Abstract
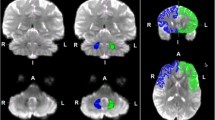
The objective of this study was to identify the decussating dentato-rubro-thalamic tract (d-DRTT) and its afferent and efferent connections in healthy humans using diffusion spectrum imaging (DSI) techniques. In the present study, the trajectory and lateralization of the d-DRTT was explored using data from subjects in the Massachusetts General Hospital-Human Connectome Project adult diffusion dataset. The afferent and efferent networks that compose the cerebello-thalamo-cerebral pathways were also reconstructed. Correlation analysis was performed to identify interrelationships between subdivisions of the cerebello-dentato-rubro-thalamic and thalamo-cerebral connections. The d-DRTT was visualized bilaterally in 28 subjects. According to a normalized quantitative anisotropy and lateralization index evaluation, the left and right d-DRTT were relatively symmetric. Afferent regions were found mainly in the posterior cerebellum, especially the entire lobule VII (crus I, II and VIIb). Efferent fibers mainly are projected to the contralateral frontal cortex, including the motor and nonmotor regions. Correlations between cerebello-thalamic connections and thalamo-cerebral connections were positive, including the lobule VIIa (crus I and II) to the medial prefrontal cortex (MPFC) and the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and lobules VI, VIIb, VIII, and IX, to the MPFC and motor and premotor areas. These results provide DSI-based tratographic evidence showing segregated and parallel cerebellar outputs to cerebral regions. The posterior cerebellum may play an important role in supporting and handling cognitive activities through d-DRTT. Future studies will allow for a more comprehensive understanding of cerebello-cerebral connections.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kelly RM, Strick PL. Cerebellar loops with motor cortex and prefrontal cortex of a nonhuman primate. J Neurosci. 2003;23:8432–44.
Stoodley CJ, Schmahmann JD. Functional topography of the human cerebellum. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;154:59–70.
Ji Q, Edwards A, Glass JO, Brinkman TM, Patay Z, Reddick WE. Measurement of Projections Between Dentate Nucleus and Contralateral Frontal Cortex in Human Brain Via Diffusion Tensor Tractography. Cerebellum. 2019;18:761–9.
Petersen KJ, Reid JA, Chakravorti S, Juttukonda MR, Franco G, Trujillo P, et al. Structural and functional connectivity of the nondecussating dentato-rubro-thalamic tract. Neuroimage. 2018;176:364–71.
Kwon HG, Hong JH, Hong CP, Lee DH, Ahn SH, Jang SH. Dentatorubrothalamic tract in human brain: diffusion tensor tractography study. Neuroradiology. 2011;53:787–91.
van Baarsen K, Kleinnijenhuis M, Konert T, van Cappellen van Walsum AM, Grotenhuis A. Tractography demonstrates dentate-rubro-thalamic tract disruption in an adult with cerebellar mutism. Cerebellum. 2013;12:617–22.
Gallay MN, Jeanmonod D, Liu J, Morel A. Human pallidothalamic and cerebellothalamic tracts: anatomical basis for functional stereotactic neurosurgery. Brain Struct Funct. 2008;212:443–63.
Middleton FA, Strick PL. Cerebellar output: motor and cognitive channels. Trends Cogn Sci. 1998;2:348–54.
Bostan AC, Dum RP, Strick PL. Cerebellar networks with the cerebral cortex and basal ganglia. Trends Cogn Sci. 2013;17:241–54.
Hoover JE, Strick PL. The organization of cerebellar and basal ganglia outputs to primary motor cortex as revealed by retrograde transneuronal transport of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Neurosci. 1999;19:1446–63.
Middleton FA, Strick PL. Cerebellar projections to the prefrontal cortex of the primate. J Neurosci. 2001;21:700–12.
Schmahmann JD, Guell X, Stoodley CJ, Halko MA. The Theory and Neuroscience of Cerebellar Cognition. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2019;42:337–64.
Salmi J, Pallesen KJ, Neuvonen T, Brattico E, Korvenoja A, Salonen O, et al. Cognitive and motor loops of the human cerebro-cerebellar system. J Cogn Neurosci. 2010;22:2663–76.
Fernandez-Miranda JC, Rhoton AL, Alvarez-Linera J, Kakizawa Y, Choi C, de Oliveira EP. Three-dimensional microsurgical and tractographic anatomy of the white matter of the human brain. Neurosurgery. 2008;62:989–1026 discussion 1026-1028.
Salamon N, Sicotte N, Drain A, Frew A, Alger JR, Jen J, et al. White matter fiber tractography and color mapping of the normal human cerebellum with diffusion tensor imaging. J Neuroradiol. 2007;34:115–28.
Fernandez-Miranda JC, Pathak S, Engh J, Jarbo K, Verstynen T, Yeh FC, et al. High-definition fiber tractography of the human brain: neuroanatomical validation and neurosurgical applications. Neurosurgery. 2012;71:430–53.
Alexander DC, Barker GJ. Optimal imaging parameters for fiber-orientation estimation in diffusion MRI. Neuroimage. 2005;27:357–67.
Le Bihan D, Poupon C, Amadon A, Lethimonnier F. Artifacts and pitfalls in diffusion MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2006;24:478–88.
Mollink J, van Baarsen KM, Dederen PJ, Foxley S, Miller KL, Jbabdi S, et al. Dentatorubrothalamic tract localization with postmortem MR diffusion tractography compared to histological 3D reconstruction. Brain Struct Funct. 2016;221:3487–501.
Behrens TE, Johansen-Berg H, Woolrich MW, Smith SM, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Boulby PA, et al. Non-invasive mapping of connections between human thalamus and cortex using diffusion imaging. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:750–7.
Karavasilis E, Christidi F, Velonakis G, Giavri Z, Kelekis NL, Efstathopoulos EP, et al. Ipsilateral and contralateral cerebro-cerebellar white matter connections: A diffusion tensor imaging study in healthy adults. J Neuroradiol. 2019;46:52–60.
Tournier JD, Calamante F, Connelly A. Robust determination of the fibre orientation distribution in diffusion MRI: non-negativity constrained super-resolved spherical deconvolution. Neuroimage. 2007;35:1459–72.
Palesi F, Tournier JD, Calamante F, Muhlert N, Castellazzi G, Chard D, et al. Contralateral cerebello-thalamo-cortical pathways with prominent involvement of associative areas in humans in vivo. Brain Struct Funct. 2015;220:3369–84.
Jeong JW, Chugani DC, Behen ME, Tiwari VN, Chugani HT. Altered white matter structure of the dentatorubrothalamic pathway in children with autistic spectrum disorders. Cerebellum. 2012;11:957–71.
van Baarsen KM, Kleinnijenhuis M, Jbabdi S, Sotiropoulos SN, Grotenhuis JA, van Cappellen van Walsum AM. A probabilistic atlas of the cerebellar white matter. Neuroimage. 2016;124:724–32.
Wedeen VJ, Hagmann P, Tseng WY, Reese TG, Weisskoff RM. Mapping complex tissue architecture with diffusion spectrum magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2005;54:1377–86.
Van AT, Granziera C, Bammer R. An introduction to model-independent diffusion magnetic resonance imaging. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;21:339–54.
Wang ZM, Wei PH, Shan Y, Han M, Zhang M, Liu H, et al. Identifying and characterizing projections from the subthalamic nucleus to the cerebellum in humans. Neuroimage. 2020;210:116573.
Granziera C, Schmahmann JD, Hadjikhani N, Meyer H, Meuli R, Wedeen V, et al. Diffusion spectrum imaging shows the structural basis of functional cerebellar circuits in the human cerebellum in vivo. PLoS One. 2009;4:e5101.
Fan Q, Witzel T, Nummenmaa A, Van Dijk KRA, Van Horn JD, Drews MK, et al. MGH-USC Human Connectome Project datasets with ultra-high b-value diffusion MRI. Neuroimage. 2016;124:1108–14.
McNab JA, Edlow BL, Witzel T, Huang SY, Bhat H, Heberlein K, et al. The Human Connectome Project and beyond: initial applications of 300 mT/m gradients. Neuroimage. 2013;80:234–45.
Setsompop K, Kimmlingen R, Eberlein E, Witzel T, Cohen-Adad J, McNab JA, et al. Pushing the limits of in vivo diffusion MRI for the Human Connectome Project. Neuroimage. 2013;80:220–33.
Yeh FC, Tseng WY. NTU-90: a high angular resolution brain atlas constructed by q-space diffeomorphic reconstruction. Neuroimage. 2011;58:91–9.
Yeh FC, Wedeen VJ, Tseng WY. Generalized q-sampling imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2010;29:1626–35.
Diedrichsen J, Maderwald S, Küper M, Thürling M, Rabe K, Gizewski ER, et al. Imaging the deep cerebellar nuclei: a probabilistic atlas and normalization procedure. Neuroimage. 2011;54:1786–94.
Akakin A, Peris-Celda M, Kilic T, Seker A, Gutierrez-Martin A, Rhoton A. The dentate nucleus and its projection system in the human cerebellum: the dentate nucleus microsurgical anatomical study. Neurosurgery. 2014;74:401–24 discussion 424-405.
Yeh FC, Verstynen TD, Wang Y, Fernández-Miranda JC, Tseng WY. Deterministic diffusion fiber tracking improved by quantitative anisotropy. PLoS One. 2013;8:e80713.
Diedrichsen J. A spatially unbiased atlas template of the human cerebellum. Neuroimage. 2006;33:127–38.
Piervincenzi C, Petrilli A, Marini A, Caulo M, Committeri G, Sestieri C. Multimodal assessment of hemispheric lateralization for language and its relevance for behavior. Neuroimage. 2016;142:351–70.
Fan L, Li H, Zhuo J, Zhang Y, Wang J, Chen L, et al. The Human Brainnetome Atlas: A New Brain Atlas Based on Connectional Architecture. Cereb Cortex. 2016;26:3508–26.
Yamada K, Akazawa K, Yuen S, Goto M, Matsushima S, Takahata A, et al. MR imaging of ventral thalamic nuclei. AJNR. 2010;31:732–5.
Coenen VA, Allert N, Paus S, Kronenbürger M, Urbach H, Mädler B. Modulation of the cerebello-thalamo-cortical network in thalamic deep brain stimulation for tremor: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Neurosurgery. 2014;75:657–69 discussion 669-670.
Tuch DS. Q-ball imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2004;52:1358–72.
Stoodley CJ, Schmahmann JD. Functional topography in the human cerebellum: a meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Neuroimage. 2009;44:489–501.
Stoodley CJ. The cerebellum and cognition: evidence from functional imaging studies. Cerebellum. 2012;11:352–65.
Kim Y, Im S, Kim SH, Park GY. Laterality of cerebellar afferent and efferent pathways in a healthy right-handed population: A diffusion tensor imaging study. J Neurosci Res. 2019;97:582–96.
Fornito A, Zalesky A, Breakspear M. Graph analysis of the human connectome: promise, progress, and pitfalls. Neuroimage. 2013;80:426–44.
O'Reilly JX, Beckmann CF, Tomassini V, Ramnani N, Johansen-Berg H. Distinct and overlapping functional zones in the cerebellum defined by resting state functional connectivity. Cereb Cortex. 2010;20:953–65.
Guell X, Schmahmann JD, Gabrieli J, Ghosh SS. Functional gradients of the cerebellum. Elife. 2018;7:e36652.
Krienen FM, Buckner RL. Segregated fronto-cerebellar circuits revealed by intrinsic functional connectivity. Cereb Cortex. 2009;19:2485–97.
Abe M, Hanakawa T. Functional coupling underlying motor and cognitive functions of the dorsal premotor cortex. Behav Brain Res. 2009;198:13–23.
Schubotz RI, Anwander A, Knösche TR, von Cramon DY, Tittgemeyer M. Anatomical and functional parcellation of the human lateral premotor cortex. Neuroimage. 2010;50:396–408.
Dum RP, Strick PL. An unfolded map of the cerebellar dentate nucleus and its projections to the cerebral cortex. J Neurophysiol. 2003;89:634–9.
Schulz R, Wessel MJ, Zimerman M, Timmermann JE, Gerloff C, Hummel FC. White Matter Integrity of Specific Dentato-Thalamo-Cortical Pathways is Associated with Learning Gains in Precise Movement Timing. Cereb Cortex. 2015;25:1707–14.
Raichle ME, MacLeod AM, Snyder AZ, Powers WJ, Gusnard DA, Shulman GL. A default mode of brain function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:676–82.
Andrews-Hanna JR, Smallwood J, Spreng RN. The default network and self-generated thought: component processes, dynamic control, and clinical relevance. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2014;1316:29–52.
Buckner RL, Krienen FM, Castellanos A, Diaz JC, Yeo BT. The organization of the human cerebellum estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity. J Neurophysiol. 2011;106:2322–45.
Hu D, Shen H, Zhou Z. Functional asymmetry in the cerebellum: a brief review. Cerebellum. 2008;7:304–13.
Schmahmann JD. The cerebellum and cognition. Neurosci Lett. 2019;688:62–75.
Strata P, Provini L, Redman S. On the concept of spinocerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:E622 author reply E623.
Makris N, Schlerf JE, Hodge SM, Haselgrove C, Albaugh MD, Seidman LJ, et al. MRI-based surface-assisted parcellation of human cerebellar cortex: an anatomically specified method with estimate of reliability. Neuroimage. 2005;25:1146–60.
Balsters JH, Cussans E, Diedrichsen J, Phillips KA, Preuss TM, Rilling JK, et al. Evolution of the cerebellar cortex: the selective expansion of prefrontal-projecting cerebellar lobules. Neuroimage. 2010;49:2045–52.
Sereno MI, Diedrichsen J, Tachrount M, Testa-Silva G, d'Arceuil H, De Zeeuw C. The human cerebellum has almost 80% of the surface area of the neocortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117:19538–43.
Steele CJ, Anwander A, Bazin PL, Trampel R, Schaefer A, Turner R, et al. Human Cerebellar Sub-millimeter Diffusion Imaging Reveals the Motor and Non-motor Topography of the Dentate Nucleus. Cereb Cortex. 2017;27:4537–48.
Bernard JA, Peltier SJ, Benson BL, Wiggins JL, Jaeggi SM, Buschkuehl M, et al. Dissociable functional networks of the human dentate nucleus. Cereb Cortex. 2014;24:2151–9.
Middleton FA, Strick PL. Cerebellar output channels. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1997;41:61–82.
Bullmore E, Sporns O. Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10:186–98.
Sarwar T, Ramamohanarao K, Zalesky A. Mapping connectomes with diffusion MRI: deterministic or probabilistic tractography? Magn Reson Med. 2019;81:1368–84.
Acknowledgments
Data were provided by the Human Connectome Project, MGH-USC Consortium (principal investigators: Bruce R. Rosen, Arthur W. Toga and Van Wedeen; U01MH093765), funded by the NIH Blueprint Initiative for Neuroscience Research grant; the National Institutes of Health grant P41EB015896; and the Instrumentation grants S10RR023043, 1S10RR023401, and 1S10RR019307.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Fig. S1
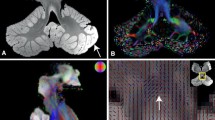
Major afferent and efferent fibers of the left cerebellar lobules. a The left cerebellar anterior lobe was connected with the spinal cord and brainstem through the ICP. b-c The cortico-ponto-cerebellar afferents from contralateral cerebrum projected to the cerebellar anterior lobe through the MCP. d-e The efferents of d-DRTT from the cerebellar anterior lobe were the minority. f The efferents of ipsilateral CTC tracts passing through the SCP were much more in number than the decussating counterparts. g-h For the left cerebellar hemisphere, the fibers from the posterior lobe projecting to the motor and premotor cerebral cortex through d-DRTT were much more than the fibers from the anterior lobe. ICP, inferior cerebellar peduncle; MCP, middle cerebellar peduncle; d-DRTT, decussating dentato-rubro-thalamic tract; CTC, cerebello-thalamo-cerebral; SCP, superior cerebellar peduncle. (PNG 1337 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ou, SQ., Wei, PH., Fan, XT. et al. Delineating the Decussating Dentato-rubro-thalamic Tract and Its Connections in Humans Using Diffusion Spectrum Imaging Techniques. Cerebellum 21, 101–115 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-021-01283-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-021-01283-2