 38, 1062–1069 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-018-1169-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-018-1169-9