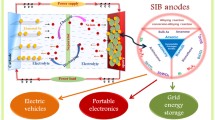
Abstract
The development of alternative electrode materials with high energy densities and power densities for batteries has been actively pursued to satisfy the power demands for electronic devices and hybrid electric vehicles. Recently, antimony (Sb)-based intermetallic compounds have attracted considerable research interests as new candidate anode materials for high-performance lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) and sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) due to their high theoretical capacity and suitable operating voltage. However, these intermetallic systems undergo large volume change during charge and discharge processes, which prohibits them from practical application. The rational construction of advanced anode with unique structures has been proved to be an effective approach to enhance its electrochemical performance. This review highlights the recent progress in improving and understanding the electrochemical performances of various Sb-based intermetallic compound anodes. The developments of synthesis and construction of Sb-based intermetallic compounds are systematically summarized. The electrochemical performances of various Sb-based intermetallic compound anodes are compared in its typical applications (LIBs or SIBs).
Graphical Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armand M, Tarascon JM. Building better batteries. Nature. 2008;451(7179):652.
Goodenough JB, Park KS. The Li-ion rechargeable battery: a perspective. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135(4):1167.
Mai L, Tian X, Xu X, Chang L, Xu L. Nanowire electrodes for electrochemical energy storage devices. Chem Rev. 2014;114(23):11828.
Slater MD, Kim D, Lee E, Johnson CS. Sodium-ion batteries. Adv Funct Mater. 2013;23(26):947.
Kim SW, Seo DH, Ma X, Ceder G, Kang K. Electrode materials for rechargeable sodium-ion batteries: potential alternatives to current lithium-ion batteries. Adv Energy Mater. 2012;2(7):710.
Palomares V, Serras P, Villaluenga I, Hueso KB, Carreterogonzález J, Rojo T. Na-ion batteries, recent advances and present challenges to become low cost energy storage systems. Energy Environ Sci. 2012;5(3):5884.
Wang X, Niu C, Meng J, Ping H, Xu X, Wei X, Zhou L, Zhao K, Luo W, Yan M, Mai L. Novel K3V2(PO4)3/C bundled nanowires as superior sodium-ion battery electrode with ultrahigh cycling stability. Adv Energy Mater. 2015;5(17):939.
Han MH, Gonzalo E, Singh G, Rojo T. A comprehensive review of sodium layered oxide: powerful cathode for Na-ion battery. Energy Environ Sci. 2014;8(1):81.
Scrosati B, Hassoun J, Sun YK. Lithium-ion batteries. A look into the future. Energy Environ Sci. 2011;4(9):3287.
Thackeray MM, Wolverton C, Isaacs ED. Electrical energy storage for transportation—approaching the limits of, and going beyond, lithium-ion batteries. Energy Environ Sci. 2012;5(7):7854.
Farbod B, Cui K, Kalisvaart WP, Kupsta M, Zahiri B, Kohandehghan A, Lotfabad EM, Li Z, Luber EJ, Mitlin D. Anodes for sodium ion batteries based on tin–germanium–antimony alloys. ACS Nano. 2014;8(5):4415.
Luo W, Zhang P, Wang X, Li Q, Dong Y, Hua J, Zhou L, Mai L. Antimony nanoparticles anchored in three-dimensional carbon network as promising sodium-ion battery anode. J Power Sources. 2016;304:340.
Chen C, Fu K, Lu Y, Zhu J, Xue L, Hu Y, Zhang X. Use of a tin antimony alloy-filled porous carbon nanofiber composite as an anode in sodium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2015;5(39):30793.
Ji L, Zhou W, Chabot V, Yu A, Xiao X. Reduced graphene oxide/tin-antimony nanocomposites as anode materials for advanced sodium ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(44):24895.
Liu J, Yang Z, Wang J, Gu L, Maier J, Yu Y. Three-dimensionally interconnected nickel–antimony intermetallic hollow nanospheres as anode material for high-rate sodium-ion batteries. Nano Energy. 2015;16:389.
Tran CCH, Autret C, Damas C, Claude-Montigny B, Santos-Peña J. An electrochemical study of Fe1.18Sb1.82 as negative electrode for sodium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta. 2015;182(9):11.
Yang J. Sub-microcrystalline Sn and Sn–SnSb powders as lithium storage materials for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochem Solid State Lett. 1999;2(4):161.
Yang J, Takeda Y, Imanishi N, Yamamoto O. Ultrafine Sn and SnSb0.14 powders for lithium storage matrices in lithium-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc. 1999;146(146):4009.
Li H, Shi L, Lu W, Huang X, Chen L. Studies on capacity loss and capacity fading of nanosized SnSb alloy anode for Li-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc. 2001;148(8):A915.
Wang Z, Zhou L, Lou XW. Metal oxide hollow nanostructures for lithium-ion batteries. ChemInform. 2012;24(24):1903.
Wang Y, Cao G. Developments in nanostructured cathode materials for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Adv Mater. 2008;20(12):2251.
Ji L, Lin Z, Alcoutlabi M, Zhang X. Recent developments in nanostructured anode materials for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Energy Environ Sci. 2011;4(8):2682.
Park CM, Kim JH, Kim H, Sohn HJ. Li-alloy based anode materials for Li secondary batteries. ChemInform. 2010;39(42):3115.
Obrovac MN, Chevrier VL. Alloy negative electrodes for Li-ion batteries. Chem Rev. 2014;114(23):11444.
Zhang WJ. A review of the electrochemical performance of alloy anodes for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2011;196(1):13.
Xie J, Cao GS, Zhao XB, Zhong YD, Zhao MJ. Electrochemical performances of nanosized intermetallic compound CoSb2 prepared by the solvothermal route. J Electrochem Soc. 2004;151(11):A1905.
Xie J, Zhao XB, Cao GS, Zhong YD, Zhao MJ, Tu JP. Solvothermal synthesis of nanosized CoSb2 alloy anode for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta. 2005;50(9):1903.
Xie J, Zhao XB, Cao GS, Zhao MJ, Su SF. Solvothermal synthesis and electrochemical performances of nanosized CoSb3 as anode materials for Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2005;140(2):350.
Xie J, Zhao XB, Cao GS, Zhao MJ. Electrochemical performance of CoSb3/MWNTs nanocomposite prepared by in situ solvothermal synthesis. Electrochim Acta. 2005;50(13):2725.
Xie J, Zhao XB, Yu HM, Qi H, Cao GS, Tu JP. Low temperature solvothermal synthesis of nanosized NiSb as a Li-ion battery anode material. J Alloy Compd. 2007;441(1–2):231.
Xie J, Zhao XB, Cao GS, Zhao MJ, Su SF. Electrochemical Li-uptake properties of nanosized NiSb2 prepared by solvothermal route. J Alloy Compd. 2005;393(1):283.
He Y, Huang L, Li X, Xiao Y, Xu GL, Li JT, Sun SG. Facile synthesis of hollow Cu2Sb@C core–shell nanoparticles as a superior anode material for lithium ion batteries. J Mater Chem. 2011;21(46):18517.
Sarakonsri T, Johnson CS. Solution route synthesis of InSb, Cu6Sn5 and Cu2Sb electrodes for lithium batteries. J Power Sources. 2006;153(2):319.
Ren J, He X, Pu W, Jiang C, Wan C. Chemical reduction of nano-scale Cu2Sb powders as anode materials for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta. 2006;52(4):1538.
Wang F, Zhao M, Song X. The improved electrochemical performance of SnSb-based alloy anode materials for Li-ion batteries. J Alloy Compd. 2009;472(1):55.
Shi L, Li H, Wang Z, Huang X, Chen L. Nano-SnSb alloy deposited on MCMB as an anode material for lithium ion batteries. J Mater Chem. 2001;11(5):1502.
Li H, Wang Q, Shi L, Chen L, Huang X. Nanosized SnSb alloy pinning on hard non-graphitic carbon spherules as anode materials for a Li ion battery. Chem Mater. 2001;14(1):103.
Chen WX, Lee JY, Liu Z. The nanocomposites of carbon nanotube with Sb and SnSb0.5 as Li-ion battery anodes. Carbon. 2003;41(5):959.
Wachtler M, Wagner MR, Schroettner H. Influence of the reductive preparation conditions on the morphology and on the electrochemical performance of Sn/SnSb. Solid State Ionics. 2004;168(1):51.
Park MS, Needham SA, Wang GX, Kang YM, Park JS, Dou SX, Liu HK. Nanostructured SnSb/carbon nanotube composites synthesized by reductive precipitation for lithium-ion batteries. Chem Mater. 2007;19(10):2406.
Li J, Ru Q, Hu S, Sun D, Zhang B, Hou X. Spherical nano-SnSb/MCMB/carbon core–shell composite for high stability lithium ion battery anodes. Electrochim Acta. 2013;113(4):505.
Fan S, Sun T, Rui X, Yan Q, Hng HH. Cooperative enhancement of capacities in nanostructured SnSb/carbon nanotube network nanocomposite as anode for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2012;201(1):288.
Tang X, Yan F, Wei Y, Zhang M, Wang T, Zhang T. Encapsulating Sn x Sb nanoparticles in multichannel graphene-carbon fibers as flexible anodes to store lithium ions with high capacities. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(39):21890.
Nithyadharseni P, Reddy MV, Nalini B, Ravindran TR, Pillai BC, Kalpana M, Chowdari BVR. Electrochemical studies of CNT/Si–SnSb nanoparticles for lithium ion batteries. Mater Res Bull. 2015;70:478.
Zhang P, Wang Y, Wang Y, Ren X, Liu K, Chen S. Electrochemical lithiation and delithiation performance of SnSb–Ag/carbon nanotube composites for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2013;233(4):166.
Li H, Wang Q, Shi L, Chen L, Huang X. Nanosized SnSb alloy pinning on hard non-graphitic carbon spherules as anode materials for a Li ion battery. ChemInform. 2002;14(13):103.
Seng KH, Guo ZP, Chen ZX, Liu HK. SnSb/Graphene composite as anode materials for lithium ion batteries. J Comput Theor Nanos. 2010;4(1):18.
Song S, Huo P, Fan W, Shi W, Yan Y. The facile synthesis of SnSb/graphene composites and their enhanced electrochemical performance for lithium-ion batteries. Sci Adv Mater. 2013;5(12):1801.
Walter M, Doswald S, Kovalenko MV. Inexpensive colloidal SnSb nanoalloys as efficient anode materials for lithium- and sodium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A. 2016;4(18):7053.
He M, Walter M, Kravchyk KV, Erni R, Widmer R, Kovalenko MV. Monodisperse SnSb nanocrystals for Li-ion and Na-ion battery anodes: synergy and dissonance between Sn and Sb. Nanoscale. 2014;7(2):455.
Zhang DL. Processing of advanced materials using high-energy mechanical milling. Prog Mater Sci. 2004;49(3–4):537.
Zhao XB, Cao GS. A study of Zn4Sb3 as a negative electrode for secondary lithium cells. Electrochim Acta. 2001;46(6):891.
Park CM, Sohn HJ. Quasi-intercalation and facile amorphization in layered ZnSb for Li-ion batteries. Adv Mater. 2010;22(1):47.
Park CM, Jeon KJ. Porous structured SnSb/C nanocomposites for Li-ion battery anodes. Chem Commun. 2010;47(7):2122.
Park CM, Sohn HJ. A mechano- and electrochemically controlled SnSb/C nanocomposite for rechargeable Li-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta. 2009;54(26):6367.
Leibowitz J, Allcorn E, Manthiram A. SnSb–TiC–C nanocomposite alloy anodes for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2015;279:549.
Darwiche A, Sougrati MT, Fraisse B, Stievano L, Monconduit L. Facile synthesis and long cycle life of SnSb as negative electrode material for Na-ion batteries. Electrochem Commun. 2013;32(32):18.
Xiao L, Cao Y, Xiao J, Wang W, Kovarik L, Nie Z, Liu J. High capacity, reversible alloying reactions in SnSb/C nanocomposites for Na-ion battery applications. Chem Commun. 2012;48(27):3321.
Kim IT, Kim SO, Manthiram A. Effect of TiC addition on SnSb–C composite anodes for sodium-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2014;269(3):848.
Tian Q, Zhang Z, Yang L, Hirano SI. Fabrication of mesoporous titanium dioxide/tin dioxide/carbon hollow microspheres as high performance anode for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2015;279:528.
Wang M, Zhao H, He J, Wang R, Chen J, Chen N. Preparation and electrochemical performance of CoSb alloy anode material for Li-ion batteries. J Alloy Compd. 2009;484(1–2):864.
Park CM, Sohn HJ. Electrochemical characteristics of TiSb2 and Sb/TiC/C nanocomposites as anodes for rechargeable Li-Ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc. 2010;157(1):A46.
Simonin L, Lafont U, Kelder EM. SnSb micron-sized particles for Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2008;180(2):859.
Guo H, Zhao H, Jia X, Qiu W, Cui F. Synthesis and electrochemical characteristics of Sn–Sb–Ni alloy composite anode for Li-ion rechargeable batteries. Mater Res Bull. 2007;42(5):836.
Yang T, Wang H, Xu J, Wang L, Song WC, Mao Y, Ma J. Preparation of a Sb/Cu2Sb/C composite as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2016;6(82):78959.
Yang YW, Liu F, Li TY, Chen YB, Wu YC, Kong MG. Electrochemical performance of template-synthesized CoSb nanowires array as an anode material for lithium ion batteries. Scripta Mater. 2012;66(7):495.
Yang YW, Li TY, Liu F, Zhu WB, Li XL, Wu YC, Kong MG. Electrodeposition of Ni5Sb2 nanowires array and its application as a high-performance anode material for lithium ion batteries. Microelectron Eng. 2013;104:1.
Saadat S, Zhu J, Shahjamali MM, Maleksaeedi S, Tay YY, Tay BY, Hng HH, Ma J, Yan Q. Template free electrochemical deposition of ZnSb nanotubes for Li ion battery anodes. Chem Commun. 2011;47(35):9849.
Bryngelsson H, Eskhult J, Nyholm L, Edström K. Thin films of Cu2Sb and Cu9Sb2 as anode materials in Li-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta. 2008;53(24):7226.
Mosby JM, Prieto AL. Direct electrodeposition of Cu2Sb for lithium-ion battery anodes. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130(32):10656.
Sun Y, Xia Y. Alloying and dealloying processes involved in the preparation of metal nanoshells through a galvanic replacement reaction. Nano Lett. 2003;3(11):1569.
Au L, Lu X, Xia Y. A comparative study of galvanic replacement reactions involving ag nanocubes and AuCl2− or AuCl4−. Adv Mater. 2008;20(13):2517.
Oh MH, Hyeon T. Galvanic replacement reactions in metal oxide nanocrystals. Science. 2013;340(6135):964.
Hou H, Cao X, Yang Y, Fang L, Pan C, Yang X, Song W, Ji X. NiSb alloy hollow nanospheres as anode materials for rechargeable lithium ion batteries. Chem Commun. 2014;50(60):8201.
Chen J, Yin Z, Sim D, Tay YY, Zhang H, Ma J, Hng HH, Yan Q. Controlled CVD growth of Cu–Sb alloy nanostructures. Nanotechnology. 2011;22(32):325602.
Xu J, Wu H, Wang F, Xia Y, Zheng G. Zn4Sb3 nanotubes as lithium ion battery anodes with high capacity and cycling stability. Adv Energy Mater. 2013;3(3):286.
Li L, Seng KH, Li D, Xia Y, Liu HK, Guo Z. SnSb@carbon nanocable anchored on graphene sheets for sodium ion batteries. Nano Res. 2014;7(10):1466.
Niu C, Meng J, Wang X, Han C, Yan M, Zhao K, Xu X, Ren W, Zhao Y, Xu L, Zhang Q, Zhao D, Mai L. General synthesis of complex nanotubes by gradient electrospinning and controlled pyrolysis. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7402.
Ren W, Zheng Z, Luo Y, Chen W, Niu C, Zhao K, Yan M, Zhang L, Meng J, Mai L. An electrospun hierarchical LiV3O8 nanowire-in-network for high-rate and long-life lithium batteries. J Mater Chem A. 2015;3(39):19850.
Shiva K, Rajendra HB, Bhattacharyya AJ. Electrospun SnSb crystalline nanoparticles inside porous carbon fibers as a high stability and rate capability anode for rechargeable batteries. Chem Plus Chem. 2014;80(3):516.
Ji L, Gu M, Shao Y, Li X, Engelhard MH, Arey BW, Wang W, Nie Z, Xiao J, Wang C, Zhang J, Liu J. Controlling SEI formation on SnSb-porous carbon nanofibers for improved Na ion storage. Adv Mater. 2014;26(18):2901.
Niu X, Zhou H, Li Z, Shan X, Xia X. Carbon-coated SnSb nanoparticles dispersed in reticular structured nanofibers for lithium-ion battery anodes. J Alloy Compd. 2015;620:308.
Caillat T, Fleurial JP, Borshchevsky A. Preparation and thermoelectric properties of semiconducting Zn4Sb3. J Phys Chem Solids. 1997;58(7):1119.
Zhao X, Cao G, Li T. Electrochemical properties of Zn4Sb3 as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Sci Lett. 2000;19(10):851.
Zhao X, Cao G, Lv C, Zhang L, Hu S, Zhu T, Zhou B. Electrochemical properties of some Sb or Te based alloys for candidate anode materials of lithium-ion batteries. J Alloy Compd. 2001;315(1):265.
Baggetto L, Marszewski M, Górka J, Jaroniec M, Veith GM. AlSb thin films as negative electrodes for Li-ion and Na-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2013;243(1):699.
Baggetto L, Allcorn E, Unocic RR, Manthiram A, Veith GM. Mo3Sb7 as a very fast anode material for lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A. 2013;1(37):11163.
Yang J, Takeda Y, Imanishi N, Ichikawa T, Yamamoto O. SnSb x based composite electrodes for lithium ion cells. Solid State Ionics. 2000;135(1):175.
Yang J, Takeda Y, Imanishi N, Xie JY, Yamamoto O. Intermetallic SnSb x compounds for lithium insertion hosts. Solid State Ionics. 2000;133(3–4):189.
Yoshida K, Sano Y, Tomii Y. Study on microstructural deformation of working Sn and SnSb anode particles for Li-ion batteries by in situ transmission X-ray microscopy. J Phys Chem C. 2011;115(44):22040.
Baggetto L, Hah HY, Jumas JC, Johnson CE, Johnson JA, Keum JK, Bridges CA, Veith GM. The reaction mechanism of SnSb and Sb thin film anodes for Na-ion batteries studied by X-ray diffraction, 119Sn and 121Sb Mössbauer spectroscopies. J Power Sources. 2014;267(267):329.
Xie J, Song W, Zheng Y, Liu S, Zhu T, Cao G, Zhao X. Preparation and Li-storage properties of SnSb/graphene hybrid nanostructure by a facile one-step solvothermal route. Int J Smart Nano Mater. 2011;2(4):1.
Birrozzi A, Maroni F, Raccichini R, Tossici R, Marassi R, Nobili F. Enhanced stability of SnSb/graphene anode through alternative binder and electrolyte additive for lithium ion batteries application. J Power Sources. 2015;294:248.
Tang X, Wei Y, Zhang H, Yan F, Zhuo M, Chen C, Xiao P, Liang J, Zhang M. The positive influence of graphene on the mechanical and electrochemical properties of Sn x Sb-graphene-carbon porous mats as binder-free electrodes for Li+ storage. Electrochim Acta. 2015;186:223.
Saadat S, Tay YY, Zhu J, Teh PF, Maleksaeedi S, Shahjamali MM, Shakerzadeh M, Srinivasan M, Tay BY, Hng HH, Ma J, Yan Q. Template-free electrochemical deposition of interconnected ZnSb nanoflakes for li-ion battery anodes. Chem Mater. 2011;23(4):1032.
Fransson LML, Vaughey JT, Benedek R, Edström K, Thomas JO, Thackeray MM. Phase transitions in lithiated Cu2Sb anodes for lithium batteries: an in situ X-ray diffraction study. Electrochem Commun. 2001;3(7):317.
Larcher D. In situ X-ray study of the electrochemical reaction of Li with Cu6Sn5. J Electrochem Soc. 2000;147(5):1658.
Johnson CS, Vaughey JT, Thackeray MM, Sarakonsri T, Hackney SA, Fransson L, Edströmc K, Thomas JO. Electrochemistry and in situ X-ray diffraction of InSb in lithium batteries. Electrochem Commun. 2000;2(8):595.
Morcrette M, Larcher D, Tarascon JM, Edström K, Vaughey JT, Thackeray MM. Influence of electrode microstructure on the reactivity of Cu2Sb with lithium. Electrochim Acta. 2007;52(17):5339.
Applestone DS. Cu2Sb–Al2O3–C nanocomposite alloy anodes for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(14):10886.
He Y, Huang L, Li JT, Sun SG. Facile Synthesis of Sb-Cu2Sb@C core-shell nanocomposite as a superior anode material for lithium ion batteries. J Interfaces Cytok Res. 2013;34(3):148.
Alcántara R, Fernández-Madrigal FJ, Lavela P, Tirado JL, Jumas JC, Olivier-Fourcade J. Electrochemical reaction of lithium with the CoSb3 skutterudite. J Mater Chem. 1999;9(10):2517.
Xie J, Zhao X, Cao G, Zhong Y, Zhao M. Ex-situ XRD studies of CoSb3 compound as the anode material for lithium ion batteries. J Electroanal Chem. 2003;542(2):1.
Tarascon JM, Morcrette M, Dupont L, Chabre Y, Payen C, Larcher D, Pralong V. On the electrochemical reactivity mechanism of CoSb3 vs. lithium. J Electrochem Soc. 2003;150(6):A732.
Park MG, Song JH, Sohn JS, Lee CK, Park CM. Co–Sb intermetallic compounds and their disproportionated nanocomposites as high-performance anodes for rechargeable Li-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A. 2014;2(29):11391.
Zhu J, Sun T, Chen J, Shi W, Zhang X, Lou X, Mhaisalkar S, Hng HH, Boey F, Ma J, Yan Q. Controlled synthesis of Sb nanostructures and their conversion to CoSb3 nanoparticle chains for li-ion battery electrodes. Chem Mater. 2010;22(18):5333.
Villevieille C, Ionica-Bousquet CM, Ducourant B, Jumas JC, Monconduit L. NiSb2 as negative electrode for Li-ion batteries: an original conversion reaction. J Power Sources. 2007;172(1):388.
Villevieille C, Ionica-Bousquet CM, Jumas JC, Monconduit L. 121Sb Mössbauer study of the electrochemical reaction of NiSb2 vs lithium. Hyperfine Interact. 2008;187(1):71.
Baggetto L, Allcorn E, Unocic R, Manthiram A, Veith G. Mo3Sb7 as a very fast anode material for lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A. 2013;1(37):11163.
Fransson L, Vaughey J, Edström K, Thackeray M. Structural transformations in intermetallic electrodes for lithium batteries an in situ X-ray diffraction study of lithiated MnSb and Mn2Sb. J Electrochem Soc. 2003;150(1):A86.
Ionica CM, Lippens PE, Fourcade JO, Jumas JC. Study of Li insertion mechanisms in transition metal antimony compounds as negative electrodes for Li-ion battery. J Power Sources. 2005;146(1):478.
Ionica-Bousquet CM, Womes M, Lippens PE, Olivier-Fourcade J, Ducourant B, Chadwick AV. Evaluation of structural and electrochemical properties of the MnSb-Li system as anode for Li-ion batteries. Heidelberg: ICAME 2005; 2006. 773.
Hewitt K, Beaulieu L, Dahn J. Electrochemistry of InSb as a Li insertion host: problems and prospects. J Electrochem Soc. 2001;148(5):A402.
Johnson C, Vaughey J, Thackeray M, Sarakonsri T, Hackney S, Fransson L, Edströmc K, Thomas JO. Electrochemistry and in situ X-ray diffraction of InSb in lithium batteries. Electrochem Commun. 2000;2(8):595.
Kropf A, Tostmann H, Johnson C, Vaughey J, Thackeray M. An in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy study of InSb electrodes in lithium batteries. Electrochem Commun. 2001;3(5):244.
Tostmann H, Kropf A, Johnson C, Vaughey J, Thackeray M. In situ X-ray absorption studies of electrochemically induced phase changes in lithium-doped InSb. Phys Rev B. 2002;66(1):014106.
Vaughey J, Fransson L, Swinger H, Edström K, Thackeray M. Alternative anode materials for lithium-ion batteries: a study of Ag3Sb. J Power Sources. 2003;119:64.
Zhao M, Zheng Q, Wang F, Qin Y, Song X. Nano-sized SnSbAg x alloy anodes prepared by reductive co-precipitation method used as lithium-ion battery materials. J Nanos Nanotechnol. 2010;10(11):7025.
Yin J, Wada M, Tanase S, Sakai T. Electrode properties and lithiation/delithiation reactions of Ag–Sb–Sn nanocomposite anodes in Li-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc. 2004;151(6):A867.
Rönnebro E, Yin J, Kitano A, Wada M, Tanase S, Sakai T. Reaction mechanism of a Ag36.4Sb15.6Sn48 nanocomposite electrode for advanced Li-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc. 2005;152(1):A152.
Gnanapoongothai T, Murugan R, Palanivel B. First-principle study on lithium intercalated antimonides Ag3Sb and Mg3Sb2. Ionics. 2015;21(5):1351.
Honda H, Sakaguchi H, Tanaka I, Esaka T. Anode behaviors of magnesium–antimony intermetallic compound for lithium secondary battery. J Power Sources. 2003;123(2):216.
Gómez-Cámer JL, Novák P. Polyacrylate bound TiSb2 electrodes for Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2015;273:174.
Marino C, Sougrati MT, Gerke B, Pottgen R, Huo H, Ménétrier M, Grey CP, Monconduit L. Role of structure and interfaces in the performance of TiSnSb as an electrode for Li-ion batteries. Chem Mater. 2012;24(24):4735.
Sougrati MT, Fullenwarth J, Debenedetti A, Fraisse B, Jumas JC, Monconduit L. TiSnSb a new efficient negative electrode for Li-ion batteries: mechanism investigations by operando-XRD and Mössbauer techniques. J Mater Chem. 2011;21(27):10069.
Larcher D, Beaulieu L, Mao O, George A, Dahn J. Study of the reaction of lithium with isostructural A2B and various Al x B alloys. J Electrochem Soc. 2000;147(5):1703.
Fernández-Madrigal FJ, Lavela P, Pérez-Vicente C, Tirado JL. Electrochemical reactions of polycrystalline CrSb2 in lithium batteries. J Electroanal Chem. 2001;501(1):205.
Park CM, Sohn HJ. Antimonides (FeSb2, CrSb2) with orthorhombic structure and their nanocomposites for rechargeable Li-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta. 2010;55(17):4987.
Villevieille C, Fraisse B, Womes M, Jumas JC, Monconduit L. A new ternary Li4FeSb2 structure formed upon discharge of the FeSb2/Li cell. J Power Sources. 2009;189(1):324.
Baggetto L, Hah H-Y, Johnson CE, Bridges CA, Johnson JA, Veith GM. The reaction mechanism of FeSb2 as anode for sodium-ion batteries. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2014;16(20):9538.
Villevieille C, Ionica-Bousquet C, Fraisse B, Zitoun D, Womes M, Jumas JC, Monconduit L. Comparative study of NiSb2 and FeSb2 as negative electrodes for Li-ion batteries. Solid State Ionics. 2011;192(1):351.
Zhao Y, Manthiram A. Amorphous Sb2S3 embedded in graphite: a high-rate, long-life anode material for sodium-ion batteries. Chem Commun. 2015;51(67):13205.
Luo W, Calas A, Tang C, Li F, Zhou L, Mai L. Ultralong Sb2Se3 nanowire based free-standing membrane anode for lithium/sodium ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(51):35219.
Zhou X, Liu X, Xu Y, Dai Z, Bao J. An SbO x /reduced graphene oxide composite as a high-rate anode material for sodium-ion batteries. J Phys Chem C. 2014;118(41):23527.
Sun Q, Ren Q, Li H, Fu Z. High capacity Sb2O4 thin film electrodes for rechargeable sodium battery. Electrochem Commun. 2011;13(12):1462.
Chen X, Ru Q, Wang Z, Hou X, Hu S. Ternary Sn–Sb–Co alloy particles embedded in reduced graphene oxide as lithium ion battery anodes. Mater Lett. 2017;191:218.
Pang XJ, Tan CH, Dai XH, Wang X, Qi GW, Zhang SY. Performance enhancement of Sn–Sb–Co alloy film anode for lithium-ion batteries via post electrodissolution treatment. J Appl Electrochem. 2015;45(2):115.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFA0202603), the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2013CB934103), the Program of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities (No. B17034), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51521001), the National Natural Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 51425204), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nos. 2016III001 and 2016-JL-004), and the China Scholarship Council (No. 201606955096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, W., Gaumet, JJ. & Mai, LQ. Antimony-based intermetallic compounds for lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries: synthesis, construction and application. Rare Met. 36, 321–338 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-017-0899-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-017-0899-4