Abstract
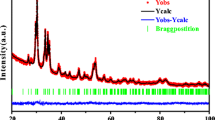
Magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effects (MCEs) of the PrSi compound were studied. The PrSi compound undergoes a second-order ferromagnetic-to-paramagnetic transition at the Curie temperature of T C = 52 K. Large MCE with no magnetic hysteresis loss is observed around T C. The maximum values of magnetic entropy change (ΔS) are found to be −8.6 and −15.3 J·kg−1·K−1 for the magnetic field changes of 0–2 T and 0–5 T, respectively. The large ΔS with no hysteresis makes PrSi compound a competitive candidate for magnetic refrigerant.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tishin AM, Spichkin YI. The magnetocaloric Effect and its Applications. Bristol: IOP Publishing; 2003. p. 1.
Gschneidner KAJr, Pecharsky VK, Tsokol AO. Recent developments in magnetocaloric materials. Rep Prog Phys. 2005;68(6):1479.
Brück E. In: Buschow KHJ, editor. Handbook of Magnetic Materials. Amsterdam: North-Holland Publishing; 2008. 235.
Shen BG, Sun JR, Hu FX, Zhang HW, Cheng ZH. Recent progress in exploring magnetocaloric materials. Adv Mater. 2009;21(45):4545.
Shen BG, Hu FX, Dong QY, Sun JR. Magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effects in NaZn13-type La(Fe, Al)13-based compounds. Chin Phys B. 2013;22(1):017502.
Pecharsky VK, Gschneidner KAJr. Giant magnetocaloric effect in Gd5(Si2Ge2). Phys Rev Lett. 1997;78(23):4494.
Hu FX, Shen BG, Sun JR, Zhang XX. Great magnetic entropy change in La(Fe, M) M = Si, Al with Co doping. Chin Phys. 2000;9(7):550.
Hu FX, Shen BG, Sun JR, Cheng ZH, Rao GH, Zhang XX. Influence of negative lattice expansion and metamagnetic transition on magnetic entropy change in the compound LaFe11.4Si1.6. Appl Phys Lett. 2001;78(23):3675.
Zhang H, Hu FX, Sun JR, Shen BG. Effects of interstitial H and/or C atoms on the magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of La(Fe, Si)13-based compounds. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron. 2013;56(12):2302.
Wada H, Tanabe Y. Giant magnetocaloric effect of MnAs1−x Sb x . Appl Phys Lett. 2001;79(20):3302.
Tegus O, Bruck E, Buschow KHJ, de Boer FR. Transition-metal-based magnetic refrigerants for room-temperature applications. Nature (London). 2002;415:150.
Hu FX, Shen BG, Sun JR. Magnetic entropy change involving martensitic transition in NiMn-based Heusler alloys. Chin Phys B. 2013;22(3):037505.
Zhang XX, Wang FW, Wen GH. Magnetic entropy change in RCoAl (R = Gd, Tb, Dy, and Ho) compounds: candidate materials for providing magnetic refrigeration in the temperature range 10 K–100 K. J Phys: Condens Matter. 2001;13(31):L747.
Chen J, Shen BG, Dong QY, Hu FX, Sun JR. Large reversible magnetocaloric effect caused by two successive magnetic transitions in ErGa compound. Appl Phys Lett. 2009;95(13):132504.
Shen J, Zhao JL, Hu FX, Wu JF, Sun JR, Shen BG. Order of magnetic transition and large magnetocaloric effect in Er3Co. Chin Phys B. 2010;19(4):047502.
Shen J, Li YX, Dong QY, Wang F, Sun JR. Magnetocaloric effect in Gd6Co1.67Si3 compound with a second-order phase transition. Chin Phys B. 2008;17(6):2268.
Dong QY, Zhang HW, Sun JR, Shen BG, Franco V. A phenomenological fitting curve for the magnetocaloric effect of materials with a second-order phase transition. J Appl Phys. 2008;103(11):116101.
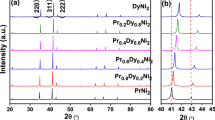
Nguyen VN, Tchéou F, Rossat-Mignod J. Magnetic structures of PrSi and NdSi intermetallic alloys. Solid State Commun. 1977;23(11):821.
Iandelli A, Palenzona A. In: Gschneidner KA, Eyring L, editors. Handbook of Physics and Chemistry of Rare Earths. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1979. 1.
Pinguet N, Weitzer F, Hiebl K, Schuster JC, Noël H. Structural chemistry, magnetism and electrical properties of binary Pr-silicides. J Alloys Compd. 2003;348(1–2):1.
Snyman JL, Strydom AM. Anomalous magnetic ground state in PrSi evidenced by the magnetocaloric effect. J Appl Phys. 2012;111(7):07A943.
Schobinger-Papamantellos P, Buschow KHJ, Rodríguez-Carvajal J. Magnetic phase diagrams of the CrB- and FeB-type HoSi compounds. J Magn Magn Mater. 2011;323(21):2592.
Feng YJ, Silevitch DM, Wang JY, Palmer A, Woo N, Yan JQ, Islam Z, Suslov AV, Littlewood PB, Rosenbaum TF. Evolution of incommensurate spin order with magnetic field and temperature in the itinerant antiferromagnet GdSi. Phys Rev B. 2013;88(13):134404.
Nirmala R, Morozkin AV, Buddhikot D, Nigam AK. Magnetocaloric effect in the binary intermetallic compound DySi. J Magn Magn Mater. 2008;320(6):1184.
Xu ZY, Shen J, Zheng XQ, Zhang H. Magnetocaloric effect in ErSi compound. IEEE Trans on Mag. 2011;47(10):2470.
Mallik R, Sampathkumaran EV, Paulose PL. Large low temperature magnetoresistance and magnetic anomalies in Tb2PdSi3 and Dy2PdSi3. Solid State Commun. 1998;106(3):169.
Singh NK, Suresh KG, Nirmala R, Nigam AK, Malik SK. Effect of magnetic polarons on the magnetic, magnetocaloric, and magnetoresistance properties of the intermetallic compound HoNiAl. J Appl Phys. 2007;101(9):093904.
Pecharsky VK, Gschneidner KAJr. Magnetocaloric effect from indirect measurements: magnetization and heat capacity. J Appl Phys. 1999;86(1):565.
Zhang H, Shen BG, Xu ZY, Shen J, Hu FX, Sun JR, Long Y. Large reversible magnetocaloric effects in ErFeSi compound under low magnetic field change around liquid hydrogen temperature. Appl Phys Lett. 2013;102(9):092401.
Wang LC, Dong QY, Lu J, Shao XP, Mo ZJ, Xu ZY, Sun JR, Hu FX, Shen BG. Low-temperature large magnetocaloric effect in the antiferromagnetic CeSi compound. J Alloys Compd. 2014;587:10.
Samanta T, Das I, Banerjee S. Giant magnetocaloric effect in antiferromagnetic ErRu2Si2 compound. Appl Phys Lett. 2007;91(15):152506.
Franco V, Blázquez JS, Conde A. Field dependence of the magnetocaloric effect in materials with a second order phase transition: a master curve for the magnetic entropy change. Appl Phys Lett. 2006;89(22):222512.
Acknowledgment
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11274357) and the Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (No. 2011AA03A404).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, LC., Shen, BG. Magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effects of PrSi. Rare Met. 33, 239–243 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0310-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0310-7