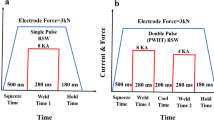
Abstract
The aim of this study is to prevent thermal cracking in the fusion zone of dissimilar resistance spot weld, which arises due to the electrical and thermal conductivity differences of austenitic steel and weathering steel. Therefore, dissimilar double pulse resistance spot welding experiments were carried out on 4-mm-thick 301LN austenitic stainless steel and 09CuPCrNi weathering steel sheets. The first low-current pulse was used for prewelding, and the second high-current pulse was used for weld generation under a high electrode force. Under these conditions, satisfactory welds that met the welding criterion without thermal cracks or central shrinkage cavities were obtained. In the fusion zone of the double pulse weld, the phases present were lath martensite, δ-ferrite, austenite and phosphorus-rich eutectic. There was a small amount of austenite in this zone, and the eutectic appeared at the grain boundaries. The failure mode of the double pulse weld was pull-out fracture. Finally, the load-bearing capacity of the double pulse weld was 35% greater than that of the single pulse weld.
Graphical Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data in this study is available to third parties.
References
J. Talonen, H. Hänninen, P. Nenonen, G. Pape, Effect of strain rate on the strain-induced γ → α′-martensite transformation and mechanical properties of austenitic stainless steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36, 421–432 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-005-0313-y
W. Liu, Z. Li, X. Wang, H. Zou, L. Wang, Effect of strain rate on strain induced α′-martensite transformation and mechanical response of austenitic stainless steels. Acta Metall. Sin. 45, 285–291 (2009). https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2008.07.002
X. Li, W. Liu, X. Guo, Z. Zhang, Z. Song, Microstructure evolution of laser welded 301LN and AISI 304 ustenitic stainless steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 54, 1186–1198 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-023-06973-6
X. Guo, W. Liu, X. Li, J. Fan, Z. Song, A new approach to improve ductility of non-penetrating laser welded lap joints of cold-rolled 301LN stainless steel. Weld. World 65, 87–93 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-020-00999-9
W. Liu, H. Fan, X. Guo, Z. Huang, X. Han, Mechanical properties of resistance spot welded components of high strength austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 32, 561–565 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2015.11.023
Z. Fu, G. Gou, Z. Zhu, C. Ma, W. Yang, L. Zhang, Y. Hu, W. Gao, Stress corrosion cracking behavior of SUS301L-MT stainless steel laser-arc hybrid welded joints. Corros. Sci. 143, 23–30 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2018.08.002
S. Ningshen, U.K. Mudali, Pitting and intergranular corrosion resistance of AISI Type 301LN stainless steels. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 19, 274–281 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-009-9441-7
M. Amra, S.R. Alavi Zaree, R. Dehmolaei, Dissimilar welding between 1.4742 ferritic and 310S austenitic stainless steels: assessment of oxidation behaviour. Met. Mater. Int. 27, 931–945 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00485-y
A.E. Hernández, L.O. Villarinho, V.A. Ferraresi, M.S. Orozco, A.S. Roca, H.C. Fals, Optimization of resistance spot welding process parameters of dissimilar DP600/AISI304 joints using the infrared thermal image processing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 108, 211–221 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05374-y
M. Pouranvari, M. Khorramifar, S.P.H. Marashi, Ferritic–austenitic stainless steels dissimilar resistance spot welds: metallurgical and failure characteristics. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 21, 438–445 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2015.1124491
F. Badkoobeh, H. Mostaan, M. Rafiei, A. Bakhtiari, A study on phase evolutions and tensile-shear performance of dissimilar resistance spot welds formed between AISI 430 ferritic stainless steel and AISI 321 austenitic stainless steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 32, 5028–5042 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07451-7
Z. Gu, S. Li, L. Zhao, L. Zhu, G. Yu, Finite element simulation and experimental investigations of cold stamping forming defect of A588-A thick weathering steel bogie lower cover. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 104, 1275–1283 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04148-5
N. Akkaş, Welding time effect on tensile-shear loading in resistance spot welding of SPA-H weathering steel sheets used in railway vehicles. Acta Phys. Pol. A 131, 52–54 (2017). https://doi.org/10.12693/APhysPolA.131.52
W. Liu, J. Liu, H. Pan, F. Cao, Z. Wu, H. Lv, Z. Xu, Synergisic effect of Mn, Cu, P with Cr content on the corrosion behavior of weathering steel as a train under the simulated industrial atmosphere. J. Alloys Compd. 834, 155095 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155095
Y. Sun, W. Liu, B. Dong, T. Zhang, L. Chen, W. Yang, H. Li, B. Zhang, J. Xie, J. Cui, Designing weathering steel with optimized Mo/Ni ratios for better corrosion resistance in simulated tropical marine atmosphere. Met. Mater. Int. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-023-01547-y
X. Li, W. Liu, H. Liu, Z. Zhang, P. Bao, Microstructure and thermal cracking susceptibility of dissimilar resistance spot welded austenitic and mild steels. Weld. World 67, 417–423 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-022-01440-z
I.A. Soomro, S.R. Pedapati, M. Awang, A review of advances in resistance spot welding of automotive sheet steels: emerging methods to improve joint mechanical performance. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 118, 1335–1366 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08002-5
Y. Jing, Y. Xu, D. Wang, L. Lu, J. Li, Y. Yu, Improving mechanical properties of welds through tailoring microstructure characteristics and fracture mechanism in multi-pulse resistance spot welding of Q&P980 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 843, 143130 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2022.143130
X. Liu, Y. Xu, R.D.K. Misra, F. Peng, Y. Wang, Y. Du, Mechanical properties in double pulse resistance spot welding of Q&P 980 Steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 263, 186–197 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.08.018
Y. Zhang, W. Xu, G. Zhang, W. Tao, S. Yang, Mechanical behavior and failure mechanism of Q&P980 steel during in situ post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) resistance spot welding. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 53, 794–809 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-021-06546-5
T. Chen, Z. Ling, M. Wang, L. Kong, Effect of post-weld tempering pulse on microstructure and mechanical properties of resistance spot welding of Q&P1180 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 831, 142164 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.142164
I.A. Soomro, S.R. Pedapati, M. Awang, M.A. Alam, Effects of double pulse welding on microstructure, texture, and fatigue behavior of DP590 steel resistance spot weld. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 125, 1271–1287 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10704-3
A. Chabok, E. van der Aa, J.T.M.D. Hosson, Y.T. Pei, Mechanical behavior and failure mechanism of resistance spot welded DP1000 dual phase steel. Mater. Des. 124, 171–182 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.03.070
H. Aghajani, M. Pouranvari, Influence of in situ thermal processing strategies on the weldability of martensitic stainless steel resistance spot welds: effect of second pulse current on the weld microstructure and mechanical properties. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 50, 5191–5209 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05443-2
O.T. Betiku, M. Shojaee, O. Sherepenko, A.R.H. Midawi, A.M. Chertov, H. Ghassemi-Armaki, R.G. Maev, E. Biro, Optimizing post-weld performance of press-hardened steel resistance spot welds by controlling fusion zone porosity. Weld. World 66, 1733–1746 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-022-01332-2
D. Zhao, N. Vdonin, L. Radionova, L. Glebov, V. Bykov, Optimization of post-weld tempering parameters for HSLA 420 steel in resistance spot welding process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 123, 1811–1823 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10319-8
M. Stadler, M. Gruber, R. Schnitzer, C. Hofer, Microstructural characterization of a double pulse resistance spot welded 1200 MPa TBF steel. Weld. World 64, 335–343 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-019-00835-9
D.Y. Choi, A. Sharma, S.H. Uhm, J.P. Jung, Liquid metal embrittlement of resistance spot welded 1180 TRIP steel: effect of electrode force on cracking behavior. Met. Mater. Int. 25, 219–228 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-018-0180-x
T. Kawakubo, K. Ushioda, H. Fujii, Grain boundary segregation and toughness of friction-stir-welded high-phosphorus weathering steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 832, 142350 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.142350
A. Almomani, A.H.I. Mourad, I. Barsoum, Effect of sulfur, phosphorus, silicon, and delta ferrite on weld solidification cracking of AISI 310S austenitic stainless steel. Eng. Fail. Anal. 139, 106488 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106488
H.S. Kim, Y. Kobayashi, K. Nagai, Simulation of the influence of phosphorus on the prior austenite grain size of high-impurity steels. Acta Mater. 54, 2441–2449 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2006.01.024
W. Liu, C. Sun, X. Xu, Y. Zuo, J. Lin, The influences of nugget diameter on the mechanical properties and the failure mode of resistance spot-welded metastable austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Des. 33, 292–299 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.06.071
S.H.M. Anijdan, M. Sabzi, M. Ghobeiti-Hasab, A. Roshan-Ghiyas, Optimization of spot welding process parameters in dissimilar joint of dual phase steel DP600 and AISI 304 stainless steel to achieve the highest level of shear-tensile strength. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 726, 120–125 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.04.072
P.R. Spena, M.D. Maddis, F. Lombardi, M. Rossini, Dissimilar resistance spot welding of Q&P and TWIP steel sheets. Mater. Manuf. Process. 31, 291–299 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1048476
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the scientific research and development project 2019J011-C of China Railway Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Liu, W., Chen, Y. et al. Experimental Study of Dissimilar Double Pulse Resistance Spot Welded Austenitic Stainless Steel and Weathering Steel. Met. Mater. Int. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-024-01667-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-024-01667-z