Abstract
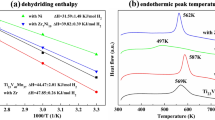
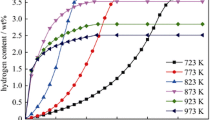
The hydrogenation behavior of Ti44Al6Nb1Cr2V (at%) alloy at temperature range of 1373–1693 K and its effect on microstructure and room-temperature mechanical properties were studied systematically in this study. The results show that hydrogen content increases with the increase in temperature, and the maximum hydrogen content is 0.126 wt% at 1693 K. The heat of solution of hydrogen is calculated as 82.9 kJ·mol−1 by curve fitting, indicating that hydrogen absorption in TiAl alloys is endothermic. Hydrogen promotes the lamellar colony size because hydrogen promotes the diffusion of elements. Hydrogen stabilizes B2 phase during hydrogenation resulting in more residual B2 phase in the hydrogenated alloy. The nanohardness and elastic modulus decrease after hydrogenation due to that hydrogen weakens the bonds. The Ti44Al6Nb1Cr2V alloy exhibits higher plasticity and lower flow stress hydrogenation with 0.039 wt% H, and the ultimate compressive strength decreases from 1220 to 1130 MPa, while the fracture strain is enhanced by 26%.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwaighofer E, Clemens H, Mayer S, Lindemann J, Klose J, Smarsly W, Güther V. Microstructural design and mechanical properties of a cast and heat-treated intermetallic multi-phase γ-TiAl based alloy. Intermetallics. 2014;44:128.
Imayev V, Oleneva T, Imayev R, Christ HJ, Fecht HJ. Microstructure and mechanical properties of low and heavy alloyed γ-TiAl + α2−Ti3Al based alloys subjected to different treatments. Intermetallics. 2012;26:91.
Pflumm R, Friedle S, Schütze M. Oxidation protection of γ-TiAl-based alloys—a review. Intermetallics. 2015;56:1.
Liang YF, Xu XJ, Lin JP. Advances in phase relationship for high Nb-containing TiAl alloys. Rare Met. 2016;35(1):15.
Jiao ZH, Yu HC, Su YJ, Kong FT, Chen YY. Tensile properties of large-sized Ti–43Al–9V–Y alloy with duplex and fully lamellar structure. Mater Mech Eng. 2014;38(3):50.
Hadi M, Shafyei A, Meratian M. A comparative study of microstructure and high temperature mechanical properties of a β-stabilized TiAl alloy modified by lanthanum and erbium. Mater Sci Eng A. 2015;624:1.
Zong Y, Shan D, Lv Y, Guo B. Effect of 0.3 wt% H addition on the high temperature deformation behaviors of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2007;32(16):3936.
Froes FH, Senkov ON, Qazi JI. Hydrogen as a temporary alloying element in titanium alloys: thermohydrogen processing. Int Mater Rev. 2004;49(3–4):227.
Shen C, Yu C, Perng T. Variation of structure and mechanical properties of Ti–6Al–4V with isothermal hydrogenation treatment. Acta Mater. 2009;57(3):868.
Wen D, Zong Y, Xu W, Shan D, Guo B. The effect of hydrogen on phase transformation and mechanical properties of a β containing γ–TiAl based alloy. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2014;39(30):17404.
Liu X, Su Y, Luo L, Liu J, Guo J, Fu H. Effect of hydrogen on hot deformation behaviors of TiAl alloys. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2010;35(24):13322.
Takasaki A. High-pressure hydrogen charging of TiAl-based titanium aluminides. Scr Mater. 1998;38(4):687.
Takasaki A, Furuya Y, Taneda Y. Hydrogen uptake in titanium aluminides in high pressure hydrogen. Mater Sci Eng A. 1997;239–240:265.
Liu Y, Hu R, Kou HC, Wang J, Zhang TB, Li JS, Zhang J. Solidification characteristics of high Nb-containing γ-TiAl-based alloys with different aluminum contents. Rare Met. 2015;34(6):381.
Erdely P, Werner R, Schwaighofer E, Clemens H, Mayer S. In-situ study of the time–temperature-transformation behaviour of a multi-phase intermetallic β-stabilised TiAl alloy. Intermetallics. 2015;57:17.
Sun F, Cao C, Kim S, Lee Y, Yan M. Alloying mechanism of beta stabilizers in a TiAl alloy. Metall Mater Trans A. 2001;32A:1573.
Takasaki A, Furuya Y, Ojima K, Taneda Y. Hydrogen solubility of two-phase (Ti3Al + TiAl) titanium aluminides. Scr Mater. 1995;32(11):1759.
Niinomi M, Gong B, Kobayashi T, Ohyabu Y, Toriyama O. Fracture characteristics of Ti–6Al–4V and Ti–5Al–2.5Fe with refined microstructure using hydrogen. Metall Mater Trans A. 1995;26(5):1141.
Chen S, Liang CP, Gong HR. Structural stability, mechanical property and elastic anisotropy of TiAl-H system. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2012;37(3):2676.
Menand A, Huguet A, Nerac-Partaix A. Interstitial solubility in γ and α2 phases of TiAl-based alloys. Acta Mater. 1996;44(12):4729.
Chen RR, Ma TF, Sun ZP, Guo JJ, Ding HS, Su YQ, Fu HZ. The hydrogen absorption behavior of high Nb contained titanium aluminides under high pressure and temperature. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2016;41(30):13254.
Sundaram PA, Wessel E, Ennis PJ, Quadakkers WJ, Singheiser L. Diffusion coefficient of hydrogen in a cast gamma titanium aluminide. Scr Mater. 1999;41(1):75.
Su Y, Liu X, Luo L, Zhao L, Guo J, Fu H. Hydrogen solubility in molten TiAl alloys. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2010;35(15):8008.
Kong FT, Xiao SL, Chen YY, Li BH. Continuous cooling phase transformation of Ti–45Al–5Nb(–0.3Y) alloys. Rare Met Mat Eng. 2009;38(1):25.
Ramanujan RV. Phase transformations in γ based titanium aluminides. Int Mater Rev. 2000;45(6):217.
Clemens H, Bartels A, Bystrzanowski S, Chladil H, Leitner H, Dehm G, Gerling R, Schimansky FP. Grain refinement in γ-TiAl-based alloys by solid state phase transformations. Intermetallics. 2006;14(12):1380.
Han XL, Wang Q, Sun DL, Zhang HX. First-principles study of the effect of hydrogen on the Ti self-diffusion characteristics in the alpha Ti–H system. Scr Mater. 2007;56(1):77.
Xu XJ, Song L, Jin XO, Han DD, Wang X, Lin JP. Microstructure and microsegregation of directionally solidified Ti–45Al–8Nb alloy with different solidification rates. Rare Met. 2016;35(1):70.
Qazi JI, Senkov ON, Rahim J, Genc A, Froes FH. Phase transformations in Ti6Al4V–xH alloys. Metall Mater Trans A. 2001;32A(9):2453.
Cao SZ, Xiao SL, Chen YY, Tian J, Xu LJ, Wang XP, Han JC, Jia Y. Microstructure evolution of Ti–46Al–6Nb–(Si, B) alloys during heat treatment with W addition. Rare Met. 2016;35(1):85.
Sundaram PA, Basu D, Steinbrech RW, Ennis PJ, Quadakkers WJ, Singheiser L. Effect of hydrogen on the elastic modulus and hardness of gamma titanium aluminides. Scr Mater. 1999;41(8):839.
Ruales M, Martell D, Vazquez F, Just FA, Sundaram PA. Effect of hydrogen on the dynamic elastic modulus of gamma titanium aluminide. J Alloy Compd. 2002;339(1–2):156.
Abanto-Bueno JL, Sundaram PA, Clemens H. Effect of hydrogen on the tensile properties of a Ti–47Al–2Cr–0.2Si sheet under electrolytic charging conditions. Scr Mater. 1998;38(1):149.
Chen Y, Niu H, Kong F, Xiao S. Microstructure and fracture toughness of a β phase containing TiAl alloy. Intermetallics. 2011;19(10):1405.
Voisin T, Monchoux J, Hantcherli M, Mayer S, Clemens H, Couret A. Microstructures and mechanical properties of a multi-phase β-solidifying TiAl alloy densified by spark plasma sintering. Acta Mater. 2014;73:107.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.51274076) and the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. NSFC51425402).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, TF., Chen, RR., Zheng, DS. et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti44Al6Nb1Cr2V alloy after gaseous hydrogen charging at 1373–1693 K. Rare Met. 42, 664–671 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-017-0946-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-017-0946-1