Abstract
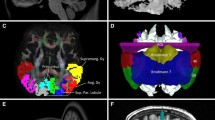
We propose a probabilistic fiber-tracking scheme to reconstruct the fiber tracts between the dentate nucleus (DN) in the cerebellum and the entire contralateral cerebral frontal cortex in the human brain. We assessed diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) data from 39 healthy controls. The connection fibers between the DN and contralateral frontal cortex of all subjects were successfully reconstructed and studied. We demonstrated that multi-fiber probabilistic models must be used to resolve the challenge of crossing fibers. We also demonstrated that the entire pathway can be reconstructed without using any synaptic regions of interest along the path and that the reconstructed tracts connected the ipsilateral superior cerebellar peduncle, contralateral red nucleus, and ventral lateral and ventral anterior nuclei of thalamus in the path traveling to the contralateral frontal cortex. The fibers in the pathway projected into all areas of the contralateral frontal cortex but were predominantly located in the primary motor and premotor areas. A large portion of fibers terminated in the prefrontal cortex, which included dorsolateral prefrontal areas, anterior prefrontal areas, and the Broca language area. Our findings provide robust, reproducible, and direct DTI-based evidence that the DN through the efferent cerebellar pathway has considerable contribution to high-level executive functions of the human brain.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patay Z, Enterkin J, Harreld JH, Yuan Y, Lobel U, Rumboldt Z, et al. MR imaging evaluation of inferior olivary nuclei: comparison of postoperative subjects with and without posterior fossa syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014;35(4):797–802.
Middleton FA, Strick PL. Cerebellar output: motor and cognitive channels. Trends Cogn Sci. 1998;2(9):348–54.
Schmahmann JD. The cerebellum and cognition. Neurosci Lett. 2019;688:62–75.
van Baarsen K, Kleinnijenhuis M, Konert T, Cappellen v, van Walsum AM, Grotenhuis A. Tractography demonstrates dentate-rubro-thalamic tract disruption in an adult with cerebellar mutism. Cerebellum. 2013;12(5):617–22.
Oh ME, Driever PH, Khajuria RK, Rueckriegel SM, Koustenis E, Bruhn H, et al. DTI fiber tractography of cerebro-cerebellar pathways and clinical evaluation of ataxia in childhood posterior fossa tumor survivors. J Neuro-Oncol. 2017;131(2):267–76.
Avula S, Mallucci C, Kumar R, Pizer B. Posterior fossa syndrome following brain tumour resection: review of pathophysiology and a new hypothesis on its pathogenesis. Childs Nerv Syst. 2015;31(10):1859–67.
Gudrunardottir T, Morgan AT, Lux AL, Walker DA, Walsh KS, Wells EM, et al. Consensus paper on post-operative pediatric cerebellar mutism syndrome: the Iceland Delphi results. Childs Nerv Syst. 2016;32(7):1195–203.
Miller NG, Reddick WE, Kocak M, Glass JO, Lobel U, Morris B, et al. Cerebellocerebral diaschisis is the likely mechanism of postsurgical posterior fossa syndrome in pediatric patients with midline cerebellar tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31(2):288–94.
Schuepbach WM, Rau J, Knudsen K, Volkmann J, Krack P, Timmermann L, et al. Neurostimulation for Parkinson's disease with early motor complications. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(7):610–22.
Flora ED, Perera CL, Cameron AL, Maddern GJ. Deep brain stimulation for essential tremor: a systematic review. Mov Disord. 2010;25(11):1550–9.
Schlaier JR, Beer AL, Faltermeier R, Fellner C, Steib K, Lange M, et al. Probabilistic vs. deterministic fiber tracking and the influence of different seed regions to delineate cerebellar-thalamic fibers in deep brain stimulation. Eur J Neurosci. 2017;45(12):1623–33.
Lehericy S, Grand S, Pollak P, Poupon F, Le Bas JF, Limousin P, et al. Clinical characteristics and topography of lesions in movement disorders due to thalamic lesions. Neurology. 2001;57(6):1055–66.
Marx JJ, Iannetti GD, Thomke F, Fitzek S, Galeotti F, Truini A, et al. Topodiagnostic implications of hemiataxia: an MRI-based brainstem mapping analysis. Neuroimage. 2008;39(4):1625–32.
Mori S, Crain BJ, Chacko VP, van Zijl PC. Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol. 1999;45(2):265–9.
Kwon HG, Hong JH, Hong CP, Lee DH, Ahn SH, Jang SH. Dentatorubrothalamic tract in human brain: diffusion tensor tractography study. Neuroradiology. 2011;53(10):787–91.
Behrens TE, Johansen-Berg H, Woolrich MW, Smith SM, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Boulby PA, et al. Non-invasive mapping of connections between human thalamus and cortex using diffusion imaging. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6(7):750–7.
Sun C, Wang Y, Cui R, Wu C, Li X, Bao Y, et al. Human thalamic-prefrontal peduncle connectivity revealed by diffusion spectrum imaging fiber tracking. Front Neuroanat. 2018;12:24.
Law N, Greenberg M, Bouffet E, Laughlin S, Taylor MD, Malkin D, et al. Visualization and segmentation of reciprocal cerebrocerebellar pathways in the healthy and injured brain. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015;36(7):2615–28.
Palesi F, Tournier JD, Calamante F, Muhlert N, Castellazzi G, Chard D, et al. Contralateral cerebello-thalamo-cortical pathways with prominent involvement of associative areas in humans in vivo. Brain Struct Funct. 2015;220(6):3369–84.
Kamali A, Kramer LA, Frye RE, Butler IJ, Hasan KM. Diffusion tensor tractography of the human brain cortico-ponto-cerebellar pathways: a quantitative preliminary study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;32(4):809–17.
Karavasilis E, Christidi F, Velonakis G, Giavri Z, Kelekis NL, Efstathopoulos EP, et al. Ipsilateral and contralateral cerebro-cerebellar white matter connections: a diffusion tensor imaging study in healthy adults. J Neuroradiol. 2018.
Tournier JD, Calamante F, Connelly A. Robust determination of the fibre orientation distribution in diffusion MRI: non-negativity constrained super-resolved spherical deconvolution. Neuroimage. 2007;35(4):1459–72.
Jeong JW, Chugani DC, Behen ME, Tiwari VN, Chugani HT. Altered white matter structure of the dentatorubrothalamic pathway in children with autistic spectrum disorders. Cerebellum. 2012;11(4):957–71.
Granziera C, Schmahmann JD, Hadjikhani N, Meyer H, Meuli R, Wedeen V, et al. Diffusion spectrum imaging shows the structural basis of functional cerebellar circuits in the human cerebellum in vivo. PLoS One. 2009;4(4):e5101.
Oldfield RC. The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia. 1971;9(1):97–113.
Fischl B, van der Kouwe A, Destrieux C, Halgren E, Segonne F, Salat DH, et al. Automatically parcellating the human cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2004;14(1):11–22.
Desikan RS, Segonne F, Fischl B, Quinn BT, Dickerson BC, Blacker D, et al. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage. 2006;31(3):968–80.
Behrens TE, Berg HJ, Jbabdi S, Rushworth MF, Woolrich MW. Probabilistic diffusion tractography with multiple fibre orientations: what can we gain? Neuroimage. 2007;34(1):144–55.
Diedrichsen J. A spatially unbiased atlas template of the human cerebellum. Neuroimage. 2006;33(1):127–38.
Besachio D, Quigley E, 3rd, Orlandi R, Harnsberger H and Wiggins R, 3rd. Myxoma of the vomer bone. J Radiol Case Rep 2013; 7(1):12–17.
Harnsberger HR. Diagnostic imaging. Head and neck. Salt Lake City: Amirsys; 2011.
Ding Z, Gore JC, Anderson AW. Classification and quantification of neuronal fiber pathways using diffusion tensor MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2003;49(4):716–21.
Elliott R. Executive functions and their disorders. Br Med Bull. 2003;65:49–59.
Chan RC, Shum D, Toulopoulou T, Chen EY. Assessment of executive functions: review of instruments and identification of critical issues. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2008;23(2):201–16.
Dronkers NF, Plaisant O, Iba-Zizen MT, Cabanis EA. Paul Broca’s historic cases: high resolution MR imaging of the brains of Leborgne and Lelong. Brain. 2007;130(Pt 5:1432–41.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, Q., Edwards, A., Glass, J.O. et al. Measurement of Projections Between Dentate Nucleus and Contralateral Frontal Cortex in Human Brain Via Diffusion Tensor Tractography. Cerebellum 18, 761–769 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-019-01035-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-019-01035-3