Abstract
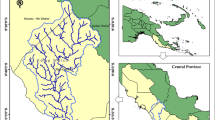
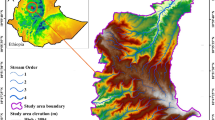
Dehradun city, capital of Uttarakhand state in India, is severely affected with increasing incidents of flooding, causing tremendous losses of life, infrastructure, and eroding years of development. This research aims to map flood hazard zones by conducting flood hazard assessment based on flood hazard index (FHI), which is constructed using 11 indicators, viz. elevation, slope, rainfall, LULC (land-use land-cover) runoff potential, and distance from drainage, drainage density, soil, geomorphology, geology, water table depth, and TWI (Total Wetness Index). The indicators are ranked and reclassified and then weighted using AHP (analytic hierarchy process) methodology. These are combined using weighted linear combination method in GIS (geographic information systems) with necessary inputs of weights of layers. Landsat8 OLI image of spatial resolution 30m, DEM 2015 of CARTOSAT-I of spatial resolution 2.5 m, and Survey of India (SOI) toposheets, scale 1:50,000, for Dehradun city are used for creating base layer and deriving indicators. The annual rainfall data of different rain gauge stations are interpolated in GIS to obtain rainfall map. As a result of final analysis, FHI is classified into 4 flood hazard zones spatially—very high risk with 29.51% area, high risk with 29.83% area, medium risk with 35.50 % area, and low risk with 5.16 % area. Thus, almost 59% of city areas are under high to very high risk. It is observed that the areas along Bindal and Rispana rivers are primarily at high risk. The results are validated by using ROC-AUC (area under the ROC curve) method using 151 high flood point samples spatially distributed well in the study area. As a further scope of research, number of socio-economic indicators may be added and flood risk assessment may be carried on. Also there is a scope of comparative assessment of other MCDA (multi-criteria decision analysis) methodologies to improve zonation accuracy in results.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelkarim A, Al-Alola SS, Alogayell HM, Mohamed SA, Alkadi II, Ismail IY (2020) Integration of GIS-based multicriteria decision analysis and analytic hierarchy process to assess flood hazard on the Al-Shamal train pathway in Al-Qurayyat region, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Water (Switzerland) 12(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/W12061702
Ahmad T, Pandey AC, Kumar A (2019) Evaluating urban growth and its implication on flood hazard and vulnerability in Srinagar City, Kashmir Valley, using geoinformatics. Arab J Geosci 12(9). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4458-1
Ahmadisharaf E, Tajrishy M, Alamdari N (2016) Integrating flood hazard into site selection of detention basins using spatial multi-criteria decision-making. J Environ Plann Manag 59(8):1397–1417. https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2015.1077104
Ajjur SB, Mogheir YK (2020) Flood hazard mapping using a multi-criteria decision analysis and GIS (case study Gaza Governorate, Palestine). Arab J Geosci 13(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-5024-6
Al-Juaidi AEM, Nassar AM, Al-Juaidi OEM (2018) Evaluation of flood susceptibility mapping using logistic regression and GIS conditioning factors. Arab J Geosci 11(24). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4095-0
Allafta H, Opp C (2021) GIS-based multi-criteria analysis for flood prone areas mapping in the trans-boundary Shatt Al-Arab Basin, Iraq-Iran. Geomat Nat Hazards Risk 12(1):2087–2116. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2021.1955755
Antony R, Abdu Rahiman KU, Vishnudas S (2022) Flood hazard mapping using geographical information system (GIS) and analytical hierarchy process (AHP). In: Kolathayar S, Mondal A, Chian SC (eds) . Springer Singapore, Singapore, pp 105–116
Armenakis, Costas, Erin Xinheng Du, Sowmya Natesan, Ravi Ancil Persad, Yong Ying Zhang, Huu Duy Nguyen, Dennis Fox, et al. 2020 “Flood vulnerability assessment using an integrated approach of multi-criteria decision-making model and geospatial techniques.” Edited by Ashraf Dewan and Robert Corner. Model Earth Syst Environ 12 (1): 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00997-2
Arora A, Pandey M, Siddiqui MA, Hong H, Mishra VN (2021) Spatial flood susceptibility prediction in Middle Ganga Plain: comparison of frequency ratio and Shannon’s entropy models. Geocarto Int 36(18):2085–2116. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2019.1687594
Asmat A, Hazali N, Sahak N, Tahir W, Ramli S (2021) Spatial rainfall rate estimation from multi-source data in Klang Valley, Malaysia. Int J Geoinform 17(2):1–8
Bansal N, Mukherjee M, Gairola A (2022) Evaluating Urban Flood Hazard Index (UFHI) of Dehradun City Using GIS and Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis. Model Earth Syst Environ, no. Talwar 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-021-01348-5
Cai S, Fan J, Yang W (2021) Flooding risk assessment and analysis based on GIS and the Tfn-Ahp method: a case study of Chongqing, China. Atmosphere 12(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050623
Central Ground Water Board. 2011 “Ground water brochure, District Dehradun, Uttarakhand.” http://cgwb.gov.in/District_Profile/Uttarakhand/Dehradun.pdf
Chen KF, Leandro J (2019) A conceptual time-varying flood resilience index for urban areas: Munich City. Water (Switzerland) 11(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040830
Costache R (2019) Flash-flood potential index mapping using weights of evidence, decision trees models and their novel hybrid integration. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 33(7):1375–1402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-019-01689-9
Costache R, Zaharia L (2017) Flash-flood potential assessment and mapping by integrating the weights-of-evidence and frequency ratio statistical methods in GIS environment – case study: Bâsca Chiojdului River catchment (Romania). J Earth Syst Sci 126(4):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-017-0828-9
CRED and UNISDR. 2015 “The Human Cost of Weather-Related Disasters 1995-2015.”
Dahri N, Abida H (2021) Hydrologic modeling and flood hydrograph reconstitution under an arid climate condition: case of Gabes Watershed, South-Eastern Tunisia. Environ Dev Sustain 24(8):10289–10308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01865-4
Dano UL, Balogun AL, Matori AN, Yusouf KW, Abubakar IR, Mohamed MAS, Aina YA, Pradhan B (2019) Flood susceptibility mapping using GIS-based analytic network process: a case study of Perlis, Malaysia. Water (Switzerland) 11(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030615
Danumah JH, Odai SN, Saley BM, Szarzynski J, Thiel M, Kwaku A, Kouame FK, Akpa LY (2016) Flood risk assessment and mapping in Abidjan district using multi-criteria analysis (AHP) model and geoinformation techniques, (Cote d’ivoire). Geoenviron Disasters 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40677-016-0044-y
Darabi H, Choubin B, Rahmati O, Haghighi AT, Pradhan B, Kløve B (2019) Urban flood risk mapping using the GARP and QUEST models: a comparative study of machine learning techniques. J Hydrol 569:142–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.12.002
Das S (2018) Geographic information system and AHP-based flood hazard zonation of Vaitarna Basin, Maharashtra, India. Arab J Geosci 11(19). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3933-4
Das S (2019) Geospatial mapping of flood susceptibility and hydro-geomorphic response to the floods in Ulhas Basin, India. Remote Sens Appl: Soc Environ 14:60–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2019.02.006
Dash P, Sar J (2020) Identification and validation of potential flood hazard area using GIS-based multi-criteria analysis and satellite data-derived water index. J Flood Risk Manag 13(3):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfr3.12620
Dung NB, Long NQ, An DT, Minh DT (2021) Multi-geospatial flood hazard modelling for a large and complex river basin with data sparsity: a case study of the Lam River Basin, Vietnam. Earth Syst Environ, no. Kieu 2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-021-00215-8
Ekmekcioğlu Ö, Koc K, Özger M (2022) Towards flood risk mapping based on multi-tiered decision making in a densely urbanized metropolitan city of Istanbul. Sustain Cities Soc 80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2022.103759
Ellis JB (2009) Managing Urban Runoff. In: In Handbook of Catchment Management, pp 155–182. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444307672.ch7
Falah F, Rahmati O, Rostami M, Ahmadisharaf E, Daliakopoulos IN, Pourghasemi HR (2019) Artificial neural networks for flood susceptibility mapping in data-scarce urban areas. In: Spatial Modeling in GIS and R for Earth and Environmental Sciences. Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-815226-3.00014-4
Feng B, Wang J, Zhang Y, Hall B, Zeng C (2020) Urban flood hazard mapping using a hydraulic–GIS combined model. Natural Hazards 100(3):1089–1104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-019-03850-7
Fernández DS, Lutz MA (2010a) Urban flood hazard zoning in Tucumán Province, Argentina, using GIS and multicriteria decision analysis. Eng Geol 111(1–4):90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.12.006
Fernández DS, Lutz MA (2010b) Urban flood hazard zoning in Tucumán Province, Argentina, using GIS and multicriteria decision analysis. Eng Geol J 8(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfr3.12715
Foudi S, Osés-Eraso N, Tamayo I (2015) Integrated spatial flood risk assessment: the case of Zaragoza. Land Use Policy 42:278–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2014.08.002
Franci F, Bitelli G, Mandanici E, Hadjimitsis D, Agapiou A (2016) Satellite remote sensing and GIS-based multi-criteria analysis for flood hazard mapping. Natural Hazards 83(1):31–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2504-9
Gigović L, Pamučar D, Bajić Z, Drobnjak S (2017) Application of GIS-interval rough AHP methodology for flood hazard mapping in urban areas. Water (Switzerland) 9(6):1–26. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9060360
Gourav P, Kumar R, Gupta A, Arif M (2020) Flood hazard zonation of Bhagirathi river basin using multi-criteria decision-analysis in Uttarakhand, India. Int J Emerg Technol 11(1):62–71
Guerriero L, Ruzza G, Guadagno FM, Revellino P (2020) Flood hazard mapping incorporating multiple probability models. J Hydrol 587:125020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125020
Gupta L, Dixit J (2022) A GIS-based flood risk mapping of Assam, India, using the MCDA-AHP approach at the regional and administrative level. Geocarto International, pp 1–33. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2022.2060329
Ha H, Bui QD, Nguyen HD, Pham BT, Lai TD, Luu C (2022a) A practical approach to flood hazard, vulnerability, and risk assessing and mapping for Quang Binh Province, Vietnam. Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-02041-4
Ha H, Bui QD, Nguyen HD, Pham BT, Lai TD, Luu C (2022b) A practical approach to flood hazard, vulnerability, and risk assessing and mapping for Quang Binh Province, Vietnam. Environ Dev Sustain (0123456789). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-02041-4
Hagos YG, Andualem TG, Yibeltal M, Mengie MA (2022) Flood hazard assessment and mapping using GIS integrated with multi-criteria decision analysis in Upper Awash River basin, Ethiopia. Appl Water Sci 12(7):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-022-01674-8
Hammami S, Dlala M, Zouhri L, Souissi D, Souei A, Zghibi A, Marzougui A (2019) Application of the GIS based multi-criteria decision analysis and analytical hierarchy process (AHP) in the flood susceptibility mapping (Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 12:1–16
Hazarika N, Barman D, Das AK, Sarma AK, Borah SB (2018) Assessing and mapping flood hazard, vulnerability and risk in the Upper Brahmaputra River valley using stakeholders’ knowledge and multicriteria evaluation (MCE). J Flood Risk Manag 11:S700–S716. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfr3.12237
Janizadeh S, Pal SC, Saha A, Chowdhuri I, Ahmadi K, Mirzaei S, Mosavi AH, Tiefenbacher JP (2021) Mapping the spatial and temporal variability of flood hazard affected by climate and land-use changes in the future. J Environ Manag 298:113551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113551
Jenks GF (1967) The data model concept in statistical mapping. International yearbook of cartography 7:186–190
JNNURM. 2007 “City Development Plan: Dehradun.”
Jung M, Kim J-G, Uranchimeg S (2020) The probabilistic estimation of inundation region using a multiple logistic regression analysis. J Korea Water Resour Assoc 53(2):121–130. https://doi.org/10.3741/JKWRA.2020.53.2.121
Kalantar B, Ueda N, Saeidi V, Janizadeh S, Shabani F, Ahmadi K, Shabani F (2021) Deep neural network utilizing remote sensing datasets for flood hazard susceptibility mapping in Brisbane, Australia. Remote Sens 13(13). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132638
Khaleghi S, Mahmoodi M (2017) Assessment of flood hazard zonation in a mountainous area based on GIS and analytical hierarchy process. Carpathian J Earth Environ Sci 12(1):311–322
Khosravi K, Nohani E, Maroufinia E, Pourghasemi HR (2016) A GIS-based flood susceptibility assessment and its mapping in Iran: a comparison between frequency ratio and weights-of-evidence bivariate statistical models with multi-criteria decision-making technique. Nat Hazards 83(2):947–987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2357-2
Kim TH, Kim B, Han KY (2019) Application of fuzzy TOPSIS to flood hazard mapping for levee failure. Water (Switzerland) 11(3):592. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030592
Koem C, Tantanee S (2021) Flash flood hazard mapping based on AHP with GIS and satellite information in Kampong Speu Province, Cambodia. Int J Disas Resil Built Environ 12(5):457–470. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJDRBE-09-2020-0099
Kongmuang C, Tantanee S, Seejata K (2020) Allocating Thailand more detailed postcode for health equity monitoring view project urban flood hazard map using GIS of Muang Sukhothai District, Thailand. Geogr Tech 15:143–152. https://doi.org/10.21163/GT_2020.151.13
Kordrostami S, Alim MA, Karim F, Rahman A (2020) Regional flood frequency analysis using an artificial neural network model. Geosciences (Switzerland) 10(4):1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10040127
Labib SM, Neema MN, Rahaman Z, Patwary SH, Shakil SH (2018) Carbon dioxide emission and bio-capacity indexing for transportation activities: a methodological development in determining the sustainability of vehicular transportation systems. J Environ Manag 223:57–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.06.010
Lee BJ, Kim S (2019) Gridded flash flood risk index coupling statistical approaches and TOPLATS land surface model for mountainous areas. Water (Switzerland) 11(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030504
Lin L, Wu Z, Liang Q (2019) Urban flood susceptibility analysis using a GIS-based multi-criteria analysis framework. Nat Hazards 97(2):455–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-019-03615-2
Liu R, Chen Y, Wu J, Gao L, Barrett D, Xu T, Li X, Li L, Huang C, Jia Y (2017) Integrating entropy-based naïve Bayes and GIS for spatial evaluation of flood hazard. Risk Anal 37(4):756–773. https://doi.org/10.1111/risa.12698
Liu WC, Hsieh TH, Liu HM (2021) Flood risk assessment in urban areas of southern Taiwan. Sustainability (Switzerland) 13(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/su13063180
Luu C, Von Meding J, Kanjanabootra S (2018) Assessing flood hazard using flood marks and analytic hierarchy process approach: a case study for the 2013 flood event in Quang Nam, Vietnam. Natural Hazards 90(3):1031–1050. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-3083-0
Lv H, Guan X, Meng Y (2020) Comprehensive evaluation of urban flood-bearing risks based on combined compound fuzzy matter-element and entropy weight model. Natural Hazards 103:1823–1841. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04056-y
Mahapatra SK, Obi Reddy GP, Ritu N, Yadav RP, Singh SK, Sharda VN (2018) Assessment of soil erosion in the fragile himalayan ecosystem of Uttarakhand, India using USLE and GIS for sustainable productivity. Curr Sci 115(1):108–121. https://doi.org/10.18520/cs/v115/i1/108-121
Malekinezhad H, Sepehri M, Pham QB, Hosseini SZ, Meshram SG, Vojtek M, Vojteková J (2021) Application of entropy weighting method for urban flood hazard mapping. Acta Geophysica (0123456789). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-021-00586-6
Manfreda S, Nardi F, Samela C, Grimaldi S, Taramasso AC, Roth G, Sole A (2014) Investigation on the use of geomorphic approaches for the delineation of flood prone areas. J Hydrol 517:863–876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.06.009
Maskong H (2019) Flood hazard mapping using on-site surveyed flood map, Hecras V.5 and GIS tool: a case study of Nakhon Ratchasima Municipality, Thailand. Int J Geomate 16(54):1–8. https://doi.org/10.21660/2019.54.81342
Meraj G, Romshoo SA, Yousuf AR, Altaf S, Altaf F (2015) Assessing the influence of watershed characteristics on the flood vulnerability of Jhelum basin in Kashmir Himalaya. Nat Hazards 77(1):153–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1605-1
Millet I, Saaty TL (2000) On the relativity of relative measures - accommodating both rank preservation and rank reversals in the AHP. Eur J Oper Res 121(1):205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(99)00040-5
Mishra K, Sinha R (2020) Flood risk assessment in the Kosi Megafan using multi-criteria decision analysis: a hydro-geomorphic approach. Geomorphology 350:106861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.106861
Morea H, Samanta S (2020) Multi-criteria decision approach to identify flood vulnerability zones using geospatial technology in the Kemp-Welch Catchment, Central Province, Papua New Guinea. Appl Geomat 12(4):427–440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-020-00315-6
Moussa R, Voltz M, Andrieux P (2002) Effects of the spatial organization of agricultural management on the hydrological behaviour of a farmed catchment during flood events. Hydrol Process 16(2):393–412. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.333
Mudashiru RB, Sabtu N, Abdullah R, Saleh A, Abustan I (2022) A comparison of three multi-criteria decision-making models in mapping flood hazard areas of Northeast Penang, Malaysia. Nat Hazards 112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-022-05250-w
Mussoorie Dehradun Development Authority (2005) Dehradun Master Plan 2005-2025. Offline Accessed 31 Dec 2018
Njoku JD, Amangabara GT, Duru PN (2013) Spatial Assessment of urban flood risks in aba metropolis, using geographical information systems technique. Glob Adv Res J Environ Sci Toxicol 2(3):86–92
Nkwunonwo UC, Whitworth M, Baily B (2020a) A review of the current status of flood modelling for urban flood risk management in the developing countries. Sci Afr 7:e00269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00269
Nkwunonwo UC, Whitworth M, Baily B, Büchele B, Kreibich H, Kron A, Thieken A et al (2020b) A review of the current status of flood modelling for urban flood risk management in the developing countries. Sci Afr 7(4):e00269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00269
North MA (2009) A method for implementing a statistically significant number of data classes in the Jenks algorithm. 6th Int Conf Fuzzy Syst Knowledge Discover FSKD 2009 1:35–38. https://doi.org/10.1109/FSKD.2009.319
Nsangou D, Kpoumié A, Mfonka Z, Ngouh AN, Fossi DH, Jourdan C, Mbele HZ, Mouncherou OF, Vandervaere JP, Ngoupayou JRN (2022) Urban flood susceptibility modelling using AHP and GIS approach: case of the Mfoundi watershed at Yaoundé in the South-Cameroon plateau. Sci Afr 15:e01043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2021.e01043
Ouma YO, Tateishi R (2014) Urban flood vulnerability and risk mapping using integrated multi-parametric AHP and GIS: methodological overview and case study assessment. Water (Switzerland) 6(6):1515–1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6061515
Parsian S, Amani M, Moghimi A, Ghorbanian A, Mahdavi S (2021) Flood hazard mapping using fuzzy logic, analytical hierarchy process, and multi-source geospatial datasets. Remote Sens 13(23). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234761
Pathan AI, Agnihotri PG, Said S, Patel D (2022) AHP and TOPSIS based flood risk assessment- a case study of the Navsari City, Gujarat, India. Environ Monit Assess 194(7):509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10111-x
Pham BT, Phong TV, Nguyen HD, Qi C, Al-Ansari N, Amini Ho LS (2020) A comparative study of kernel logistic regression, radial basis function classifier, multinomial naïve bayes, and logistic model tree for flash flood susceptibility mapping. Water 12(1):239
Popovska C (2010) Storm sewer system analysis in urban areas and flood risk assessment. Model Civil 1:1–7
Pourghasemi HR, Pradhan B, Gokceoglu C (2012) Application of fuzzy logic and analytical hierarchy process (AHP) to landslide susceptibility mapping at Haraz watershed, Iran. Nat Hazards 63(2):965–996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0217-2
Pradhan B, Hagemann U, Tehrany MS, Prechtel N (2014) An easy to use ArcMap based texture analysis program for extraction of flooded areas from TerraSAR-X satellite image. Comput Geosci 63:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2013.10.011
Qin CZ, Xing Zhu A, Pei T, Li BL, Scholten T, Behrens T, Zhou CH (2011) An approach to computing topographic wetness index based on maximum downslope gradient. Precis Agric 12(1):32–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-009-9152-y
Radwan F, Alazba AA, Mossad A (2019) Flood risk assessment and mapping using AHP in arid and semiarid regions. Acta Geophys 67(1):215–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-018-0233-z
Rahman M, Chen N, Islam MM, Mahmud GI, Pourghasemi HR, Alam M, Rahim MA, Baig MA, Bhattacharjee A, Dewan A (2021) Development of flood hazard map and emergency relief operation system using hydrodynamic modeling and machine learning algorithm. J Clean Prod 311:127594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127594
Rahmati O, Pourghasemi HR, Zeinivand H (2016a) Flood susceptibility mapping using frequency ratio and weights-of-evidence models in the Golastan Province, Iran. Geocarto Int 31(1):42–70. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2015.1041559
Rahmati O, Zeinivand H, Besharat M (2016b) Flood hazard zoning in Yasooj Region, Iran, using GIS and multi-criteria decision analysis. Geomat Nat Hazards Risk 7(3):1000–1017. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2015.1045043
Rehman J, Sohaib O, Asif M, Pradhan B (2019) Applying systems thinking to flood disaster management for a sustainable development. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 36:101101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2019.101101
Rubinato M, Nichols A, Peng Y, Zhang JM, Lashford C, Cai YP, Lin PZ, Tait S (2019) Urban and river flooding: comparison of flood risk management approaches in the UK and China and an assessment of future knowledge needs. Water Sci Eng 12(4):274–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wse.2019.12.004
Saaty TL, Vargas LG (1993) Experiments on rank preservation and reversal in relative measurement. Math Comput Model 17(4–5):13–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/0895-7177(93)90171-T
Saha AK, Agrawal S (2020) Mapping and assessment of flood risk in Prayagraj District, India: A GIS and remote sensing study. Nanotechnol Environ Eng 5(2):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41204-020-00073-1
Samanta S, Koloa C, Pal DK, Palsamanta B (2016) Flood risk analysis in lower part of markham river based on multi-criteria decision approach (MCDA). Hydrology 3(3):1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology3030029
Satty TL (1980) The Analytical Hierarchy Process: Planning, Priority Setting, Resource Allocation. McGraw-Hill, New York
Seejata K, Yodying A, Wongthadam T, Mahavik N, Tantanee S (2018) Assessment of flood hazard areas using analytical hierarchy process over the lower Yom Basin, Sukhothai Province. Proc Eng 212:340–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2018.01.044
Sepehri M, Malekinezhad H, Hosseini SZ, Ildoromi AR (2019) Assessment of flood hazard mapping in urban areas using entropy weighting method: a case study in Hamadan City, Iran. Acta Geophys 67(5):1435–1449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-019-00342-x
Shivaprasad Sharma SV, Roy PS, Chakravarthi V, Srinivasa Rao G (2018) Flood risk assessment using multi-criteria analysis: a case study from Kopili River Basin, Assam, India. Geomat Nat Hazards Risk 9(1):79–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2017.1408705
Siahkamari S, Haghizadeh A, Zeinivand H, Tahmasebipour N, Rahmati O (2018) Spatial prediction of flood-susceptible areas using frequency ratio and maximum entropy models. Geocarto Int 33(9):927–941. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2017.1316780
Sinha S, Sinha R (2016) Geomorphic evolution of Dehra Dun, NW Himalaya: tectonics and climatic coupling. Geomorphology 266:20–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.05.002
Sørensen R, Zinko U, Seibert J (2006) On the calculation of the topographic wetness index: evaluation of different methods based on field observations. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 10(1):101–112. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-10-101-2006
Swain KC, Singha C, Nayak L (2020) Flood susceptibility mapping through the GIS-AHP technique using the cloud. ISPRS Int J Geo-Inform 9(12):720. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9120720
Tang Z, Yi S, Wang C, Xiao Y (2018) Incorporating probabilistic approach into local multi-criteria decision analysis for flood susceptibility assessment. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 32(3):701–714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-017-1431-y
Tehrany MS, Lee MJ, Pradhan B, Jebur MN, Lee S (2014) Flood susceptibility mapping using integrated bivariate and multivariate statistical models. Environ Earth Sci 72(10):4001–4015. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3289-3
Triantaphyllou E, Mann SH (1995) Using the analytic hierarchy process for decision making in engineering applications: some challenges. Int J Ind Eng: Theory, Appl Pract 2(1):35–44
Urban Development Department - Government of Uttarakhand (2007) City Development Plan : Dehradun Revised (Issue May 2007) under JNNURM Mission. http://udd.uk.gov.in/files/CDP_DDUN.PDF. Accessed 31 Dec 2018
Vahidnia MH, Alesheikh AA, Alimohammadi A, Hosseinali F (2009) Design and development of an intelligent extension for mapping landslide susceptibility using artificial neural network. In: Computational Science and Its Applications–ICCSA 2009: International Conference, Seoul, Korea, June 29-July 2, 2009, Proceedings, Part I 9. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 17–32
Vaishnavi B, Kiran Y, Karthikeyan J, Thirumalai C (2017) An assessment framework for precipitation decision making using AHP. In: Proceedings of 2017 11th International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Control, ISCO 2017. IEEE, pp 418–421. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCO.2017.7856030
Van Westen CJ, Montoya L, Boerboom L, Coto EB (2002) Multi-hazard risk assessment using GIS in urban areas: a case study for the city of Turrialba, Costa Rica. Proc. Regional workshop on Best Practise in Disaster Mitigation, Bali, pp 120–136. https://ris.utwente.nl/ws/portalfiles/portal/6147961/multihazard_risk_assessment.pdf
Varo J, Sekac T, Jana SK (2020) Flood hazard micro zonation from a Geomatic perspective on Vitilevu Island, Fiji. Int J Geoinform 16(3):37–47
Vazhuthi HI, Kumar A (2020) Causes and impacts of urban floods in Indian cities: a review. Int J Emerg Technol 11(4):140–147
Vishwanath VH, Tomaszewski B (2018) Flood hazard, vulnerability and risk assessments for Uttarakhand State in India. In: Proceedings of the International ISCRAM Conference 2018. ISCRAM, pp 362–375
Zhao G, Xu Z, Pang B, Tongbi T, Xu L, Longgang D (2019) An enhanced inundation method for urban flood hazard mapping at the large catchment scale. J Hydrol 571:873–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.02.008
Zhu H, Liu F (2021) A group-decision-making framework for evaluating urban flood resilience: a case study in Yangtze River. Sustainability (Switzerland) 13(2):1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020665
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Biswajeet Pradhan
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bansal, N., Mukherjee, M. & Gairola, A. GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis for mapping flood-prone areas in Dehradun city, India. Arab J Geosci 16, 501 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11605-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11605-9