Abstract
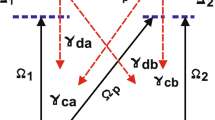
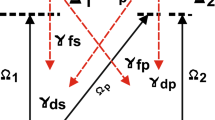
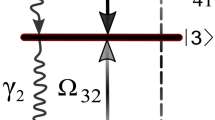
A four-level ladder-type atomic configuration of the sodium atom from the \(D_1\)-line is driven by the probe field and two interacting control fields is used to manipulate and control coherently the magnetic spin density of the probe field via electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT). In this technique, a weak probe laser beam is applied in the presence of a strong control laser beam, which creates a transparency window in the medium, allowing the probe beam to pass through with minimal absorption. By controlling the relative phase and polarization of the probe and control beams, the angular momentum of the probe beam can be manipulated and controlled coherently. Substantial variation is investigated in the behavior of the graphs of two interfering waves with the Rabi frequencies of the control field, detuning of the probe and control fields and the angle between the two interfering waves. Magnetic spin vector field distribution and magnetic spin density of circularly, diagonally and linearly polarized probe light field are coherently controlled and modified. The major role in this modification is played by the detuning of the probe field and the parameters of the control fields. This modified work in magnetic spin density and magnetic spin AM vector field arrow distribution is useful in the unidirectional optical interfaces, birefringence and the quantum spin Hall effect of the light beam.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data are associated with the manuscript.
References
L. Allen, S.M. Barnett, M.J. Padgett (eds.), Optical Angular Momentum (IoP Publishing, Bristol, 2003)
A. Bekshaev, M. Soskin, M. Vasnetsov, Paraxial Light Beams with Angular Momentum (Nova Science Publishers, New York, 2008)
D.L. Andrews (ed.), Structured Light and Its Applications (Academic Press, Amsterdam, 2008)
J.P. Torres, L. Torner (eds.), Twisted Photons (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2011)
D.L. Andrews, M. Babiker (eds.), The Angular Momentum of Light (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2013)
L. Allen, M.J. Padgett, M. Babiker, The orbital angular momentum of light. Prog. Opt. 39, 291–372 (1999)
G. Molina-Terriza, J.P. Torres, L. Torner, Twisted photons. Nat. Phys. 3, 305–310 (2007)
S. Franke-Arnold, L. Allen, M.J. Padgett, Advances in optical angular momentum. Laser Photonics Rev. 2, 299–313 (2008)
A.M. Yao, M.J. Padgett, Optical angular momentum: origins, behavior, and applications. Adv. Opt. Photonics 3, 161–204 (2011)
A. Bekshaev, K.Y. Bliokh, M. Soskin, Internal flows and energy circulation in light beams. J. Opt. 13, 053001 (2011)
M.E.J. Friese, T.A. Nieminen, N.R. Heckenberg, H. Rubinsztein-Dunlop, Optical alignment and spinning of laser-trapped microscopic particles. Nature 394, 348–350 (1995)
S. Stenholm, The semiclassical theory of laser cooling. Rev. Mod. Phys. 58, 699 (1986)
C. Cohen-Tannoudji, J. Dupont-Roc, G. Grynberg, Atom–Photon Interactions (Wiley-VCH, New York, 2004)
D.G. Grier, A revolution in optical manipulation. Nature (London) 424, 810 (2003)
M. Aspelmeyer, T.J. Kippenberg, F. Marquardt, Cavity optomechanics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 86, 1391 (2014)
M.E.J. Friese, T.A. Nieminen, N.R. Heckenberg, H. Rubinsztein-Dunlop, Optical alignment and spinning of laser-trapped microscopic particles. Nature (London) 394, 348 (1998)
A.T. O’Neil, I. MacVicar, L. Allen, M.J. Padgett, Intrinsic and extrinsic nature of the orbital angular momentum of a light beam. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 053601 (2002)
V. Garcés-Chávez, D. McGloin, M.J. Padgett, W. Dultz, H. Schmitzer, K. Dholakia, Observation of the transfer of the local angular momentum density of a multiringed light beam to an optically trapped particle. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 093602 (2003)
R. Loudon, C. Baxter, Contribution of John Henry Poynting to the understanding of radiation pressure. Proc. R. Soc. A 468, 1825 (2012)
J.D. Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 3rd edn. (Wiley, New York, 1999)
R.A. Beth, Mechanical detection and measurement of the angular momentum of light. Phys. Rev. 50, 115–125 (1936)
S. Huard, C. Imbert, Measurement of exchanged momentum during interaction between surface-wave and moving atom. Opt. Commun. 24, 185 (1978)
M.R. Dennis, A.C. Hamilton, J. Courtial, Superoscillations in speckle patterns. Opt. Lett. 33, 2976 (2008)
K.Y. Bliokh, A.Y. Bekshaev, A.G. Kofman, F. Nori, Photon trajectories, anomalous velocities, and weak measurements: a classical interpretation. New J. Phys. 15, 073022 (2013)
S.M. Barnett, M.V. Berry, Superweak momentum transfer near optical vortices. J. Opt. 15, 125701 (2013)
K.Y. Bliokh, F. Nori, Transverse spin of a surface polariton. Phys. Rev. A 85, 061801(R) (2012)
K.Y. Bliokh, A.Y. Bekshaev, F. Nori, Extraordinary momentum and spin in evanescent waves. Nat. Commun. 5, 3300 (2014)
A. Canaguier-Durand, C. Genet, Transverse spinning of a sphere in plasmonic field. Phys. Rev. A 89, 033841 (2014)
C. Junge, D. O’Shea, J. Volz, A. Rauschenbeutel, Strong coupling between single atoms and nontransversal photons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 213604 (2013)
J. Petersen, J. Volz, A. Rauschenbeutel, Chiral nanophotonic waveguide interface based on spin-orbit coupling of light. Science 346, 67 (2014)
H. Zhang et al., Coherent control of optical spin-to-orbital angular momentum conversion in metasurface. Adv. Mater. 29(6), 1604252 (2017)
J. Chen, C. Wan, Q. Zhan, Engineering photonic angular momentum with structured light: a review. Adv. Photonics 3(6), 064001 (2021)
L. Marrucci, C. Manzo, D. Paparo, Optical spin-to-orbital angular momentum conversion in inhomogeneous anisotropic media. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96(16), 163905 (2006)
F. Bouchard et al., Optical spin-to-orbital angular momentum conversion in ultra-thin metasurfaces with arbitrary topological charges. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105(10), 101905 (2014)
S.M. Barnett, M. Babiker, M.J. Padgett, Optical orbital angular momentum. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 375(2087), 20150444 (2017)
Y. Zhao et al., Spin-to-orbital angular momentum conversion in a strongly focused optical beam. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99(7), 073901 (2007)
L. Marrucci et al., Spin-to-orbital conversion of the angular momentum of light and its classical and quantum applications. J. Opt. 13(6), 064001 (2011)
D.L.P. Vitullo et al., Observation of interaction of spin and intrinsic orbital angular momentum of light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118(8), 083601 (2017)
A.Y. Bekshaev, K.Y. Bliokh, F. Nori, Transverse spin and momentum in two-wave interference. Phys. Rev. X 5, 011039 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mr. R and Dr. MT have worked in four-level model of rubidium-87 and also derive the relationship between the magnetic spin density of light and control field parameters of the medium. Dr. MT and AH worked in the results and contribution section in explaining the graphs and giving physical interpretation to it. Dr. MT supervised the whole manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Safi, R., Tariq, M. & Hamza, A. Coherent manipulation of optical magnetic spin angular momentum of two-wave interference in atomic medium. J Opt 52, 2199–2206 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01133-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01133-w