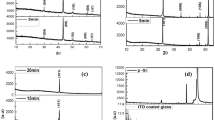
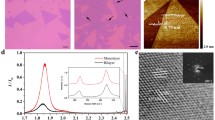
Abstract
The optical, thermal and electrical properties of ultra-thin two-dimensional (2D) crystal materials are highly related to their thickness. Therefore, identifying the atomic planes of few-layer crystal materials rapidly is crucial to fundamental study. Here, a simple technique was demonstrated based on optical contrast for counting atomic planes (n) of few-layer MoSe2 on SiO2/Si substrates. It is found that the optical contrast of single-layer MoSe2 depends on light wavelength and thickness of SiO2 on Si substrate. The data calculated based on a Fresnel law-based model as well as atomic force microscopy (AFM) measurements fit well with the values measured by spectroscopic ellipsometer. Furthermore, the calculated and measured contrasts were integral and plotted, which can be used to determine the MoSe2 atomic planes (1 ≤ n ≤ 4) accurately and rapidly.
Graphical Abstract
The optical contrast of thin-layer (1 ≤ n ≤ 4) MoSe2 sample was calculated by Fresnel’s law, and the contrast was measured by OM image. By combining these two group data, a function of layer numbers and contrast was developed: C (contrast) = 0.07N + 0.177. This proves that contrast is linear to layer numbers of MoSe2 when layer number is less than 4.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov SV, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos SV, Grigorieva IV, Firsov AA. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science. 2004;306(5696):666.
Geim AK, Novoselov KS. The rise of graphene. Nat Mater. 2007;6(3):183.
Neto AHC, Guinea F, Peres NMR, Novoselov KS, Geim AK. The electronic properties of graphene. Rev Mod Phys. 2009;81(1):109.
Lee C, Yan H, Brus LE, Heinz TF, Hone J, Ryu S. Anomalous lattice vibrations of single- and few-layer MoS2. ACS Nano. 2010;4(5):2695.
Sun JF, Cheng F. Spin and valley transport in monolayers of MoS2. J Appl Phys. 2014;115(13):133703.
Nath M, Govindaraj A, Rao CNR. Simple synthesis of MoS2 and WS2 nanotubes. Adv Mater. 2001;13(4):283.
Matte HS, Gomathi A, Manna AK, Late DJ, Datta R, Pati SK, Rao CN. MoS2 and WS2 analogues of graphene. Angew Chem. 2010;49(24):4059.
Huang CM, Wu SF, Sanchez AM, Peters JJP, Beanland R, Ross JS, Rivera P, Yao W, Cobden DH, Xu XD. Lateral heterojunctions within monolayer MoSe2–WSe2 semiconductors. Nat Mater. 2014;13(12):1096.
Zhang HM, He XB, Qu XH, Liu Q, Shen XY. Microstructure and thermal properties of copper matrix composites reinforced with titanium-coated graphite fibers. Rare Met. 2013;32(1):75.
Xu HT, He DW, Fu M, Wang WS, Wu HP, Wang YS. Optical identification of MoS2/graphene heterostructure on SiO2/Si substrate. Opt Express. 2014;22(13):15969.
Tongay S, Zhou J, Ataca C, Lo K, Matthews TS, Li JB, Grossman JC, Wu JQ. Thermally driven crossover from indirect toward direct bandgap in 2D semiconductors: MoSe2 versus MoS2. Nano Lett. 2012;12(11):5576.
Ni ZJ, Wang YY, Yu T, Shen ZX. Raman spectroscopy and imaging of graphene. Nano Res. 2008;1(4):273.
Meyer JC, Scardaci V, Casiraghi C, Lazzeri M, Mauri F, Piscanec S, Jiang D, Novoselov KS, Roth S, Geim AK, Ferrari AC. Raman spectrum of graphene and graphene layers. Phys Rev Lett. 2006;97(18):187401.
Koh YK, Bae M-H, Cahill DG, Pop E. Reliably counting atomic planes of few-layer graphene (n > 4). ACS Nano. 2011;5(1):269.
Wang XF, Zhao M, Nolte DD. Optical contrast and clarity of graphene on an arbitrary substrate. Appl Phys Lett. 2009;95(8):81102.
Li H, Lu G, Yin ZY, He QY, Li H, Zhang Q, Zhang H. Optical identification of single- and few-layer MoS2 sheets. Small. 2012;8(5):682.
Li H, Wu J, Huang X, Lu G, Yang J, Lu X, Xiong QH, Zhang H. Rapid and reliable thickness identification of two-dimensional nanosheets using optical microscopy. ACS Nano. 2013;7(11):10344.
Blake P, Hill EW, Castro NAH, Novoselov KS, Jiang D, Yang R, Booth TJ, Geim AK. Making graphene visible. Appl Phys Lett. 2007;91(6):63124.
Shaw JC, Zhou HL, Chen Y, Weiss NO, Liu Y, Huang Y, Duan XF. Chemical vapor deposition growth of monolayer MoSe2 nanosheets. Nano Res. 2014;7(4):511.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Research Funds of Renmin University of China (Nos. 13XNLF02 and 14XNLQ07) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11304381, 11004245, 11174366 and 51202200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YP., Zhou, HJ., Zhao, GH. et al. Rapidly counting atomic planes of ultra-thin MoSe2 nanosheets (1 ≤ n ≤ 4) on SiO2/Si substrate. Rare Met. 35, 632–636 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0776-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0776-6