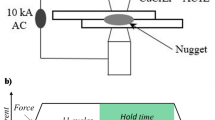
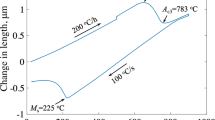
Abstract
The use of resistance spot welding (RSW) in the automotive industry is by far the most preferred and widely used joining technique for sheet metal parts and is likely to continue for the foreseeable future. Advanced high strength steels (AHSSs) are most commonly used in automotive structural components due to their attractive strength-ductility combinations. However, several challenges are faced during RSW including (1) complex phase transformations such as hardening of nugget due to brittle martensitic structure and softening in the heat affected zone due to martensite tempering present in base metal, cast like solidification structure of nugget (2) elemental segregation leading to grain boundary embrittlement, (3) solidification defects such as porosity and void formation in nugget, and (4) liquid metal embrittlement cracking. All of above factors contributes in degradation of joint mechanical properties. In recent years, interlayer assisted RSW, magnetically assisted RSW, and pulsed-RSW have emerged as potential methods to improve the joint mechanical performance. This review paper seeks to summarize the recent technological advances of three modified RSW processes. A comprehensive analysis of the effect of welding process parameters on metallurgical features of the weld joint, mechanical performance, and failure behaviour under different loading conditions, i.e. cross tension, tensile shear, and cyclic (i.e. fatigue), is presented. In addition, the process feasibility to various AHSS grades is also discussed. Finally, current challenges and new opportunities arising from three modified RSW processes are discussed to provide a basis for future research.
































Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time because this being a review article, it was taken from the published literature.
Code availability
Not applicable
Change history
10 March 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09025-2
References
Hall JN, Fekete JR (2017) Steels for auto bodies: a general overview in Automotive steels design, metallurgy, processing and applications. R. Rana, S. B. Singh (ed), Woodhead Publishing, pp 19-44
Joost WJ (2012) Reducing vehicle weight and improving U.S. energy efficiency using integrated computational materials engineering. JOM 64:1032–1038. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-012-0424-z
Lesch C, Kwiaton N, Klose FB (2017) Advanced high strength steels (Ahss) for automotive applications−tailored properties by smart microstructural adjustments. Steel Res Int 88(1-21):1700210. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201700210
Mallick PK (2010) Overview in materials, design and manufacturing for lightweight vehicles, Mallick PK (ed) Woodhead Publishing. pp 1-30
Keeler S, Kimchi M, Mconey PJ (2017) Advanced high strength steels application guidelines version 6.0. World Auto Steel Report.
Hilditch TB, de Souza T, Hodgson PD (2015) Properties and automotive applications of advanced high-strength steels (ahss) in welding and joining of advanced high strength steels (ahss): Woodhead Publishing, pp 9-28
Hovorun TP, Berladir KV, Pererva VI, Rudenko SG, Martynov AI (2017) Modern materials for automotive industry. J Eng Sci 4(2):f8–f18. https://doi.org/10.21272/jes.2017.4(2).f8
Nanda T, Singh V, Chakraborty A, Sharma S (2016) Third generation of advanced high-strength steels: processing routes and properties. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part L: J Mater Des Appl 233:209–238. https://doi.org/10.1177/1464420716664198
Bhargava M, Chakrabarty S, Barnwal VK, Tewari A, Mishra SK (2018) Effect of microstructure evolution during plastic deformation on the formability of Transformation Induced Plasticity and Quenched & Partitioned AHSS. Mater Des 152:65–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2018.04.068
Demeri MY (2013) Dual phase steels in advanced high-strength steels: science, technology, and applications, Demeri MY (ed) ASM International, United States, pp 95-105
Zhao J, Jiang Z (2018) Thermomechanical processing of advanced high strength steels. Prog Mater Sci 94:174–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2018.01.006
Frómeta D, Lara A, Molas S, Casellas D, Rehrl J, Suppan C, Larour P, Calvo J (2019) On the correlation between fracture toughness and crash resistance of advanced high strength steels. Eng Fract Mech 205:319–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.10.005
Aydin H, Essadiqi E, Jung I-H, Yue S (2013) Development of 3rd generation AHSS with medium Mn content alloying compositions. Mater Sci Eng A 564:501–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.11.113
Horvath CD (2010) Advanced steels for lightweight automotive structures in Materials, design and manufacturing for lightweight vehicles, P. K. Mallick (ed) Woodhead Publishing, pp 35-77
Wu X (2011) Advanced high-strength steel tailor welded blanks (AHSS-TWBs) in Tailor welded blanks for advanced manufacturing, B. L. Kinsey and X. Wu (ed). Woodhead Publishing, pp 118-163
Bhargava M, Tewari A, Mishra S (2015) Forming limit diagram of advanced high strength steels (AHSS) based on strain-path diagram. Mater Des 85:149–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.06.147
Shome M, Tumuluru M. (2015) Introduction to welding and joining of advanced high-strength steels (AHSS) in welding and joining of advanced high strength steels (AHSS), M. Shome and M. Tumuluru (ed) Woodhead Pulishing, Elsevier, UK pp 1-8
Shojaee M, Midawi ARH, Barber B, Ghassemi-Armaki H, Worswick M, Biro E (2021) Mechanical properties and failure behavior of resistance spot welded third-generation advanced high strength steels. J Manuf Process 65:364–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.03.047
Matlock DK, Speer JG (2009) Third generation of AHSS: microstructure design concepts in microstructure and texture in steels. Springer, London, pp 185–205
Li S, Yang S, Lu Q, Luo H, Tao W (2018) A novel shim-assisted resistance spot welding process to improve weldability of medium-mn transformation-induced plasticity steel. Metall Mater Trans B Process Metall Mater Process Sci 50:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-018-1463-9
Wan X, Wang Y, Zhang P (2014) Modelling the effect of welding current on resistance spot welding of DP600 steel. J Mater Process Technol 214:2723–2729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2014.06.009
Pouranvari M, Marashi SPH (2013) Critical review of automotive steels spot welding: process, structure and properties. Sci Technol Weld Join 18(361-403):20–403. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171813y.0000000120
Eshraghi M, Tschopp MA, Asle Zaeem M, Felicelli SD (2014) Effect of resistance spot welding parameters on weld pool properties in a DP600 dual-phase steel: a parametric study using thermomechanically-coupled finite element analysis. Mater Des 56:387–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.11.026
Bhattacharya D (2018) Liquid metal embrittlement during resistance spot welding of Zn-coated high-strength steels. Mater Sci Technol 34:1809–1829. https://doi.org/10.1080/02670836.2018.1461595
H. Zhang, Senkara J (2011) Electrothermal processes of welding in resistance welding: fundamentals and applications second ed. CRC Press pp 53-71
Kim JW, Murugan SP, Yoo J-H, Ashiri R, Park Y-D (2019) Enhancing nugget size and weldable current range of ultra-high-strength steel using multi-pulse resistance spot welding. Sci Technol Weld Join 25:235–242. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2019.1680483
Messler JRW, Jou M (1996) Review of control systems for resistance spot welding: past and current practices and emerging trends. Sci Technol Weld Join 1:1–9. 1996/02/01 1996. https://doi.org/10.1179/stw.1996.1.1.1
Rao SS, Chhibber R, Arora KS, Shome M (2017) Resistance spot welding of galvannealed high strength interstitial free steel. J Mater Process Technol 246:252–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.03.027
Luo Y, Rui W, Xie X, Zhu Y (2016) Study on the nugget growth in single-phase AC resistance spot welding based on the calculation of dynamic resistance. J Mater Process Technol 229:492–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.10.006
Podržaj P, Simončič S (2013) Resistance spot welding control based on the temperature measurement. Sci Technol Weld Join 18:551–557. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171813Y.0000000131
Vijayan V, Murugan S, Son S-G, Park YD (2019) Shrinkage void formation in resistance spot welds: its effect on advanced high-strength-steel weld strength and failure modes. J Mater Eng Perform 28:7514–7526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04465-6
Zhang H, Hu SJ, Senkara J, Cheng S (2000) A statistical analysis of expulsion limits in resistance spot welding. J Manuf Sci Eng 122:501–510
Jahandideh AR, Hamedi M, Mansourzadeh SA, Rahi A (2013) An experimental study on effects of post-heating parameters on resistance spot welding of SAPH440 steel. Sci Technol Weld Join 16:669–675. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171811y.0000000053
Feujofack Kemda BV, Barka N, Jahazi M, Osmani D (2020) Optimization of resistance spot welding process applied to A36 mild steel and hot dipped galvanized steel based on hardness and nugget geometry. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 106:2477–2491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04707-w
Doruk E, Pakdil M, Çam G, Durgun İ, Kumru U (2016) Resistance spot welding applications in automotive industry. Mühendis ve Makina 57:48–53 Retrieved from https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/muhendismakina/issue/49071/626131. Accessed 15 Aug 2021
Jaber HL, Pouranvari M, Salim RK, Hashim FA, Marashi SPH (2016) Peak load and energy absorption of DP600 advanced steel resistance spot welds. Ironmak Steelmak 44:699–706. https://doi.org/10.1080/03019233.2016.1229880
Wang W, Zhu Q, Liu C, Wei X (2018) An investigation on the resultant-based failure criterion for resistance spot welding joint in crush test. Int J Crashworthiness 24:152–162. https://doi.org/10.1080/13588265.2017.1421012
Pouranvari M, Sobhani S, Goodarzi F (2018) Resistance spot welding of MS1200 martensitic advanced high strength steel: microstructure-properties relationship. J Manuf Processes 31:867–874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.01.009
Chao Y (2003) Ultimate strength and failure mechanism of resistance spot weld subjected to tensile, shear, or combined tensile/shear loads. J Eng Mater Technol-trans Asme 125:125–132
Pouranvari M, Hoveida Marashi SP, Jaber HL (2015) DP780 dual-phase-steel spot welds: critical fusion-zone size ensuring the pull-out failure mode. Materiali in Tehnol 49:579–585. https://doi.org/10.17222/mit.2014.184
Mousavi Anijdan SH, Sabzi M, Ghobeiti-Hasab M, Roshan-Ghiyas A (2018) Optimization of spot welding process parameters in dissimilar joint of dual phase steel DP600 and AISI 304 stainless steel to achieve the highest level of shear-tensile strength. Mater Sci Eng A 726:120–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.04.072
Chao YJ, Wang K, Miller KW, Zhu XK (2009) Dynamic separation of resistance spot welded joints: part i-experiments. Exp Mech 50:889–900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-009-9276-z
Marashi P, Pouranvari M, Sanaee SMH, Abedi A, Abootalebi SH, Goodarzi M (2013) Relationship between failure behaviour and weld fusion zone attributes of austenitic stainless steel resistance spot welds. Mater Sci Technol 24:1506–1512. https://doi.org/10.1179/174328408x262418
Nikoosohbat F, Kheirandish S, Goodarzi M, Pouranvari M, Marashi SPH (2013) Microstructure and failure behaviour of resistance spot welded DP980 dual phase steel. Mater Sci Technol 26:738–744. https://doi.org/10.1179/174328409x414995
Pouranvari M (2013) Failure mode transition in similar and dissimilar resistance spot welds of HSLA and low carbon steels. Can Metall Q 51:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1179/1879139511y.0000000020
Khan MI, Kuntz ML, Zhou Y (2013) Effects of weld microstructure on static and impact performance of resistance spot welded joints in advanced high strength steels. Sci Technol Weld Join 13:294–304. https://doi.org/10.1179/174329308x271733
Pouranvari M (2012) Susceptibility to interfacial failure mode in similar and dissimilar resistance spot welds of DP600 dual phase steel and low carbon steel during cross-tension and tensile-shear loading conditions. Mater Sci Eng A 546:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.03.040
Gould J, Khurana S, Li T (2006) Predictions of microstructures when welding automotive advanced high-strength steels. Weld J 85:111S–116S
Chabok A, van der Aa E, De Hosson JTM, Pei YT (2017) Mechanical behavior and failure mechanism of resistance spot welded DP1000 dual phase steel. Mater Des 124:171–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.03.070
Mimer M, Svensson LE, Johansson R (2004) Process adjustments to improve fracture behaviour in resistance spot welds of ehss and uhss. Weld World 48:14–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03266421
Soomro IA, Pedapati SR, Awang M (2020) Optimization of postweld tempering pulse parameters for maximum load bearing and failure energy absorption in dual phase (DP590) steel resistance spot welds. Mater Sci Eng A 803:140713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.140713
Sajjadi-Nikoo S, Pouranvari M, Abedi A, Ghaderi AA (2017) In situ postweld heat treatment of transformation induced plasticity steel resistance spot welds. Sci Technol Weld Join 23:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2017.1323174
Tamizi M, Pouranvari M, Movahedi M (2021) The role of haz softening on cross-tension mechanical performance of martensitic advanced high strength steel resistance spot welds. Metall Mater Trans A 52:655–667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-020-06104-5
Baltazar Hernandez VH, Nayak SS, Zhou Y (2011) Tempering of martensite in dual-phase steels and its effects on softening behavior. Metall Mater Trans A 42:3115–3129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0739-3
Baltazar Hernandez VH, Panda SK, Kuntz ML, Zhou Y (2010) Nanoindentation and microstructure analysis of resistance spot welded dual phase steel. Mater Lett 64(207-210):2010–2210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2009.10.040
Baltazar Hernandez VH, Panda SK, Okita Y, Zhou NY (2009) A study on heat affected zone softening in resistance spot welded dual phase steel by nanoindentation. J Mater Sci 45:1638–1647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-4141-0
Biro E, Vignier S, Kaczynski C, Mcdermid JR, Lucas E, Embury JD, Zhou YN (2013) Predicting transient softening in the sub-critical heat-affected zone of dual-phase and martensitic steel welds. ISIJ Int 53:110–118. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.53.110
Nayak SS, Biro E, Zhou Y (2012) Resistance spot welding of dual-phase steels: heat affected zone softening and tensile properties. Trends in Welding Research, Proceedings of the 9th International Conference, Chicago, pp 641–649
Pouranvari M (2011) Effect of resistance spot welding parameters on the HAZ softening of DP980 ferrite-martensite dual phase steel welds. World Appl Sci J 15:1454–1458
Lu Y, Peer A, Abke T, Kimchi M, Zhang W (2018) Subcritical heat affected zone softening in hot-stamped boron steel during resistance spot welding. Mater Des 155:170–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2018.05.067
Biro E, McDermid JR, Embury JD, Zhou Y (2010) Softening kinetics in the subcritical heat-affected zone of dual-phase steel welds. Metall Mater Trans A 41:2348–2356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-010-0323-2
Nayak SS, Baltazar Hernandez VH, Zhou Y (2011) Effect of chemistry on nonisothermal tempering and softening of dual-phase steels. Metall Mater Trans A 42:3242–3248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0868-8
Arabi SH, Pouranvari M, Movahedi M (2018) Pathways to improve the austenite–ferrite phase balance during resistance spot welding of duplex stainless steels. Sci Technol Weld Join 24:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2018.1468949
Arabi S, Pouranvari M, Movahedi M (2017) Eelding metallurgy of duplex stainless steel during resistance spot welding. Weld J 96:307s–318s
Pouranvari M, Alizadeh-Sh M, Marashi SPH (2015) Welding metallurgy of stainless steels during resistance spot welding Part I: fusion zone. Sci Technol Weld Join 20:502–511. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171815y.0000000015
Duan R, Luo Z, Li Y, Zhang Y, Liu ZM (2014) Novel postweld heat treatment method for improving mechanical properties of resistance spot weld. Sci Technol Weld Join 20(100-105):2014–2105. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171814y.0000000262
Chao Y (2003) Failure mode of spot welds: interfacial versus pullout. Sci Technol Weld Join 8:133–137
Amirthalingam M, van der Aa EM, Kwakernaak C, Hermans MJM, Richardson IM (2015) Elemental segregation during resistance spot welding of boron containing advanced high strength steels. Weld World 59:743–755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-015-0250-3
Eftekharimilani P, van der Aa EM, Hermans MJM, Richardson IM (2017) The microstructural evolution and elemental distribution of a 3rd generation 1 GPa advanced high strength steel during double pulse resistance spot welding. Weld World 61:691–701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-017-0459-4
Joaquin A, Elliott AN, Jiang C (2007) Reducing shrinkage voids in resistance spot welds. Weld J 86:24–27
Zhao D, Wang Y, Liang D, Zhang P (2017) An investigation into weld defects of spot-welded dual-phase steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92:3043–3050. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0398-7
Saha DC, Chang I, Park YD (2014) Heat-affected zone liquation crack on resistance spot welded TWIP steels. Mater Charact 93:40–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2014.03.016
Kim YG, Kim IJ, Kim JS, Chung YI, Choi DY (2014) Evaluation of surface crack in resistance spot welds of zn-coated steel. Mater Trans 55:171–175. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.M2013244
Ghatei Kalashami A, DiGiovanni C, Razmpoosh MH, Goodwin F, Zhou NY (2020) The effect of silicon content on liquid-metal-embrittlement susceptibility in resistance spot welding of galvanized dual-phase steel. J Manuf Process 57:370–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.07.008
Wintjes E, DiGiovanni C, He L, Biro E, Zhou NY (2019) Quantifying the link between crack distribution and resistance spot weld strength reduction in liquid metal embrittlement susceptible steels. Weld World 63:807–814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-019-00712-5
He L, DiGiovanni C, Han X, Mehling C, Wintjes E, Biro E, Zhou NY (2019) Suppression of liquid metal embrittlement in resistance spot welding of TRIP steel. Sci Technol Weld Join 24:579–586. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2019.1573011
Ling Z, Wang M, Kong L, Chen K (2020) Towards an explanation of liquid metal embrittlement cracking in resistance spot welding of dissimilar steels. Mater Des 195:109055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.109055
Kim JU, Murugan SP, Kim JS, Yook W, Lee CY, Ji C, Jeon JB, Park YD (2021) Liquid metal embrittlement during the resistance spot welding of galvannealed steels: synergy of liquid Zn, α-Fe(Zn) and tensile stress. Sci Technol Weld Join 26:196–204. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2021.1880816
DiGiovanni C, Biro E, Zhou NY (2019) Impact of liquid metal embrittlement cracks on resistance spot weld static strength. Sci Technol Weld Join 24:218–224. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2018.1518363
Pouranvari M, Mousavizadeh SM, Marashi SPH, Goodarzi M, Ghorbani M (2011) Influence of fusion zone size and failure mode on mechanical performance of dissimilar resistance spot welds of AISI 1008 low carbon steel and DP600 advanced high strength steel. Mater Des 32:1390–1398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2010.09.010
Pouranvari M, Marashi SPH (2013) Key factors influencing mechanical performance of dual phase steel resistance spot welds. Sci Technol Weld Join 15:149–155. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217109x12590746472535
Tan N, Hong J, Lei M, Jin X, Zheng H, Luo Z (2020) Tensile-shear fracture behaviour of resistance spot-welded hot stamping sheet steel with Al–Si coating. Sci Technol Weld Join 25:525–534. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2020.1751404
Wakabayashi C, Furusako S, Miyazaki Y (2015) Strengthening spot weld joint by autotempering acceleration at heat affected zone. Sci Technol Weld Join 20:468–472. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171815Y.0000000023
(1997) Recommended practices for test methods for evaluating the resistance spot welding behavior of automotive sheet steel materials. D8.9M, AWS
(2017) Method of inspection and acceptance levels for resistance spot welds JIS Z 3140, J. I. Standards, Tokyo
(1989) Resistance spot welding DVS 2923, Düsseldorf Germany
Sheikhi M, Jaderian S, Mazaheri Y, Pouranvari M (2020) Prediction of the failure mode of automotive steels resistance spot welds. Sci Technol Weld Join 25:511–517. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2020.1747765
Pouranvari M, Marashi SPH, Safanama DS (2011) Failure mode transition in AHSS resistance spot welds. Part II: Experimental investigation and model validation. Mater Sci Eng A 528:8344–8352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.08.016
Pouranvari M, Marashi SPH (2011) Failure mode transition in AHSS resistance spot welds. Part I. Controlling factors. Mater Sci Eng A 528:8337–8343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.08.017
Pouranvari M, Marashi SPH (2013) Factors affecting mechanical properties of resistance spot welds. Mater Sci Technol 26:1137–1144. https://doi.org/10.1179/174328409x459301
Pouranvari M (2018) Understanding the factors controlling the interfacial failure strength of advanced high-strength steel resistance spot welds: hardness vs. fracture toughness. Sci Technol Weld Join 23:520–526. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2017.1421303
Aghajani H, Pouranvari M (2018) A pathway to produce strong and tough martensitic stainless steels resistance spot welds. Sci Technol Weld Join 24:185–192. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2018.1483065
Azhari-Saray H, Sarkari-Khorrami M, Nademi-Babahadi A, Kashani-Bozorg SF (2020) Dissimilar resistance spot welding of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy/St-12 carbon steel using a high entropy alloy interlayer. Intermet 124:106876 ISSN 0966-9795; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2020.106876
Pouranvari M (2017) Critical assessment 27: dissimilar resistance spot welding of aluminium/steel: challenges and opportunities. Mater Sci Technol 33:1705–1712. https://doi.org/10.1080/02670836.2017.1334310
Arghavani MR, Movahedi M, Kokabi AH (2016) Role of zinc layer in resistance spot welding of aluminium to steel. Mater Des 102:106–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.04.033
Feng Y, Li Y, Luo Z, Ling Z, Wang Z (2016) Resistance spot welding of Mg to electro-galvanized steel with hot-dip galvanized steel interlayer. J Mater Process Technol 236:114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.05.015
Oikawa H, Ohmiya S, Yoshimura T, Saitoh T (1999) Resistance spot welding of steel and aluminium sheet using insert metal sheet. Sci Technol Weld Join 4:80–88. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217199101537608
Ren D, Liu L (2014) Interface microstructure and mechanical properties of arc spot welding Mg–steel dissimilar joint with Cu interlayer. Mater Des 59:369–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.03.006
Fang Y, Jiang X, Mo D, Zhu D, Luo Z (2019) A review on dissimilar metals’ welding methods and mechanisms with interlayer. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 102:2845–2863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03353-6
Mookam N (2019) Optimization of resistance spot brazing process parameters in AHSS and AISI 304 stainless steel joint using filler metal. Def Technol 15:450–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dt.2019.03.005
Das T, Sahoo B, Kumar P, Paul J (2019) Effect of graphene interlayer on resistance spot welded AISI-1008 steel joints. Mater Res Expr 6:0865c3. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab23d6
Das T, Rawal S, Panda SK, Paul J (2021) Resistance spot-welding of AISI-1008 steel joints with MWCNT coating interlayer. Mater Manuf Process 36:448–456. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2020.1843667
Peterson W (1997) Dilution of weld metal to eliminate interfacial fractures of spot welds in high and ultra-high strength steels, presented at the International Conference. Advances in Welding Technology, Columbus
Li YB, Li DL, David SA, Lim YC, Feng Z (2016) Microstructures of magnetically assisted dual-phase steel resistance spot welds. Sci Technol Weld Join 21:555–563. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2016.1141493
Li Y (2013) Magnetically assisted resistance spot welding of dual-phase steel. Weld J 92:124S–132S
Huang M, Zhang Q, Qi L, Deng L, Li Y (2020) Effect of external magnetic field on resistance spot welding of aluminum alloy AA6061-T6. J Manuf Process 50:456–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.01.005
Li Y, Lin Z, Lai X, Chen G, Zhang K (2010) Induced electromagnetic stirring behavior in a resistance spot weld nugget. Sci China Technol Sci 53:1271–1277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-010-0086-4
Li Y, Luo Z, Bai Y, Ao SS (2013) Investigation of induced magnetic force on liquid nugget during resistance spot welding. Sci Technol Weld Join 18:329–336. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171813y.0000000110
Li Y, Luo Z, Yan F, Duan R, Yao Q (2014) Effect of external magnetic field on resistance spot welds of aluminum alloy. Mater Des 56:1025–1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.12.005
Li YB, Li DL, Lin ZQ, David SA, Feng Z, Tang W (2013) Review: magnetically assisted resistance spot welding. Sci Technol Weld Join 21:59–74. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171815y.0000000059
Li YB, Shen Q, Lin ZQ, Hu SJ (2013) Quality improvement in resistance spot weld of advanced high strength steel using external magnetic field. Sci Technol Weld Join 16:465–469. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171811y.0000000002
Li YB, Zhang QX, Qi L, David SA (2018) Improving austenitic stainless steel resistance spot weld quality using external magnetic field. Sci Technol Weld Join 23:619–627. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2018.1443997
Qi L, Li F, Chen R, Zhang Q, Li Y (2020) Improve resistance spot weld quality of advanced high strength steels using bilateral external magnetic field. J Manuf Process 52:270–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.02.030
Qi L, Li F, Zhang Q, Xu Y, Han X, Li Y (2021) Improvement of single-sided resistance spot welding of austenitic stainless steel using radial magnetic field. J Manuf Sci Eng 143:031004. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4048048
Shen Q, Li Y, Lin Z, Chen G (2011) Impact of external magnetic field on weld quality of resistance spot welding. J Manuf Sci Eng 133:051001. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4004794
Shen Q, Li YB, Lin ZQ, Chen GL (2011) Effect of external constant magnetic field on weld nugget of resistance spot welded dual-phase steel DP590. IEEE Trans Magn 47:4116–4119. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmag.2011.2157316
Yao Q, Luo Z, Li Y, Yan FY, Duan R (2014) Effect of electromagnetic stirring on the microstructures and mechanical properties of magnesium alloy resistance spot weld. Mater Des 63:200–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.06.004
Popov VA (1993) Effect of the magnetic field on the formation of the joint in resistance spot welding. Weld Int 7:905–907. https://doi.org/10.1080/09507119309548515
Li Y, Lin Z, Hu SJ, Chen G (2008) Magnetohydrodynamic behaviors in a resistance spot weld nugget under different welding currents. Sci. China Ser E Technol Sci 51:1507–1515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-008-0115-8
Villafuerte J, Kerr H (1990) Electromagnetic stirring and grain refinement in stainless steel GTA welds. Weld J 69:1–13
Watanabe Y, Takeda T, Sato H (2006) Effect of magnetic field on weld zone by spot welding in stainless steel. ISIJ Int 46:1292–1296. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.46.1292
Eftekharimilani P, van der Aa EM, Hermans MJM, Richardson IM (2017) Microstructural characterisation of double pulse resistance spot welded advanced high strength steel. Sci Technol Weld Join 22:545–554. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2016.1274848
Liu XD, Xu YB, Misra RDK, Peng F, Wang Y, Du YB (2019) Mechanical properties in double pulse resistance spot welding of Q&P 980 steel. J Mater Process Technol 263:186–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.08.018
Subrammanian A, Senthiil PV, Jabaraj DB, Devakumar D (2019) Improving mechanical performance of resistance spot welded joints of AISI 409M steel by double pulse current. Mater Today: Proc 16:949–955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.05.181
Zhong N, Liao X, Wang M, Wu Y, Rong Y (2011) Improvement of microstructures and mechanical properties of resistance spot welded dp600 steel by double pulse technology. Mater Trans 52(12):2143–2150. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.M2011135
Aghajani H, Pouranvari M (2019) Influence of in situ thermal processing strategies on the weldability of martensitic stainless steel resistance spot welds: effect of second pulse current on the weld microstructure and mechanical properties. Metall Mater Trans A 50:5191–5209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05443-2
Soomro IA, Pedapati SR (2019) Application of in situ post weld heat treatment using double pulse technology and its effect on microstructure and mechanical performance of resistance spot welded HSLA350 steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 105:3249–3260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04569-2
Soomro IA, Pedapati SR, Awang M (2021) Influence of in situ postweld heat treatment on microstructure and failure behavior of dual-phase steel resistance spot weld. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 114:3739–3750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07134-y
Lee HT, Chang YC (2020) Effect of double pulse resistance spot welding process on 15B22 hot stamped boron steel. Metals 10:1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10101279
Zhang Y, Fu C, Yi R, Ju J (2020) Optimization of double-pulse process in resistance spot welding of hot stamped steel sheet. ISIJ Int 60:1284–1290. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational
Chabok A, van der Aa E, Basu I, De Hosson J, Pei Y (2018) Effect of pulse scheme on the microstructural evolution, residual stress state and mechanical performance of resistance spot welded DP1000-GI steel. Sci Technol Weld Join 23(8):649–658. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2018.1452875
Stadler M, Gruber M, Schnitzer R, Hofer C (2019) Microstructural characterization of a double pulse resistance spot welded 1200 MPa TBF steel. Weld World 64:335–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-019-00835-9
E. M. Aa et al. (2015) Improved resistance spot weldability of 3rd generation ahss for automotive applications, in 11th International Seminar on Numerical Analysis of Weldability, Graz, Seggau, Austria, Sept 2015
Soomro IA, Pedapati SR (2020) Effect of multi pulse current treatment on microstructure and microhardness of resistance spot welded dual phase steel DP590. Mater Werkst 51:699–705. https://doi.org/10.1002/mawe.201900239
Wang B, Hua L, Wang X, Li J (2016) Effects of multi-pulse tempering on resistance spot welding of DP590 steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 86:2927–2935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8361-6
Soomro IA, Pedapati SR, Awang M (2021) Double pulse resistance spot welding of dual phase steel: parametric study on microstructure, failure mode and low dynamic tensile shear properties. Materials 14:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040802
Hernandez VB, Okita Y, Zhou Y (2012) Second pulse current in resistance spot welded TRIP steel-Effects on the microstructure and mechanical behavior. Weld J 91:278–285
Hajiannia I, Shamanian M, Atapour M, Ashiri R, Ghassemali E (2019) The assessment of second pulse effects on the microstructure and fracture behavior of the resistance spot welding in advanced ultrahigh-strength steel. TRIP1100. Iran J Mater Sci Eng 16:79–88. https://doi.org/10.22068/ijmse.16.2.79
Terekhov APIAA (2013) Mechanical properties of resistance spot welded joints in zinc-plated TRIP steel. Weld Int 28:324–328. https://doi.org/10.1080/09507116.2013.796684
Nikoosohbat F, Kheirandish S, Goodarzi M, Pouranvari M (2015) Effect of tempering on the microstructure and mechanical properties of resistance-spot-welded DP980 dual-phase steel. Mater Technol 49:133–138
Pouranvari M, Aghajani H, Ghasemi A (2019) Enhanced mechanical properties of martensitic stainless steels resistance spot welds enabled by in situ rapid tempering. Sci Technol Weld Join 25:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2019.1641962
Ashiri R, Shamanian M, Salimijazi HR, Haque MA, Bae JH, Ji CW, Chin KG, Park YD (2016) Liquid metal embrittlement-free welds of Zn-coated twinning induced plasticity steels. Scr Mater 114:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2015.11.027
Wintjes E, DiGiovanni C, He L, Bag S, Goodwin F, Biro E, Zhou Y (2019) Effect of multiple pulse resistance spot welding schedules on liquid metal embrittlement severity. J Manuf Sci Eng 141(10):101001. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4044099
Taniguchi K, Matsuda H, Ikeda R, Oi K (2016) Heat distribution in welds by short-time high-current post-heating and its improving effect on cross tension strength: development of resistance spot welding with pulsed current pattern for ultrahigh-strength steel sheets. Weld Int 30:817–825. https://doi.org/10.1080/09507116.2016.1142194
Sawanishi C, Ogura T, Taniguchi K, Ikeda R, Oi K, Yasuda K, Hirose A (2013) Mechanical properties and microstructures of resistance spot welded DP980 steel joints using pulsed current pattern. Sci Technol Weld Join 19:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171813y.0000000165
Chuko WL, Gould JE (2002) Development of appropriate resistance spot welding practice for transformation-hardened steels. A repeatable and effective methodology for producing a temper diagram for different steels is demonstrated. Weld J 81:1S–7S
Matsushita M, Taniguchi K, Oi K (2013) Development of next generation resistance spot welding technologies contributing to auto body weight reduction. JFE Tech Rep 18:111–117
Eftekharimilani P, van der Aa EM, Petrov R, Hermans MJM, Richardson IM (2018) Understanding the effect of a paint bake cycle on the microstructure–mechanical properties relationship of a resistance spot welded advanced high strength steel. Metall Mater Trans A 49:6185–6196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4912-9
Zhao B, Wang Y, Ding K, Wu G, Wei T, Pan H, Gao Y (2021) Enhanced cross-tension property of the resistance spot welded medium-mn steel by in situ microstructure tailoring. Int J Steel Struct 21:666–675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-021-00464-3
Wei ST, Lv D, Liu RD, Lin L, Xu RJ, Guo JY, Wang KQ (2014) Similar and dissimilar resistance spot welding of advanced high strength steels: welding and heat treatment procedures, structure and mechanical properties. Sci Technol Weld Join 19(427-435):2014–2435. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171814y.0000000211
Maki T (2012) Morphology and substructure of martensite in steels in Phase Transformations in Steels, pp 34-58
Hidalgo J, Santofimia MJ (2016) Effect of prior austenite grain size refinement by thermal cycling on the microstructural features of as-quenched lath martensite. Metall Mater Trans A 47:5288–5301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3525-4
Perlade A, Antoni A, Besson R, Caillard D, Callahan M, Emo J, Gourgues AF, Maugis P, Mestrallet A, Thuinet L, Tonizzo Q, Schmitt JH (2019) Development of 3rd generation medium Mn duplex steels for automotive applications. Mater Sci Technol 35:204–219. https://doi.org/10.1080/02670836.2018.1549303
Ling Z, Chen T, Kong L, Wang M, Pan H, Lei M (2019) Liquid metal embrittlement cracking during resistance spot welding of galvanized Q&P980 Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 50:5128–5142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05388-6
Takahashi M, Nakata M, Imai K, Kojima N, Otsuka N (2017) Liquid metal embrittlement of hot stamped galvannealed boron steel sheet-effect of heating time on crack formation. ISIJ Int 57:1094–1101. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2016-730
Murugan SP, Kim J, Kim J, Wan Y, Lee C, Jeon JB, Park YD (2020) Role of liquid Zn and α-Fe(Zn) on liquid metal embrittlement of medium Mn steel: An ex-situ microstructural analysis of galvannealed coating during high temperature tensile test. Surf Coat Technol 398:126069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.126069
Cheon JY, Vijayan V, Murgun S, Park YD, Kim JH, Yu JY, Ji C (2019) Optimization of pulsed current in resistance spot welding of Zn-coated hot-stamped boron steels. J Mech Sci Technol 33:1615–1621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-019-0313-2
DiGiovanni C, Bag S, Mehling C, Choi KW, Macwan A, Biro E, Zhou NY (2019) Reduction in liquid metal embrittlement cracking using weld current ramping. Weld World 63:1583–1591. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-019-00790-5
Funding
The authors received financial support from the Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS Malaysia through Graduate Research Assistantship and YUTP grant (015LC0-185).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soomro, I.A., Pedapati, S.R. & Awang, M. A review of advances in resistance spot welding of automotive sheet steels: emerging methods to improve joint mechanical performance. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 118, 1335–1366 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08002-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08002-5